[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-25753: Structure of the yeast clamp loader (Replication Factor C RFC) bo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-25753 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
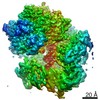
| Title | Structure of the yeast clamp loader (Replication Factor C RFC) bound to the open sliding clamp (Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen PCNA) | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Density modified map (with resolve_cryo_em) | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | sliding clamp / DNA replication / AAA+ / clamp loader / REPLICATION | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA clamp unloading / Rad17 RFC-like complex / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / meiotic mismatch repair / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / Elg1 RFC-like complex / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex ...DNA clamp unloading / Rad17 RFC-like complex / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / meiotic mismatch repair / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / Elg1 RFC-like complex / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Polymerase switching / positive regulation of DNA metabolic process / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / DNA clamp loader activity / maintenance of DNA trinucleotide repeats / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / PCNA complex / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / lagging strand elongation / postreplication repair / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / sister chromatid cohesion / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / error-free translesion synthesis / leading strand elongation / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / mismatch repair / translesion synthesis / positive regulation of DNA repair / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / positive regulation of DNA replication / replication fork / nucleotide-excision repair / DNA-templated DNA replication / mitotic cell cycle / chromosome, telomeric region / cell division / DNA repair / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gaubitz C / Demo G / Stone NP / Hayes JA / Liu X / Pajak J / Kelch BA | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Czech Republic, 4 items Czech Republic, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM structures reveal high-resolution mechanism of a DNA polymerase sliding clamp loader. Authors: Christl Gaubitz / Xingchen Liu / Joshua Pajak / Nicholas P Stone / Janelle A Hayes / Gabriel Demo / Brian A Kelch /   Abstract: Sliding clamps are ring-shaped protein complexes that are integral to the DNA replication machinery of all life. Sliding clamps are opened and installed onto DNA by clamp loader AAA+ ATPase complexes. ...Sliding clamps are ring-shaped protein complexes that are integral to the DNA replication machinery of all life. Sliding clamps are opened and installed onto DNA by clamp loader AAA+ ATPase complexes. However, how a clamp loader opens and closes the sliding clamp around DNA is still unknown. Here, we describe structures of the clamp loader Replication Factor C (RFC) bound to its cognate sliding clamp Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) en route to successful loading. RFC first binds to PCNA in a dynamic, closed conformation that blocks both ATPase activity and DNA binding. RFC then opens the PCNA ring through a large-scale 'crab-claw' expansion of both RFC and PCNA that explains how RFC prefers initial binding of PCNA over DNA. Next, the open RFC:PCNA complex binds DNA and interrogates the primer-template junction using a surprising base-flipping mechanism. Our structures indicate that initial PCNA opening and subsequent closure around DNA do not require ATP hydrolysis, but are driven by binding energy. ATP hydrolysis, which is necessary for RFC release, is triggered by interactions with both PCNA and DNA, explaining RFC's switch-like ATPase activity. Our work reveals how a AAA+ machine undergoes dramatic conformational changes for achieving binding preference and substrate remodeling. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25753.map.gz emd_25753.map.gz | 8.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25753-v30.xml emd-25753-v30.xml emd-25753.xml emd-25753.xml | 23 KB 23 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_25753_fsc.xml emd_25753_fsc.xml | 8.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_25753.png emd_25753.png | 53.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25753.cif.gz emd-25753.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_25753_additional_1.map.gz emd_25753_additional_1.map.gz emd_25753_half_map_1.map.gz emd_25753_half_map_1.map.gz emd_25753_half_map_2.map.gz emd_25753_half_map_2.map.gz | 40.7 MB 40.8 MB 40.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25753 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25753 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25753 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25753 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_25753_validation.pdf.gz emd_25753_validation.pdf.gz | 914.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_25753_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_25753_full_validation.pdf.gz | 914.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_25753_validation.xml.gz emd_25753_validation.xml.gz | 13.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_25753_validation.cif.gz emd_25753_validation.cif.gz | 18.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25753 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25753 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25753 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25753 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7ti8MC  7thjC  7thvC  7tibC  7ticC  7tidC  7tkuC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25753.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 9.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25753.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 9.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Density modified map (with resolve_cryo_em) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
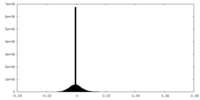
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unsharpened Map
| File | emd_25753_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened Map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
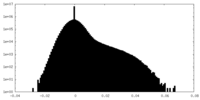
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_25753_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_25753_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Replication Factor C (RFC) bound to the open sliding clamp Prolif...
| Entire | Name: Replication Factor C (RFC) bound to the open sliding clamp Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Replication Factor C (RFC) bound to the open sliding clamp Prolif...
| Supramolecule | Name: Replication Factor C (RFC) bound to the open sliding clamp Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 336 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: PCNA
| Macromolecule | Name: PCNA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: GPHMASMLEA KFEEASLFKR IIDGFKDCV QLVNFQCKED G IIAQAVDD SRVLLVSLEI GV EAFQEYR CDHPVTLGMD LTS LSKILR CGNNTDTLTL IADN TPDSI ILLFEDTKKD RIAEY SLKL MDIDADFLKI EELQYD STL SLPSSEFSKI VRDLSQL SD ...String: GPHMASMLEA KFEEASLFKR IIDGFKDCV QLVNFQCKED G IIAQAVDD SRVLLVSLEI GV EAFQEYR CDHPVTLGMD LTS LSKILR CGNNTDTLTL IADN TPDSI ILLFEDTKKD RIAEY SLKL MDIDADFLKI EELQYD STL SLPSSEFSKI VRDLSQL SD SINIMITKET IKFVADGD I GSGSVIIKPF VDMEHPETS IKLEMDQPVD LTFGAKYLLD IIKGSSLSD RVGIRLSSEA P ALFQFDLK SGFLQFFLAP KF NDEE UniProtKB: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
-Macromolecule #4: Rfc1
| Macromolecule | Name: Rfc1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: MVNISDFFGK NKKSVRSSTS RPTRQVGSSK PEVIDLDTES DQESTNKTPK KMPVSNVIDV SETPEGEKKL PLPAKRKASS PTVKPASSKK TKPSSKSSDS ASNITAQDVL DKIPSLDLSN VHVKENAKFD FKSANSNADP DEIVSEIGSF PEGKPNCLLG LTIVFTGVLP ...String: MVNISDFFGK NKKSVRSSTS RPTRQVGSSK PEVIDLDTES DQESTNKTPK KMPVSNVIDV SETPEGEKKL PLPAKRKASS PTVKPASSKK TKPSSKSSDS ASNITAQDVL DKIPSLDLSN VHVKENAKFD FKSANSNADP DEIVSEIGSF PEGKPNCLLG LTIVFTGVLP TLERGASEAL AKRYGARVTK SISSKTSVVV LGDEAGPKKL EKIKQLKIKA IDEEGFKQLI AGMPAEGGDG EAAEKARRKL EEQHNIATKE AELLVKKEEE RSKKLAATRV SGGHLERDNV VREEDKLWTV KYAPTNLQQV CGNKGSVMKL KNWLANWENS KKNSFKHAGK DGSGVFRAAM LYGPPGIGKT TAAHLVAQEL GYDILEQNAS DVRSKTLLNA GVKNALDNMS VVGYFKHNEE AQNLNGKHFV IIMDEVDGMS GGDRGGVGQL AQFCRKTSTP LILICNERNL PKMRPFDRVC LDIQFRRPDA NSIKSRLMTI AIREKFKLDP NVIDRLIQTT RGDIRQVINL LSTISTTTKT INHENINEIS KAWEKNIALK PFDIAHKMLD GQIYSDIGSR NFTLNDKIAL YFDDFDFTPL MIQENYLSTR PSVLKPGQSH LEAVAEAANC ISLGDIVEKK IRSSEQLWSL LPLHAVLSSV YPASKVAGHM AGRINFTAWL GQNSKSAKYY RLLQEIHYHT RLGTSTDKIG LRLDYLPTFR KRLLDPFLKQ GADAISSVIE VMDDYYLTKE DWDSIMEFFV GPDVTTAIIK KIPATVKSGF TRKYNSMTHP VAIYRTGSTI GGGGVGTSTS TPDFEDVVDA DDNPVPADDE ETQDSSTDLK KDKLIKQKAK PTKRKTATSK PGGSKKRKTK A UniProtKB: Replication factor C subunit 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: Rfc2
| Macromolecule | Name: Rfc2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: MFEGFGPNKK RKISKLAAEQ SLAQQPWVEK YRPKNLDEVT AQDHAVTVLK KTLKSANLPH MLFYGPPGTG KTSTILALTK ELYGPDLMKS RILELNASDE RGISIVREKV KNFARLTVSK PSKHDLENYP CPPYKIIILD EADSMTADAQ SALRRTMETY SGVTRFCLIC ...String: MFEGFGPNKK RKISKLAAEQ SLAQQPWVEK YRPKNLDEVT AQDHAVTVLK KTLKSANLPH MLFYGPPGTG KTSTILALTK ELYGPDLMKS RILELNASDE RGISIVREKV KNFARLTVSK PSKHDLENYP CPPYKIIILD EADSMTADAQ SALRRTMETY SGVTRFCLIC NYVTRIIDPL ASRCSKFRFK ALDASNAIDR LRFISEQENV KCDDGVLERI LDISAGDLRR GITLLQSASK GAQYLGDGKN ITSTQVEELA GVVPHDILIE IVEKVKSGDF DEIKKYVNTF MKSGWSAASV VNQLHEYYIT NDNFDTNFKN QISWLLFTTD SRLNNGTNEH IQLLNLLVKI SQL UniProtKB: Replication factor C subunit 2 |
