[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-27796: Cryo-EM structure of bundle-forming pilus extension ATPase from E... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
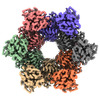
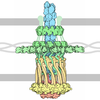
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of bundle-forming pilus extension ATPase from E.coli in the presence of AMP-PNP (class-2) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | BfpD / AAA-ATPase / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Type 4 pilus accessory protein | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology | Type II/IV secretion system protein / Type II/IV secretion system protein / ATP hydrolysis activity / P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase / ATP binding / plasma membrane / BfpD Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
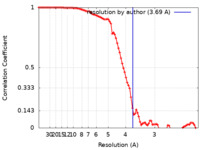
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.69 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nayak AR / Zhao J / Donnenberg MS / Samso M | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2022 Journal: mBio / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM Structure of the Type IV Pilus Extension ATPase from Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Authors: Ashok R Nayak / Pradip K Singh / Jinlei Zhao / Montserrat Samsó / Michael S Donnenberg /  Abstract: Type 4 pili (T4P) are retractable surface appendages found on numerous bacteria and archaea that play essential roles in various microbial functions, including host colonization by pathogens. An ...Type 4 pili (T4P) are retractable surface appendages found on numerous bacteria and archaea that play essential roles in various microbial functions, including host colonization by pathogens. An ATPase is required for T4P extension, but the mechanism by which chemical energy is transduced to mechanical energy for pilus extension has not been elucidated. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the BfpD ATPase from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) in the presence of either ADP or a mixture of ADP and AMP-PNP. Both structures, solved at 3 Å resolution, reveal the typical toroid shape of AAA+ ATPases and unambiguous 6-fold symmetry. This 6-fold symmetry contrasts with the 2-fold symmetry previously reported for other T4P extension ATPase structures, all of which were from thermophiles and solved by crystallography. In the presence of the nucleotide mixture, BfpD bound exclusively AMP-PNP, and this binding resulted in a modest outward expansion in comparison to the structure in the presence of ADP, suggesting a concerted model for hydrolysis. molecular models reveal a partially open configuration of all subunits where the nucleotide binding site may not be optimally positioned for catalysis. ATPase functional studies reveal modest activity similar to that of other extension ATPases, while calculations indicate that this activity is insufficient to power pilus extension. Our results reveal that, despite similarities in primary sequence and tertiary structure, T4P extension ATPases exhibit divergent quaternary configurations. Our data raise new possibilities regarding the mechanism by which T4P extension ATPases power pilus formation. Type 4 pili are hairlike surface appendages on many bacteria and archaea that can be extended and retracted with tremendous force. They play a critical role in disease caused by several deadly human pathogens. Pilus extension is made possible by an enzyme that converts chemical energy to mechanical energy. Here, we describe the three-dimensional structure of such an enzyme from a human pathogen in unprecedented detail, which reveals a mechanism of action that has not been seen previously among enzymes that power type 4 pilus extension. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27796.map.gz emd_27796.map.gz | 51.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27796-v30.xml emd-27796-v30.xml emd-27796.xml emd-27796.xml | 17.8 KB 17.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27796_fsc.xml emd_27796_fsc.xml | 8.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27796.png emd_27796.png | 178.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27796.cif.gz emd-27796.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27796_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27796_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27796_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27796_half_map_2.map.gz | 50.8 MB 50.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27796 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27796 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27796 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27796 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_27796_validation.pdf.gz emd_27796_validation.pdf.gz | 944.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_27796_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_27796_full_validation.pdf.gz | 944.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_27796_validation.xml.gz emd_27796_validation.xml.gz | 16.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_27796_validation.cif.gz emd_27796_validation.cif.gz | 21.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27796 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27796 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27796 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27796 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8dzfMC  8dzeC  8dzgC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27796.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27796.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_27796_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
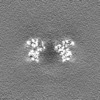
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
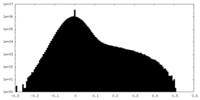
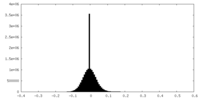
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_27796_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
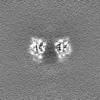
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
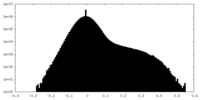
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Bundle-forming pilus extension ATPase from enteropathogenic E.col...
| Entire | Name: Bundle-forming pilus extension ATPase from enteropathogenic E.coli in the presence of AMP-PNP |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Bundle-forming pilus extension ATPase from enteropathogenic E.col...
| Supramolecule | Name: Bundle-forming pilus extension ATPase from enteropathogenic E.coli in the presence of AMP-PNP type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: BfpD ATPase with 5 mM Mgcl2, 1 mM ADP, 2 mM ATP and 2.5 mM AMP-PNP |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 362 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: BfpD
| Macromolecule | Name: BfpD / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.440062 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVNKTEKTSD LMFERFKRNV SEIVTGDGGE LELTVEQRKY FLIFKNGDFL VSSCHMKHHL VQMLREIATR KGYPNLTIYE VNLKDIRLL YEASLKTVQN NGQDLLPVEK RASMLLFECA EMRVSDLHIK VYDAEADIYI RKDGDMELLR QIESNTAHSI L ASLYNNAD ...String: MVNKTEKTSD LMFERFKRNV SEIVTGDGGE LELTVEQRKY FLIFKNGDFL VSSCHMKHHL VQMLREIATR KGYPNLTIYE VNLKDIRLL YEASLKTVQN NGQDLLPVEK RASMLLFECA EMRVSDLHIK VYDAEADIYI RKDGDMELLR QIESNTAHSI L ASLYNNAD DSDATYKINA YQAARIVASK SRLALPPVIQ AVRLQFNPLG QGGRYLIARF LYTDKSEKQK EMDPTRFGFH HS HAESFSR MRNLPIGINI ISGPTGSGKS TTLKNLLELL YIEKKKKVNI ISIEDPPEYE IDGTAQLPIT NVETEAQRGE EYR KAITAA LRSDPDIIMP GEARDAEVIN LLFTAAMTGH QVWTSLHANN ALAIFDRLKD QGVDEFKLTD PELITGLVAQ RLVR KLCAQ CSITLTEYIA SGGGISDTDR KIISGHETSV RFPNPRAKKC CRDGYNGRTI LAEVIEPDSK LLRLVAEGKR EDAQH YWLT SLHGMALKEH AWLKIISGEI CVMDAVNKIS GIDNITEERK KYLFSRDNEI UniProtKB: BfpD |
-Macromolecule #2: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: ANP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 506.196 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ANP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 Details: 20 mM Tris (pH 7.6), 0.1 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT, 0.5 mM CHAPSO, 1 mM ADP, 2 mM ATP and 2.5 mM AMP-PNP |
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Slit width: 10 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 3 / Number real images: 10132 / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8dzf: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z
Z Y
Y X
X