[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-26655: Native Lassa glycoprotein in complex with neutralizing antibodies... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
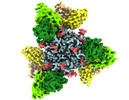
| Title | Native Lassa glycoprotein in complex with neutralizing antibodies 12.1F and 37.2D | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell Golgi membrane / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / membrane / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Lassa virus Lassa virus | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.75 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li H / Saphire EO | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Transl Med / Year: 2022 Journal: Sci Transl Med / Year: 2022Title: A cocktail of protective antibodies subverts the dense glycan shield of Lassa virus. Authors: Haoyang Li / Tierra Buck / Michelle Zandonatti / Jieyun Yin / Alex Moon-Walker / Jingru Fang / Anatoliy Koval / Megan L Heinrich / Megan M Rowland / Ruben Diaz Avalos / Sharon L Schendel / ...Authors: Haoyang Li / Tierra Buck / Michelle Zandonatti / Jieyun Yin / Alex Moon-Walker / Jingru Fang / Anatoliy Koval / Megan L Heinrich / Megan M Rowland / Ruben Diaz Avalos / Sharon L Schendel / Diptiben Parekh / Dawid Zyla / Adrian Enriquez / Stephanie Harkins / Brian Sullivan / Victoria Smith / Onyeka Chukwudozie / Reika Watanabe / James E Robinson / Robert F Garry / Luis M Branco / Kathryn M Hastie / Erica Ollmann Saphire /  Abstract: Developing potent therapeutics and effective vaccines are the ultimate goals in controlling infectious diseases. Lassa virus (LASV), the causative pathogen of Lassa fever (LF), infects hundreds of ...Developing potent therapeutics and effective vaccines are the ultimate goals in controlling infectious diseases. Lassa virus (LASV), the causative pathogen of Lassa fever (LF), infects hundreds of thousands annually, but effective antivirals or vaccines against LASV infection are still lacking. Furthermore, neutralizing antibodies against LASV are rare. Here, we describe biochemical analyses and high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of a therapeutic cocktail of three broadly protective antibodies that target the LASV glycoprotein complex (GPC), previously identified from survivors of multiple LASV infections. Structural and mechanistic analyses reveal compatible neutralizing epitopes and complementary neutralization mechanisms that offer high potency, broad range, and resistance to escape. These antibodies either circumvent or exploit specific glycans comprising the extensive glycan shield of GPC. Further, they require mammalian glycosylation, native GPC cleavage, and proper GPC trimerization. These findings guided engineering of a next-generation GPC antigen suitable for future neutralizing antibody and vaccine discovery. Together, these results explain protective mechanisms of rare, broad, and potent antibodies and identify a strategy for the rational design of therapeutic modalities against LF and related infectious diseases. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_26655.map.gz emd_26655.map.gz | 254.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-26655-v30.xml emd-26655-v30.xml emd-26655.xml emd-26655.xml | 20.7 KB 20.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_26655.png emd_26655.png | 110.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_26655_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26655_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26655_half_map_2.map.gz emd_26655_half_map_2.map.gz | 475.3 MB 475.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26655 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26655 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26655 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26655 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_26655_validation.pdf.gz emd_26655_validation.pdf.gz | 969.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_26655_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_26655_full_validation.pdf.gz | 969.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_26655_validation.xml.gz emd_26655_validation.xml.gz | 18.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_26655_validation.cif.gz emd_26655_validation.cif.gz | 22.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26655 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26655 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26655 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26655 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7uovMC  7uotC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_26655.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_26655.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.66 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_26655_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
