[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
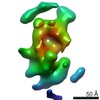
Yorodumi- EMDB-23868: Human N-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav2.2 at 3.1 Angstrom... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23868 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human N-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav2.2 at 3.1 Angstrom resolution | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / NCAM1 interactions ...regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / NCAM1 interactions / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuromuscular junction development / neuronal dense core vesicle / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / response to amyloid-beta / regulation of calcium ion transport / calcium channel regulator activity / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / sarcoplasmic reticulum / Regulation of insulin secretion / protein localization to plasma membrane / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport / T cell receptor signaling pathway / amyloid-beta binding / chemical synaptic transmission / neuronal cell body / synapse / calcium ion binding / extracellular exosome / ATP binding / membrane / metal ion binding / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yan N / Gao S / Yao X | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structure of human Ca2.2 channel blocked by the painkiller ziconotide. Authors: Shuai Gao / Xia Yao / Nieng Yan /  Abstract: The neuronal-type (N-type) voltage-gated calcium (Ca) channels, which are designated Ca2.2, have an important role in the release of neurotransmitters. Ziconotide is a Ca2.2-specific peptide pore ...The neuronal-type (N-type) voltage-gated calcium (Ca) channels, which are designated Ca2.2, have an important role in the release of neurotransmitters. Ziconotide is a Ca2.2-specific peptide pore blocker that has been clinically used for treating intractable pain. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human Ca2.2 (comprising the core α1 and the ancillary α2δ-1 and β3 subunits) in the presence or absence of ziconotide. Ziconotide is thoroughly coordinated by helices P1 and P2, which support the selectivity filter, and the extracellular loops (ECLs) in repeats II, III and IV of α1. To accommodate ziconotide, the ECL of repeat III and α2δ-1 have to tilt upward concertedly. Three of the voltage-sensing domains (VSDs) are in a depolarized state, whereas the VSD of repeat II exhibits a down conformation that is stabilized by Ca2-unique intracellular segments and a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate molecule. Our studies reveal the molecular basis for Ca2.2-specific pore blocking by ziconotide and establish the framework for investigating electromechanical coupling in Ca channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23868.map.gz emd_23868.map.gz | 78.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23868-v30.xml emd-23868-v30.xml emd-23868.xml emd-23868.xml | 17.3 KB 17.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23868.png emd_23868.png | 34.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23868 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23868 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23868 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23868 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_23868_validation.pdf.gz emd_23868_validation.pdf.gz | 510.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_23868_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_23868_full_validation.pdf.gz | 510.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_23868_validation.xml.gz emd_23868_validation.xml.gz | 6.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_23868_validation.cif.gz emd_23868_validation.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23868 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23868 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23868 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23868 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7miyMC  7mixC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23868.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23868.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.114 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Cav2.2
+Supramolecule #1: Cav2.2
+Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent N-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1B
+Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-3
+Macromolecule #3: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
+Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #8: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #9: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
+Macromolecule #10: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #11: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
+Macromolecule #12: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tr...
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 20 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: blot for 6 seconds before plunging. |
| Details | Cav2.2 |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 56615 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller