+Search query
-Structure paper
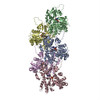
| Title | Near-atomic structure of jasplakinolide-stabilized malaria parasite F-actin reveals the structural basis of filament instability. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 114, Issue 40, Page 10636-10641, Year 2017 |
| Publish date | Oct 3, 2017 |
 Authors Authors | Sabrina Pospich / Esa-Pekka Kumpula / Julian von der Ecken / Juha Vahokoski / Inari Kursula / Stefan Raunser /    |
| PubMed Abstract | During their life cycle, apicomplexan parasites, such as the malaria parasite , use actomyosin-driven gliding motility to move and invade host cells. For this process, actin filament length and ...During their life cycle, apicomplexan parasites, such as the malaria parasite , use actomyosin-driven gliding motility to move and invade host cells. For this process, actin filament length and stability are temporally and spatially controlled. In contrast to canonical actin, actin 1 (Act1) does not readily polymerize into long, stable filaments. The structural basis of filament instability, which plays a pivotal role in host cell invasion, and thus infectivity, is poorly understood, largely because high-resolution structures of Act1 filaments were missing. Here, we report the near-atomic structure of jasplakinolide (JAS)-stabilized Act1 filaments determined by electron cryomicroscopy. The general filament architecture is similar to that of mammalian F-actin. The high resolution of the structure allowed us to identify small but important differences at inter- and intrastrand contact sites, explaining the inherent instability of apicomplexan actin filaments. JAS binds at regular intervals inside the filament to three adjacent actin subunits, reinforcing filament stability by hydrophobic interactions. Our study reveals the high-resolution structure of a small molecule bound to F-actin, highlighting the potential of electron cryomicroscopy for structure-based drug design. Furthermore, our work serves as a strong foundation for understanding the structural design and evolution of actin filaments and their function in motility and host cell invasion of apicomplexan parasites. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:28923924 / PubMed:28923924 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.8 Å |
| Structure data | |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-9UE: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / F-actin / Plasmodium / malaria parasite / cytoskeleton / cryo-EM / JAS / Jasplakinolide / filament / glideosome / gliding motility / thin filament |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers