[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28844: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain expressed in a serotype a strain - Classification and subtomogram averaging - Class 8 | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain expressed in a serotype a strain - Classification and subtomogram averaging - Class 8 | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Extracellular matrix protein adhesin A Bacterial Adhesin Glycosylated protein Trimeric Autotransporter / CELL ADHESION | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (bacteria) Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging / negative staining / Resolution: 15.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ruiz T / Radermacher M / Mintz KP / Tang-Siegel GG | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Bacteriol / Year: 2022 Journal: J Bacteriol / Year: 2022Title: Serotype-Specific Sugars Impact Structure but Not Functions of the Trimeric Autotransporter Adhesin EmaA of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Authors: Gaoyan G Tang-Siegel / Michael Radermacher / Keith P Mintz / Teresa Ruiz /  Abstract: The human oral pathobiont Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans expresses multiple virulence factors, including the trimeric, extracellular matrix protein adhesin A (EmaA). The posttranslational ...The human oral pathobiont Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans expresses multiple virulence factors, including the trimeric, extracellular matrix protein adhesin A (EmaA). The posttranslational modification of EmaA is proposed to be dependent on the sugars and enzymes associated with -polysaccharide (O-PS) synthesis of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS). This modification is important for the structure and function of this adhesin. To determine if the composition of the sugars alters structure and/or function, the prototypic 202-kDa protein was expressed in a non-serotype b, mutant strain. The transformed strain displayed EmaA adhesins similar in appearance to the prototypic adhesin as observed by two-dimensional (2D) electron microscopy of whole-mount negatively stained bacterial preparations. Biochemical analysis indicated that the protein monomers were posttranslationally modified. 3D electron tomographic reconstruction and structure analyses of the functional domain revealed three well-defined subdomains (SI, SII, and SIII) with a linker region between SII and SIII. Structural changes were observed in all three subdomains and the linker region of the adhesins synthesized compared with the known structure. These changes, however, did not affect the ability of the strain to bind collagen or form biofilms. The data suggest that changes in the composition of the glycan moiety alter the 3D structure of the molecule without negatively affecting the function(s) associated with this adhesin. The human oral pathogen A. actinomycetemcomitans is a causative agent of periodontal and several systemic diseases. EmaA is a trimeric autotransporter protein adhesin important for colonization by this pathobiont . This adhesin is modified with sugars associated with the -polysaccharide (O-PS), and the modification is mediated using the enzymes involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) biosynthesis. The interaction with collagen is not mediated by the specific binding between the glycans and collagen but is attributed to changes in the final quaternary structure necessary to maintain an active adhesin. In this study, we have determined that the composition of the sugars utilized in the posttranslational modification of this adhesin is exchangeable without compromising functional activities. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28844.map.gz emd_28844.map.gz | 23.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28844-v30.xml emd-28844-v30.xml emd-28844.xml emd-28844.xml | 23.6 KB 23.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_28844_fsc.xml emd_28844_fsc.xml | 8.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_28844.png emd_28844.png | 31.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28844.cif.gz emd-28844.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28844_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28844_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28844_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28844_half_map_2.map.gz | 24.3 MB 24.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28844 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28844 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_28844_validation.pdf.gz emd_28844_validation.pdf.gz | 365.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_28844_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_28844_full_validation.pdf.gz | 365.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_28844_validation.xml.gz emd_28844_validation.xml.gz | 13.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_28844_validation.cif.gz emd_28844_validation.cif.gz | 17.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28844 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28844 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28844.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 25.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28844.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 25.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain expressed in a serotype a strain - Classification and subtomogram averaging - Class 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 3.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter...
| File | emd_28844_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain expressed in a serotype a strain - Half-Map-Odd - Class 8 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter...
