+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | The structure-function relationship of a signaling-competent, dimeric Reelin fragment. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Structure, Vol. 29, Issue 10, Page 1156-11170.e6, Year 2021 |
| 掲載日 | 2021年10月7日 |
 著者 著者 | Liam S Turk / Xuyuan Kuang / Valentina Dal Pozzo / Khush Patel / Muyuan Chen / Kevin Huynh / Michael J Currie / Daniel Mitchell / Renwick C J Dobson / Gabriella D'Arcangelo / Wei Dai / Davide Comoletti /     |
| PubMed 要旨 | Reelin operates through canonical and non-canonical pathways that mediate several aspects of brain development and function. Reelin's dimeric central fragment (CF), generated through proteolytic ...Reelin operates through canonical and non-canonical pathways that mediate several aspects of brain development and function. Reelin's dimeric central fragment (CF), generated through proteolytic cleavage, is required for the lipoprotein-receptor-dependent canonical pathway activation. Here, we analyze the signaling properties of a variety of Reelin fragments and measure the differential binding affinities of monomeric and dimeric CF fragments to lipoprotein receptors to investigate the mode of canonical signal activation. We also present the cryoelectron tomography-solved dimeric structure of Reelin CF and support it using several other biophysical techniques. Our findings suggest that Reelin CF forms a covalent parallel dimer with some degree of flexibility between the two protein chains. As a result of this conformation, Reelin binds to lipoprotein receptors in a manner inaccessible to its monomeric form and is capable of stimulating canonical pathway signaling. |
 リンク リンク |  Structure / Structure /  PubMed:34089653 PubMed:34089653 |
| 手法 | EM (サブトモグラム平均) |
| 解像度 | 20.0 Å |
| 構造データ | 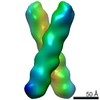 EMDB-23091: |
| 由来 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




