+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Open and closed structures reveal allostery and pliability in the HIV-1 envelope spike. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 547, Issue 7663, Page 360-363, Year 2017 |
| Publish date | Jul 20, 2017 |
 Authors Authors | Gabriel Ozorowski / Jesper Pallesen / Natalia de Val / Dmitry Lyumkis / Christopher A Cottrell / Jonathan L Torres / Jeffrey Copps / Robyn L Stanfield / Albert Cupo / Pavel Pugach / John P Moore / Ian A Wilson / Andrew B Ward /  |
| PubMed Abstract | For many enveloped viruses, binding to a receptor(s) on a host cell acts as the first step in a series of events culminating in fusion with the host cell membrane and transfer of genetic material for ...For many enveloped viruses, binding to a receptor(s) on a host cell acts as the first step in a series of events culminating in fusion with the host cell membrane and transfer of genetic material for replication. The envelope glycoprotein (Env) trimer on the surface of HIV is responsible for receptor binding and fusion. Although Env can tolerate a high degree of mutation in five variable regions (V1-V5), and also at N-linked glycosylation sites that contribute roughly half the mass of Env, the functional sites for recognition of receptor CD4 and co-receptor CXCR4/CCR5 are conserved and essential for viral fitness. Soluble SOSIP Env trimers are structural and antigenic mimics of the pre-fusion native, surface-presented Env, and are targets of broadly neutralizing antibodies. Thus, they are attractive immunogens for vaccine development. Here we present high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of subtype B B41 SOSIP Env trimers in complex with CD4 and antibody 17b, or with antibody b12, at resolutions of 3.7 Å and 3.6 Å, respectively. We compare these to cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of B41 SOSIP Env trimers with no ligand or in complex with either CD4 or the CD4-binding-site antibody PGV04 at 5.6 Å, 5.2 Å and 7.4 Å resolution, respectively. Consequently, we present the most complete description yet, to our knowledge, of the CD4-17b-induced intermediate and provide the molecular basis of the receptor-binding-induced conformational change required for HIV-1 entry into host cells. Both CD4 and b12 induce large, previously uncharacterized conformational rearrangements in the gp41 subunits, and the fusion peptide becomes buried in a newly formed pocket. These structures provide key details on the biological function of the type I viral fusion machine from HIV-1 as well as new templates for inhibitor design. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:28700571 / PubMed:28700571 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.6 - 10.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-8713: Cryo-EM reconstruction of B41 SOSIP.664 in complex with soluble CD4 (D1-D2) and fragment antigen binding of 17b 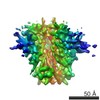 EMDB-8714: 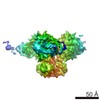 EMDB-8715: 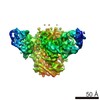 EMDB-8716: EMDB-8717: Cryo-EM reconstruction of B41 SOSIP.664 in complex with fragment antigen binding of b12 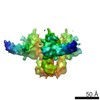 EMDB-8729:  EMDB-8730: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / Viral fusion / HIV-1 / envelope glycoprotein / CD4 receptor binding / neutralizing antibody / receptor binding site |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 human immunodeficiency virus 1
human immunodeficiency virus 1 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)