+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 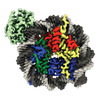 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of S. cerevisiae Hop1 CBR bound to a nucleosome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Nucleosome CBR | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | meiosis / recombination / chromosome axis / nucleosome / PHD / winged helix / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
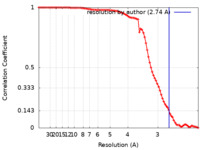
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.74 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gu Y / Ur SN / Milano CR / Tromer EC / Vale-Silva LA / Hochwagen A / Corbett KD | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024Title: Chromatin binding by HORMAD proteins regulates meiotic recombination initiation. Authors: Carolyn R Milano / Sarah N Ur / Yajie Gu / Jessie Zhang / Rachal Allison / George Brown / Matthew J Neale / Eelco C Tromer / Kevin D Corbett / Andreas Hochwagen /    Abstract: The meiotic chromosome axis coordinates chromosome organization and interhomolog recombination in meiotic prophase and is essential for fertility. In S. cerevisiae, the HORMAD protein Hop1 mediates ...The meiotic chromosome axis coordinates chromosome organization and interhomolog recombination in meiotic prophase and is essential for fertility. In S. cerevisiae, the HORMAD protein Hop1 mediates the enrichment of axis proteins at nucleosome-rich islands through a central chromatin-binding region (CBR). Here, we use cryoelectron microscopy to show that the Hop1 CBR directly recognizes bent nucleosomal DNA through a composite interface in its PHD and winged helix-turn-helix domains. Targeted disruption of the Hop1 CBR-nucleosome interface causes a localized reduction of axis protein binding and meiotic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in axis islands and leads to defects in chromosome synapsis. Synthetic effects with mutants of the Hop1 regulator Pch2 suggest that nucleosome binding delays a conformational switch in Hop1 from a DSB-promoting, Pch2-inaccessible state to a DSB-inactive, Pch2-accessible state to regulate the extent of meiotic DSB formation. Phylogenetic analyses of meiotic HORMADs reveal an ancient origin of the CBR, suggesting that the mechanisms we uncover are broadly conserved. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27030.map.gz emd_27030.map.gz | 32.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27030-v30.xml emd-27030-v30.xml emd-27030.xml emd-27030.xml | 25 KB 25 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27030_fsc.xml emd_27030_fsc.xml | 8.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27030.png emd_27030.png | 166.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27030.cif.gz emd-27030.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27030_additional_1.map.gz emd_27030_additional_1.map.gz emd_27030_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27030_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27030_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27030_half_map_2.map.gz | 32.2 MB 59.4 MB 59.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27030 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27030 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27030 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27030 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8cwwMC  7ubaC  8czeC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27030.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27030.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Nucleosome CBR | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: local map for CBR
| File | emd_27030_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | local map for CBR | ||||||||||||
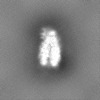
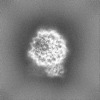
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
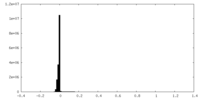
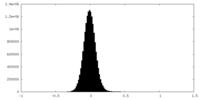
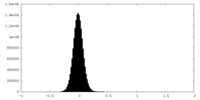
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_27030_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
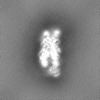
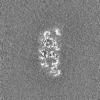
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
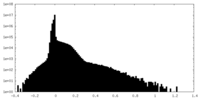
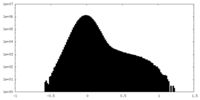
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_27030_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
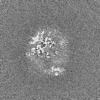
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of Hop1 CBR domain bound to nucleosome
| Entire | Name: Complex of Hop1 CBR domain bound to nucleosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of Hop1 CBR domain bound to nucleosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of Hop1 CBR domain bound to nucleosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#7 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 223 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Meiosis-specific protein HOP1
| Macromolecule | Name: Meiosis-specific protein HOP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: GenBank:DAA08478.1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.239928 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SNASNNPVTG ICSCECGLEV PKAATVLKTC KSCRKTLHGI CYGNFLHSSI EKCFTCIFGP SLDTKWSKFQ DLMMIRKVFR FLVRKKKGF PASITELIDS FINVEDQNNE VKERVAFALF VFFLDETLCL DNGGKPSQTI RYVTSSVLVD VKGIVIPNTR K QLNVNHEY ...String: SNASNNPVTG ICSCECGLEV PKAATVLKTC KSCRKTLHGI CYGNFLHSSI EKCFTCIFGP SLDTKWSKFQ DLMMIRKVFR FLVRKKKGF PASITELIDS FINVEDQNNE VKERVAFALF VFFLDETLCL DNGGKPSQTI RYVTSSVLVD VKGIVIPNTR K QLNVNHEY KWHFTTSSPK AESFYQEVLP NSRKQVESWL QDITNLRKVY SEALS |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H3
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: GenBank:CAD89679.1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.30393 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ARTKQTARKS TGGKAPRKQL ATKAARKSAP ATGGVKKPHR YRPGTVALRE IRRYQKSTEL LIRKLPFQRL VREIAQDFKT DLRFQSSAV MALQEASEAY LVALFEDTNL CAIHAKRVTI MPKDIQLARR IRGERA |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Details: GenBank:NP_001087926.1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.263231 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SGRGKGGKGL GKGGAKRHRK VLRDNIQGIT KPAIRRLARR GGVKRISGLI YEETRGVLKV FLENVIRDAV TYTEHAKRKT VTAMDVVYA LKRQGRTLYG FGG |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2A
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Details: GenBank:CAD89676.1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.978241 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SGRGKQGGKT RAKAKTRSSR AGLQFPVGRV HRLLRKGNYA ERVGAGAPVY LAAVLEYLTA EILELAGNAA RDNKKTRIIP RHLQLAVRN DEELNKLLGR VTIAQGGVLP NIQSVLLPKK TESSKSAKSK |
-Macromolecule #5: Histone H2B
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Details: GenBank:CAD89678.1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.524752 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: AKSAPAPKKG SKKAVTKTQK KDGKKRRKTR KESYAIYVYK VLKQVHPDTG ISSKAMSIMN SFVNDVFERI AGEASRLAHY NKRSTITSR EIQTAVRLLL PGELAKHAVS EGTKAVTKYT SAK |
-Macromolecule #6: Widom 601 DNA (146-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: Widom 601 DNA (146-MER) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.27484 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DA) |
-Macromolecule #7: Widom 601 DNA (146-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: Widom 601 DNA (146-MER) / type: dna / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.85657 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DG)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #8: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.8 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: 20mM Tris 7.5, 50mM NaCl, 1mM DTT, 1mM EDTA |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8cww: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



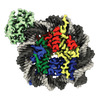

 Z
Z Y
Y X
X