+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structures of KdpFABC suggest a K transport mechanism via two inter-subunit half-channels. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Commun, Vol. 9, Issue 1, Page 4971, Year 2018 |
| 掲載日 | 2018年11月26日 |
 著者 著者 | C Stock / L Hielkema / I Tascón / D Wunnicke / G T Oostergetel / M Azkargorta / C Paulino / I Hänelt /    |
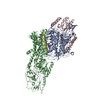
| PubMed 要旨 | P-type ATPases ubiquitously pump cations across biological membranes to maintain vital ion gradients. Among those, the chimeric K uptake system KdpFABC is unique. While ATP hydrolysis is accomplished ...P-type ATPases ubiquitously pump cations across biological membranes to maintain vital ion gradients. Among those, the chimeric K uptake system KdpFABC is unique. While ATP hydrolysis is accomplished by the P-type ATPase subunit KdpB, K has been assumed to be transported by the channel-like subunit KdpA. A first crystal structure uncovered its overall topology, suggesting such a spatial separation of energizing and transporting units. Here, we report two cryo-EM structures of the 157 kDa, asymmetric KdpFABC complex at 3.7 Å and 4.0 Å resolution in an E1 and an E2 state, respectively. Unexpectedly, the structures suggest a translocation pathway through two half-channels along KdpA and KdpB, uniting the alternating-access mechanism of actively pumping P-type ATPases with the high affinity and selectivity of K channels. This way, KdpFABC would function as a true chimeric complex, synergizing the best features of otherwise separately evolved transport mechanisms. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:30478378 / PubMed:30478378 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.7 - 4.0 Å |
| 構造データ | |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-K: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / P-type ATPase superfamily of K+ transporters (SKT) potassium uptake system four subunit complex |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について