+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | S. cerevisiae Chs1 in complex with UDP and GlcNAc | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ANTIFUNGAL PROTEIN-INHIBITOR complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationchitosome / chitin synthase / chitin synthase activity / chitin biosynthetic process / septum digestion after cytokinesis / cell septum / cell periphery / cell wall organization / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.06 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bai L / Chen D | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structure, catalysis, chitin transport, and selective inhibition of chitin synthase. Authors: Dan-Dan Chen / Zhao-Bin Wang / Le-Xuan Wang / Peng Zhao / Cai-Hong Yun / Lin Bai /  Abstract: Chitin is one of the most abundant natural biopolymers and serves as a critical structural component of extracellular matrices, including fungal cell walls and insect exoskeletons. As a linear ...Chitin is one of the most abundant natural biopolymers and serves as a critical structural component of extracellular matrices, including fungal cell walls and insect exoskeletons. As a linear polymer of β-(1,4)-linked N-acetylglucosamine, chitin is synthesized by chitin synthases, which are recognized as targets for antifungal and anti-insect drugs. In this study, we determine seven different cryo-electron microscopy structures of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae chitin synthase in the absence and presence of glycosyl donor, acceptor, product, or peptidyl nucleoside inhibitors. Combined with functional analyses, these structures show how the donor and acceptor substrates bind in the active site, how substrate hydrolysis drives self-priming, how a chitin-conducting transmembrane channel opens, and how peptidyl nucleoside inhibitors inhibit chitin synthase. Our work provides a structural basis for understanding the function and inhibition of chitin synthase. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36861.map.gz emd_36861.map.gz | 38.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36861-v30.xml emd-36861-v30.xml emd-36861.xml emd-36861.xml | 15.3 KB 15.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_36861.png emd_36861.png | 77.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36861.cif.gz emd-36861.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36861_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36861_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36861_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36861_half_map_2.map.gz | 37.6 MB 37.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36861 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36861 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36861 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36861 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_36861_validation.pdf.gz emd_36861_validation.pdf.gz | 867.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_36861_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_36861_full_validation.pdf.gz | 866.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_36861_validation.xml.gz emd_36861_validation.xml.gz | 11.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_36861_validation.cif.gz emd_36861_validation.cif.gz | 12.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36861 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36861 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36861 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36861 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8k3uMC  8k3pC  8k3qC  8k3rC  8k3tC  8k3vC  8k3wC  8k3xC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36861.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 40.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36861.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 40.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36861_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
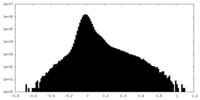
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36861_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : S. cerevisiae Chs1 in complex with UDP and GlcNAc
| Entire | Name: S. cerevisiae Chs1 in complex with UDP and GlcNAc |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: S. cerevisiae Chs1 in complex with UDP and GlcNAc
| Supramolecule | Name: S. cerevisiae Chs1 in complex with UDP and GlcNAc / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Chitin synthase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Chitin synthase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: chitin synthase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 130.001141 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSDQNNRSRN EYHSNRKNEP SYELQNAHSG LFHSSNEELT NRNQRYTNQN ASMGSFTPVQ SLQFPEQSQQ TNMLYNGDDG NNNTINDNE RDIYGGFVNH HRQRPPPATA EYNDVFNTNS QQLPSEHQYN NVPSYPLPSI NVIQTTPELI HNGSQTMATP I ERPFFNEN ...String: MSDQNNRSRN EYHSNRKNEP SYELQNAHSG LFHSSNEELT NRNQRYTNQN ASMGSFTPVQ SLQFPEQSQQ TNMLYNGDDG NNNTINDNE RDIYGGFVNH HRQRPPPATA EYNDVFNTNS QQLPSEHQYN NVPSYPLPSI NVIQTTPELI HNGSQTMATP I ERPFFNEN DYYYNNRNSR TSPSIASSSD GYADQEARPI LEQPNNNMNS GNIPQYHDQP FGYNNGYHGL QAKDYYDDPE GG YIDQRGD DYQINSYLGR NGEMVDPYDY ENSLRHMTPM ERREYLHDDS RPVNDGKEEL DSVKSGYSHR DLGEYDKDDF SRD DEYDDL NTIDKLQFQA NGVPASSSVS SIGSKESDII VSNDNLTANR ALKRSGTEIR KFKLWNGNFV FDSPISKTLL DQYA TTTEN ANTLPNEFKF MRYQAVTCEP NQLAEKNFTV RQLKYLTPRE TELMLVVTMY NEDHILLGRT LKGIMDNVKY MVKKK NSST WGPDAWKKIV VCIISDGRSK INERSLALLS SLGCYQDGFA KDEINEKKVA MHVYEHTTMI NITNISESEV SLECNQ GTV PIQLLFCLKE QNQKKINSHR WAFEGFAELL RPNIVTLLDA GTMPGKDSIY QLWREFRNPN VGGACGEIRT DLGKRFV KL LNPLVASQNF EYKMSNILDK TTESNFGFIT VLPGAFSAYR FEAVRGQPLQ KYFYGEIMEN EGFHFFSSNM YLAEDRIL C FEVVTKKNCN WILKYCRSSY ASTDVPERVP EFILQRRRWL NGSFFASVYS FCHFYRVWSS GHNIGRKLLL TVEFFYLFF NTLISWFSLS SFFLVFRILT VSIALAYHSA FNVLSVIFLW LYGICTLSTF ILSLGNKPKS TEKFYVLTCV IFAVMMIYMI FCSIFMSVK SFQNILKNDT ISFEGLITTE AFRDIVISLG STYCLYLISS IIYLQPWHML TSFIQYILLS PSYINVLNIY A FCNVHDLS WGTKGAMANP LGKINTTEDG TFKMEVLVSS SEIQANYDKY LKVLNDFDPK SESRPTEPSY DEKKTGYYAN VR SLVIIFW VITNFIIVAV VLETGGIADY IAMKSISTDD TLETAKKAEI PLMTSKASIY FNVILWLVAL SALIRFIGCS IYM IVRFFK KVTFR UniProtKB: Chitin synthase 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #4: URIDINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: URIDINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: UDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 404.161 Da |
| Chemical component information | 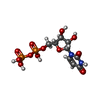 ChemComp-UDP: |
-Macromolecule #5: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(tri...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: POV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-POV: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.06 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 184449 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)