| File | emd_28844_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain expressed in a serotype a strain - Half-Map-Even - Class 8 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter ...
| Entire | Name: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain expressed in a serotype a strain - Class 8 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter ...
| Supramolecule | Name: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain expressed in a serotype a strain - Class 8 type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (bacteria) Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter ...
| Macromolecule | Name: EmaA (extracellular matrix protein adhesin A) of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype b strain type: other / ID: 1 / Classification: other |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (bacteria) Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MNKVFKVIWC KTSQTWIAVS ELSKAFSLST TTDIPKKTKI FIAAAPLLFL SFNTNAYIAI GSVENNSVK SEGAEASPNK RKGSQALNYY NPGSKSYDDK DKPSNPERRY SNGEAYGIAI G KNTDVRDS SKDSNGIALG DYSKATGGLA MALGSFSRAE KNGGIAIGIA ...String: MNKVFKVIWC KTSQTWIAVS ELSKAFSLST TTDIPKKTKI FIAAAPLLFL SFNTNAYIAI GSVENNSVK SEGAEASPNK RKGSQALNYY NPGSKSYDDK DKPSNPERRY SNGEAYGIAI G KNTDVRDS SKDSNGIALG DYSKATGGLA MALGSFSRAE KNGGIAIGIA SRSSGINSLA MM RQSAATG DYSTAIGSVA WAAGQSSFAL GASATAKGNQ SIAIGSLEQK ISPNGSGVPI TKY NGLDNT QTNGNRSMAL GTAAKTNGDD SFAIGYKAHT GEFKVEHDNY LKENVTSPDL SKKA DKAIA VGTSALAQKE SAIAFGYQAN ASGINAISLG ANAKASQDNV VAIGKDATAT ESGSM AIGQ GAKSTFKNSL ALGTGTIVNS VDGGQSKFTA QNYDANNGVV AVANAGKERR IINVAG GRN DTDAVNVAQL KFVNDNLAKS IAGAGYNGYE TDGHTYKAPV FSIKNTNYHD VKTAVEA AQ TNYVSVNSTN TAADSNYDNK GAKAVGSIAL GEKATTGRAA MNSIAIGLNS NVSGQNTV A LGANITATTN GSVILGNSST TEGSHPVSNV SSATVNGYTY SGFTGTVKES GHFVSIGSK GNERQIKNVA AGNVAANSTD AVNGSQLFAV ASRVEQGWQI TSGVENGGTQ NGAASTATIK PSNQVKLLA GKNLAVKQNG TNFTFSTQEN VTFTNVTTQD LTATGNTTVK NFSVQNGGTI N MGNNRITG VAEGTQDDDA VNFKQLKSLL GGSASTEIVE KKAAQAGDEN LADISVANGK NA GDMGAKY EVSVSKKAVQ SAAKEAVKVT GSAPINVNKT DVNGVDTYAV TFNGTEAAKS IPL TYKANG SGDKTVMLDK GLNFTNGMMT TASVANDGVM KYDVNLSTIK VEDGKAAVAG TPGT NGANG TDGKDGVATV KNVVEALNNA AWTITASKSD GEVVSNASNS VKNGDTVTYD AGKNI KITQ RDKKFSFATK DNVEFTSVTT GNTKLTGNGV EITNGPKLTQ SGVDAGGKKI TNVADG VIA ANSKDAVNGG QLFAETAKAK TTVEKGDDNI QITSETATDG HINYKVALNP SLTVGPR TN GHPITIDGNN GYITGLTNTS WTGAPTTGRA ATEDQLSIVD KKFDNKVSLG GDNGSTTE K SLSHNGGIKF NIKGGDSQKY VTTSGSGDDV TVDLAQTTKN KIDNAADKDL ANITDNGKK VITALGAVVK AADSTITVTD ETDNTTGQKT YKIKANIPTP EKTAMAPGNN TTIEGDGSAA NPFKVNLKD DLALGQKDAN GVTGKDSSIK VNGKDGSGVA INGKDGSIAL NGKDGANPVT I KTAQGPAG VNETNPKDRL MVNNDAVATL KDGLKFAGDN STEVITKTLN QKLEIVGGAD KN KLSDNNI GVNANNGKLE VKLAKELNEL TSAQFKNGDN TTVINGNGIT ITPKDPTKAV SLT DKGLNN GGNQIVNIDS GLKQADGSTV ALKDASGDTL KNAANIGDLQ KSINDITDAS KNGG FGLSD DNGATAKANL GETVKVKGDG SVITKVVTDN GKPTLQVGLS NDITVGDDAQ AGTIS VKGE NGKDGVSING KEASVTFAKD GQPGMSIAAT RSADGKDALT LKGKDGKDGI SFQEDG RIT QVADGVNDKD AVNKSQLDRS IAQAKSGVSA GKNITVTPQK NADGSTTYTV ETQKDVE FS TVKTGDTTLD SNGVNINGGP SVTKDGIHAN DKKITGVKDG EISAHSKEAV NGSQLHQT N QNVTNLANNV DKGLNFQGDN QEVTVNRKLG DQLNIRGGAD PKKLTQNNIG VTADKNGTM TVQLAKEVNL GADGSLTVGN TTVNNDGVTI KDGPSMTSHG INAGGKRIAN VAKGKAPTDA VNMSQLQDV GSAINNRIDN IDKRVKKMDK RRKAGTASAL ATAGLMQPHR DGQSALVAAV G QYQSETAV AVGYSRISDN GKYGVKVSFS TNSQGEVGGT AGAGYFW |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: NanoW Details: Electron microscopy grids were prepared as previously described. Briefly, a 5 ul aliquot of bacterial suspension was placed on either 300 or 200 mesh carbon-coated grids, and deep stained ...Details: Electron microscopy grids were prepared as previously described. Briefly, a 5 ul aliquot of bacterial suspension was placed on either 300 or 200 mesh carbon-coated grids, and deep stained with NanoW (Nanoprobes, Yaphank, NY). For 3D electron tomography, the grids were pretreated with Poly-L-lysine (1000-5000 Da. Sigma, St. Louis, MO) and colloidal gold (SPI, West Chester, PA) to be used as fiducial markers. | |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Homemade / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 20 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 12 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F216 (2k x 2k) / Number real images: 80 / Average electron dose: 3.0 e/Å2 Details: Data were collected using a Tecnai 12 electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR) equipped with a LaB6 cathode (Kimball Physics, Wilton, NH), operated in point-mode, a 2048 by 2048 pixel CCD ...Details: Data were collected using a Tecnai 12 electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR) equipped with a LaB6 cathode (Kimball Physics, Wilton, NH), operated in point-mode, a 2048 by 2048 pixel CCD camera with a pixel size of 14 um, (TVIPS, Gauting, Germany) and a dual axis tilt tomography holder (Fischione, Export, PA). All images were recorded on the CCD camera at an acceleration voltage of 100 kV and a nominal magnification of 42,000, which corresponds to 0.308 nm pixel size on the specimen scale. Tomographic tilt series were acquired at least within a +/-64 degree angular range in 2 degree angular intervals. Data were collected under low dose exposure conditions (0.10 e-/nm2 for 2D imaging and 0.03 e-/nm2 per image for the tomographic tilt series data) as previously described. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 100 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.3 µm / Nominal magnification: 42000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FISCHIONE INSTRUMENTS DUAL AXIS TOMOGRAPHY HOLDER Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





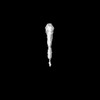

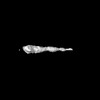


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)

































 IMOD
IMOD
