+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural ensemble of a glutamate transporter homologue in lipid nanodisc environment. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 11, Issue 1, Page 998, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Feb 21, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Valentina Arkhipova / Albert Guskov / Dirk J Slotboom /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Glutamate transporters are cation-coupled secondary active membrane transporters that clear the neurotransmitter L-glutamate from the synaptic cleft. These transporters are homotrimers, with each ...Glutamate transporters are cation-coupled secondary active membrane transporters that clear the neurotransmitter L-glutamate from the synaptic cleft. These transporters are homotrimers, with each protomer functioning independently by an elevator-type mechanism, in which a mobile transport domain alternates between inward- and outward-oriented states. Using single-particle cryo-EM we have determined five structures of the glutamate transporter homologue Glt, a Na- L-aspartate symporter, embedded in lipid nanodiscs. Dependent on the substrate concentrations used, the protomers of the trimer adopt a variety of asymmetrical conformations, consistent with the independent movement. Six of the 15 resolved protomers are in a hitherto elusive state of the transport cycle in which the inward-facing transporters are loaded with Na ions. These structures explain how substrate-leakage is prevented - a strict requirement for coupled transport. The belt protein of the lipid nanodiscs bends around the inward oriented protomers, suggesting that membrane deformations occur during transport. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:32081874 / PubMed:32081874 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.22 - 3.47 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-10632, PDB-6xwn: EMDB-10633, PDB-6xwo: EMDB-10634, PDB-6xwp: EMDB-10635, PDB-6xwq: EMDB-10636, PDB-6xwr: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-TB1: 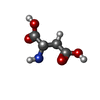 ChemComp-ASP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / AMINO ACID TRANSPORTER / ASPARTATE TRANSPORT / GLUTAMATE TRANSPORTER HOMOLOGUE / MEMBRANE PROTEIN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




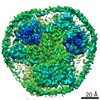

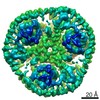
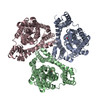
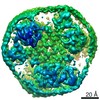


 Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1 (archaea)
Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1 (archaea)