+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Single-particle EM reveals the higher-order domain architecture of soluble guanylate cyclase. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 111, Issue 8, Page 2960-2965, Year 2014 |
| Publish date | Feb 25, 2014 |
 Authors Authors | Melody G Campbell / Eric S Underbakke / Clinton S Potter / Bridget Carragher / Michael A Marletta /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is the primary nitric oxide (NO) receptor in mammals and a central component of the NO-signaling pathway. The NO-signaling pathways mediate diverse physiological ...Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is the primary nitric oxide (NO) receptor in mammals and a central component of the NO-signaling pathway. The NO-signaling pathways mediate diverse physiological processes, including vasodilation, neurotransmission, and myocardial functions. sGC is a heterodimer assembled from two homologous subunits, each comprised of four domains. Although crystal structures of isolated domains have been reported, no structure is available for full-length sGC. We used single-particle electron microscopy to obtain the structure of the complete sGC heterodimer and determine its higher-order domain architecture. Overall, the protein is formed of two rigid modules: the catalytic dimer and the clustered Per/Art/Sim and heme-NO/O2-binding domains, connected by a parallel coiled coil at two hinge points. The quaternary assembly demonstrates a very high degree of flexibility. We captured hundreds of individual conformational snapshots of free sGC, NO-bound sGC, and guanosine-5'-[(α,β)-methylene]triphosphate-bound sGC. The molecular architecture and pronounced flexibility observed provides a significant step forward in understanding the mechanism of NO signaling. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:24516165 / PubMed:24516165 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 30.0 Å |
| Structure data | 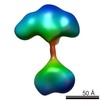 EMDB-5861:  EMDB-5862:  EMDB-5863: 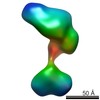 EMDB-5864: 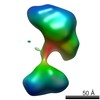 EMDB-5865:  EMDB-5866: 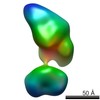 EMDB-5867:  EMDB-5868:  EMDB-5869:  EMDB-5870:  EMDB-5871:  EMDB-5872:  EMDB-5873:  EMDB-5874:  EMDB-5875: 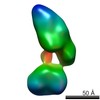 EMDB-5876: 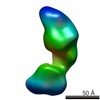 EMDB-5877:  EMDB-5878: 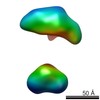 EMDB-5879: 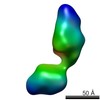 EMDB-5880: 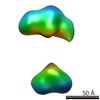 EMDB-5881: 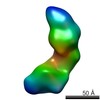 EMDB-5882: 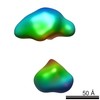 EMDB-5883: 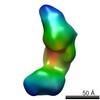 EMDB-5884: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




