+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural insights into the gating mechanism of human SLC26A9 mediated by its C-terminal sequence. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Cell Discov, Vol. 6, Page 55, Year 2020 |
| 掲載日 | 2020年8月10日 |
 著者 著者 | Ximin Chi / Xueqin Jin / Yun Chen / Xiaoli Lu / Xinyu Tu / Xiaorong Li / Yuanyuan Zhang / Jianlin Lei / Jing Huang / Zhuo Huang / Qiang Zhou / Xiaojing Pan /  |
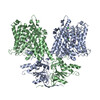
| PubMed 要旨 | The human SLC26 transporter family exhibits various transport characteristics, and family member SLC26A9 performs multiple roles, including acting as Cl/HCO exchangers, Cl channels, and Na ...The human SLC26 transporter family exhibits various transport characteristics, and family member SLC26A9 performs multiple roles, including acting as Cl/HCO exchangers, Cl channels, and Na transporters. Some mutations of SLC26A9 are correlated with abnormalities in respiration and digestion systems. As a potential target colocalizing with CFTR in cystic fibrosis patients, SLC26A9 is of great value in drug development. Here, we present a cryo-EM structure of the human SLC26A9 dimer at 2.6 Å resolution. A segment at the C-terminal end is bound to the entry of the intracellular vestibule of the putative transport pathway, which has been proven by electrophysiological experiments to be a gating modulator. Multiple chloride and sodium ions are resolved in the high-resolution structure, identifying novel ion-binding pockets for the first time. Together, our structure takes important steps in elucidating the structural features and regulatory mechanism of SLC26A9, with potential significance in the treatment of cystic fibrosis. |
 リンク リンク |  Cell Discov / Cell Discov /  PubMed:32818062 / PubMed:32818062 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.6 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-30368: cryo_EM map of SLC26A9 |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-CL:  ChemComp-NA:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)