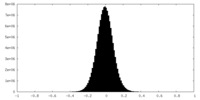
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_26655_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Native Lassa glycoprotein in complex with 12.1F-scFv and 37.2D-scFv
| Entire | Name: Native Lassa glycoprotein in complex with 12.1F-scFv and 37.2D-scFv |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Native Lassa glycoprotein in complex with 12.1F-scFv and 37.2D-scFv
| Supramolecule | Name: Native Lassa glycoprotein in complex with 12.1F-scFv and 37.2D-scFv type: complex / Chimera: Yes / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#6 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: 12.1F heavy chain (variable domain)
| Macromolecule | Name: 12.1F heavy chain (variable domain) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 12.731153 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QVQLQESGAG LLKPSETLSL SCTVDGESFN GFFWTWIRQP PGKGLEWIGE INHLASTGYN PSLKSRVTIS VDTSKNQFSL KLTSVTAAD TAVYYCARGY SYGFAWPNYH YLDVW |
-Macromolecule #2: 12.1F light chain (variable domain)
| Macromolecule | Name: 12.1F light chain (variable domain) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.602884 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EIVLTQSPAT LSLSPGERAT LSCRASQSVS SYLAWYQHKP GQAPRLLIYG ASKRATGIPS RFSGSGSGTD FSLTISSLEP EDFAVYYCQ HRSDWRTTFG QGTRLEI |
-Macromolecule #3: Glycoprotein G1
| Macromolecule | Name: Glycoprotein G1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Lassa virus / Strain: Mouse/Sierra Leone/Josiah/1976 Lassa virus / Strain: Mouse/Sierra Leone/Josiah/1976 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 29.064402 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGQIVTFFQE VPHVIEEVMN IVLIALSVLA VLKGLYNFAT CGLVGLVTFL LLCGRSCTTS LYKGVYELQT LELNMETLNM TMPLSCTKN NSHHYIMVGN ETGLELTLTN TSIINHKFCN LSDAHKKNLY DHALMSIIST FHLSIPNFNQ YEAMSCDFNG G KISVQYNL ...String: MGQIVTFFQE VPHVIEEVMN IVLIALSVLA VLKGLYNFAT CGLVGLVTFL LLCGRSCTTS LYKGVYELQT LELNMETLNM TMPLSCTKN NSHHYIMVGN ETGLELTLTN TSIINHKFCN LSDAHKKNLY DHALMSIIST FHLSIPNFNQ YEAMSCDFNG G KISVQYNL SHSYAGDAAN HCGTVANGVL QTFMRMAWGG SYIALDSGRG NWDCIMTSYQ YLIIQNTTWE DHCQFSRPSP IG YLGLLSQ RTRDIYISRR LL |
-Macromolecule #4: Glycoprotein G2
| Macromolecule | Name: Glycoprotein G2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Lassa virus / Strain: Mouse/Sierra Leone/Josiah/1976 Lassa virus / Strain: Mouse/Sierra Leone/Josiah/1976 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 26.797973 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GTFTWTLSDS EGKDTPGGYC LTRWMLIEAE LKCFGNTAVA KCNEKHDEEF CDMLRLFDFN KQAIQRLKAE AQTSIQLINK AVNALINDQ LIMKNHLRDI MGIPYCNYSK YWYLNHTTTG RTSLPKCWLV SNGSYLNETH FSDDIEQQAD NMITEMLQKE Y MERQGKTP ...String: GTFTWTLSDS EGKDTPGGYC LTRWMLIEAE LKCFGNTAVA KCNEKHDEEF CDMLRLFDFN KQAIQRLKAE AQTSIQLINK AVNALINDQ LIMKNHLRDI MGIPYCNYSK YWYLNHTTTG RTSLPKCWLV SNGSYLNETH FSDDIEQQAD NMITEMLQKE Y MERQGKTP LGLVDLFVFS TSFYLISIFL HLVKIPTHRH IVGKSCPKPH RLNHMGICSC GLYKQPGVPV KWKR |
-Macromolecule #5: 37.2D light chain (variable domain)
| Macromolecule | Name: 37.2D light chain (variable domain) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.412506 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ETTLTQSPAT LSVSPGETAT LSCRASQNVI NNLAWYQQKP GQAPRLLIYG ASTRATGIPA RFSGSGSGTE FTLTISSMQS EDFAVYYCQ QYNDWPRSFG QGTRLD |
-Macromolecule #6: 37.2D heavy chain (variable domain)
| Macromolecule | Name: 37.2D heavy chain (variable domain) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.946536 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EVQLVQSGAE VKKPGASVKV SCKASGYTFT KYGISWVRQA PGQGLEWMGW ISAFNGYTRY GQRFQGKVTM TTDTSTNTAS LEVRTLTSN DTAVYYCARQ YPDQYSSSGW PRLFAMDVWG QGTTVTV |
-Macromolecule #13: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 13 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.75 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 286170 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z
Z Y
Y X
X