-Macromolecule #6: Rfc3
| Macromolecule | Name: Rfc3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: MSTSTEKRSK ENLPWVEKYR PETLDEVYGQ NEVITTVRKF VDEGKLPHLL FYGPPGTGKT STIVALAREI YGKNYSNMVL ELNASDDRGI DVVRNQIKDF ASTRQIFSKG FKLIILDEAD AMTNAAQNAL RRVIERYTKN TRFCVLANYA HKLTPALLSR CTRFRFQPLP ...String: MSTSTEKRSK ENLPWVEKYR PETLDEVYGQ NEVITTVRKF VDEGKLPHLL FYGPPGTGKT STIVALAREI YGKNYSNMVL ELNASDDRGI DVVRNQIKDF ASTRQIFSKG FKLIILDEAD AMTNAAQNAL RRVIERYTKN TRFCVLANYA HKLTPALLSR CTRFRFQPLP QEAIERRIAN VLVHEKLKLS PNAEKALIEL SNGDMRRVLN VLQSCKATLD NPDEDEISDD VIYECCGAPR PSDLKAVLKS ILEDDWGTAH YTLNKVRSAK GLALIDLIEG IVKILEDYEL QNEETRVHLL TKLADIEYSI SKGGNDQIQG SAVIGAIKAS FENETVKANV UniProtKB: Replication factor C subunit 3 |
-Macromolecule #7: Rfc4
| Macromolecule | Name: Rfc4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: MSKTLSLQLP WVEKYRPQVL SDIVGNKETI DRLQQIAKDG NMPHMIISGM PGIGKTTSVH CLAHELLGRS YADGVLELNA SDDRGIDVVR NQIKHFAQKK LHLPPGKHKI VILDEADSMT AGAQQALRRT MELYSNSTRF AFACNQSNKI IEPLQSRCAI LRYSKLSDED ...String: MSKTLSLQLP WVEKYRPQVL SDIVGNKETI DRLQQIAKDG NMPHMIISGM PGIGKTTSVH CLAHELLGRS YADGVLELNA SDDRGIDVVR NQIKHFAQKK LHLPPGKHKI VILDEADSMT AGAQQALRRT MELYSNSTRF AFACNQSNKI IEPLQSRCAI LRYSKLSDED VLKRLLQIIK LEDVKYTNDG LEAIIFTAEG DMRQAINNLQ STVAGHGLVN ADNVFKIVDS PHPLIVKKML LASNLEDSIQ ILRTDLWKKG YSSIDIVTTS FRVTKNLAQV KESVRLEMIK EIGLTHMRIL EGVGTYLQLA SMLAKIHKLN NKA UniProtKB: Replication factor C subunit 4 |
-Macromolecule #8: Rfc5
| Macromolecule | Name: Rfc5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: MSLWVDKYRP KSLNALSHNE ELTNFLKSLS DQPRDLPHLL LYGPNGTGKK TRCMALLESI FGPGVYRLKI DVRQFVTASN RKLELNVVSS PYHLEITPSD MGNNDRIVIQ ELLKEVAQME QVDFQDSKDG LAHRYKCVII NEANSLTKDA QAALRRTMEK YSKNIRLIMV ...String: MSLWVDKYRP KSLNALSHNE ELTNFLKSLS DQPRDLPHLL LYGPNGTGKK TRCMALLESI FGPGVYRLKI DVRQFVTASN RKLELNVVSS PYHLEITPSD MGNNDRIVIQ ELLKEVAQME QVDFQDSKDG LAHRYKCVII NEANSLTKDA QAALRRTMEK YSKNIRLIMV CDSMSPIIAP IKSRCLLIRC PAPSDSEIST ILSDVVTNER IQLETKDILK RIAQASNGNL RVSLLMLESM ALNNELALKS SSPIIKPDWI IVIHKLTRKI VKERSVNSLI ECRAVLYDLL AHCIPANIIL KELTFSLLDV ETLNTTNKSS IIEYSSVFDE RLSLGNKAIF HLEGFIAKVM CCLD UniProtKB: Replication factor C subunit 5 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.3000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)