+Search query
-Structure paper
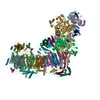
| Title | Structure of the Deactive State of Mammalian Respiratory Complex I. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Structure, Vol. 26, Issue 2, Page 312-319.e3, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Feb 6, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | James N Blaza / Kutti R Vinothkumar / Judy Hirst /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) is central to energy metabolism in mammalian mitochondria. It couples NADH oxidation by ubiquinone to proton transport across the energy-conserving inner ...Complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) is central to energy metabolism in mammalian mitochondria. It couples NADH oxidation by ubiquinone to proton transport across the energy-conserving inner membrane, catalyzing respiration and driving ATP synthesis. In the absence of substrates, active complex I gradually enters a pronounced resting or deactive state. The active-deactive transition occurs during ischemia and is crucial for controlling how respiration recovers upon reperfusion. Here, we set a highly active preparation of Bos taurus complex I into the biochemically defined deactive state, and used single-particle electron cryomicroscopy to determine its structure to 4.1 Å resolution. We show that the deactive state arises when critical structural elements that form the ubiquinone-binding site become disordered, and we propose reactivation is induced when substrate binding to the NADH-reduced enzyme templates their reordering. Our structure both rationalizes biochemical data on the deactive state and offers new insights into its physiological and cellular roles. |
 External links External links |  Structure / Structure /  PubMed:29395787 / PubMed:29395787 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 4.13 - 7.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-3731, PDB-5o31:  EMDB-3733: |
| Chemicals | 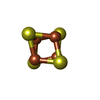 ChemComp-SF4: 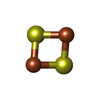 ChemComp-FES: 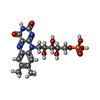 ChemComp-FMN:  ChemComp-NAP:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | OXIDOREDUCTASE / Complex I / redox enzyme / proton pump / membrane protein |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers