[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44183: Filament of D-TLKIVWR, a D-peptide that disaggregates Alzheimer's... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Filament of D-TLKIVWR, a D-peptide that disaggregates Alzheimer's Paired Helical Filaments, determined by Cryo-EM | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Alzheimer's disease / Tau / fibril / cryo-EM / helix / UNKNOWN FUNCTION | ||||||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hou K / Ge P / Sawaya MR / Eisenberg DS | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024Title: How short peptides can disassemble ultra-stable tau fibrils extracted from Alzheimer's disease brain by a strain-relief mechanism. Authors: Ke Hou / Peng Ge / Michael R Sawaya / Joshua L Dolinsky / Yuan Yang / Yi Xiao Jiang / Liisa Lutter / David R Boyer / Xinyi Cheng / Justin Pi / Jeffrey Zhang / Jiahui Lu / Shixin Yang / ...Authors: Ke Hou / Peng Ge / Michael R Sawaya / Joshua L Dolinsky / Yuan Yang / Yi Xiao Jiang / Liisa Lutter / David R Boyer / Xinyi Cheng / Justin Pi / Jeffrey Zhang / Jiahui Lu / Shixin Yang / Zhiheng Yu / Juli Feigon / David S Eisenberg Abstract: Reducing fibrous aggregates of protein tau is a possible strategy for halting progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previously we found that the D-peptide D-TLKIVWC disassembles tau fibrils from ...Reducing fibrous aggregates of protein tau is a possible strategy for halting progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previously we found that the D-peptide D-TLKIVWC disassembles tau fibrils from AD brains (AD-tau) into benign segments with no energy source present beyond ambient thermal agitation. This disassembly by a short peptide was unexpected, given that AD-tau is sufficiently stable to withstand disassembly in boiling SDS detergent. To consider D peptide-mediated disassembly as a potential therapeutic for AD, it is essential to understand the mechanism and energy source of the disassembly action. We find assembly of D-peptides into amyloid-like fibrils is essential for tau fibril disassembly. Cryo-EM and atomic force microscopy reveal that these D-peptide fibrils have a right-handed twist and embrace tau fibrils which have a left-handed twist. In binding to the AD-tau fibril, the oppositely twisted D-peptide fibril produces a strain, which is relieved by disassembly of both fibrils. This strain-relief mechanism appears to operate in other examples of amyloid fibril disassembly and provides a new direction for the development of first-in-class therapeutics for amyloid diseases. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44183.map.gz emd_44183.map.gz | 91.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44183-v30.xml emd-44183-v30.xml emd-44183.xml emd-44183.xml | 16.3 KB 16.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44183_fsc.xml emd_44183_fsc.xml | 11.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44183.png emd_44183.png | 76.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_44183_msk_1.map emd_44183_msk_1.map | 125 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44183.cif.gz emd-44183.cif.gz | 5.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44183_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44183_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44183_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44183_half_map_2.map.gz | 9 MB 9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44183 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44183 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44183 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44183 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_44183_validation.pdf.gz emd_44183_validation.pdf.gz | 623.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_44183_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_44183_full_validation.pdf.gz | 623.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_44183_validation.xml.gz emd_44183_validation.xml.gz | 19.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_44183_validation.cif.gz emd_44183_validation.cif.gz | 25.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44183 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44183 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44183 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44183 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9b4kMC  9b4iC 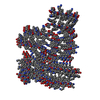 9b4jC  9b4lC  9b4mC  9b4nC  9b4oC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44183.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44183.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.067 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
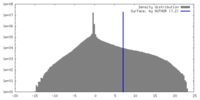
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_44183_msk_1.map emd_44183_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
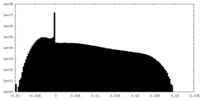
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44183_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44183_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : D-peptide TLKIVWR
| Entire | Name: D-peptide TLKIVWR |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: D-peptide TLKIVWR
| Supramolecule | Name: D-peptide TLKIVWR / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) / Synthetically produced: Yes |
-Macromolecule #1: DTH-DLE-DLY-DIL-DVA-DTR-DAR
| Macromolecule | Name: DTH-DLE-DLY-DIL-DVA-DTR-DAR / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 52 / Enantiomer: DEXTRO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 916.142 Da |
| Sequence | String: (DTH)(DLE)(DLY)(DIL)(DVA)(DTR)(DAR) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 10 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7 / Details: Dissolved in de-ionized water |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9b4k: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)