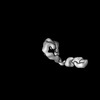
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21912 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mdn1-DeltaC plus MIDAS | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 25.55 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mickolajczyk KJ / Niu Y | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: Long-range intramolecular allostery and regulation in the dynein-like AAA protein Mdn1. Authors: Keith J Mickolajczyk / Paul Dominic B Olinares / Yiming Niu / Nan Chen / Sara E Warrington / Yusuke Sasaki / Thomas Walz / Brian T Chait / Tarun M Kapoor /  Abstract: Mdn1 is an essential mechanoenzyme that uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to physically reshape and remodel, and thus mature, the 60S subunit of the ribosome. This massive (>500 kDa) protein has an ...Mdn1 is an essential mechanoenzyme that uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to physically reshape and remodel, and thus mature, the 60S subunit of the ribosome. This massive (>500 kDa) protein has an N-terminal AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) ring, which, like dynein, has six ATPase sites. The AAA ring is followed by large (>2,000 aa) linking domains that include an ∼500-aa disordered (D/E-rich) region, and a C-terminal substrate-binding MIDAS domain. Recent models suggest that intramolecular docking of the MIDAS domain onto the AAA ring is required for Mdn1 to transmit force to its ribosomal substrates, but it is not currently understood what role the linking domains play, or why tethering the MIDAS domain to the AAA ring is required for protein function. Here, we use chemical probes, single-particle electron microscopy, and native mass spectrometry to study the AAA and MIDAS domains separately or in combination. We find that Mdn1 lacking the D/E-rich and MIDAS domains retains ATP and chemical probe binding activities. Free MIDAS domain can bind to the AAA ring of this construct in a stereo-specific bimolecular interaction, and, interestingly, this binding reduces ATPase activity. Whereas intramolecular MIDAS docking appears to require a treatment with a chemical inhibitor or preribosome binding, bimolecular MIDAS docking does not. Hence, tethering the MIDAS domain to the AAA ring serves to prevent, rather than promote, MIDAS docking in the absence of inducing signals. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21912.map.gz emd_21912.map.gz | 10.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21912-v30.xml emd-21912-v30.xml emd-21912.xml emd-21912.xml | 16.5 KB 16.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21912.png emd_21912.png | 32.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21912 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21912 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21912 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21912 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_21912_validation.pdf.gz emd_21912_validation.pdf.gz | 77.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_21912_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_21912_full_validation.pdf.gz | 76.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_21912_validation.xml.gz emd_21912_validation.xml.gz | 492 B | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21912 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21912 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21912 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-21912 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21912.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21912.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.71 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Mdn1(1-3911) plus SNAP-MIDAS
| Entire | Name: Mdn1(1-3911) plus SNAP-MIDAS |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Mdn1(1-3911) plus SNAP-MIDAS
| Supramolecule | Name: Mdn1(1-3911) plus SNAP-MIDAS / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: MAP of Mdn1(1-3911) with MIDAS domain bound to the AAA ring |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 453 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: Mdn1(1-3911)
| Supramolecule | Name: Mdn1(1-3911) / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: SNAP-tagged MIDAS domain of Mdn1
| Supramolecule | Name: SNAP-tagged MIDAS domain of Mdn1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Mdn1(1-3911)
| Macromolecule | Name: Mdn1(1-3911) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: Rbin-1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSYYHHHHHH DYDIPTTENL YFQGAMGIRN SKAYVDMDVL IEWVAIYPQI YDILEHINYV PSNTLQRLRL HQPWSKIDYD VWFLYASDEI RETCKVKYYG ETKTYGEVFV LENERISQLH RLFVSWTVSE RAEHLKNLLF DAGLSNLPLV ELGGNVFFNS HVPLPCSLVL ...String: MSYYHHHHHH DYDIPTTENL YFQGAMGIRN SKAYVDMDVL IEWVAIYPQI YDILEHINYV PSNTLQRLRL HQPWSKIDYD VWFLYASDEI RETCKVKYYG ETKTYGEVFV LENERISQLH RLFVSWTVSE RAEHLKNLLF DAGLSNLPLV ELGGNVFFNS HVPLPCSLVL TKSTQENLNR ITPYLVQKRP ILLAGPEGIG KKFLITQIAA KLGQQIIRIH LSDSTDPKML IGTYTSPKPG EFEWQPGVLT QAVITGKWIL FTNIEHAPSE VLSVLLPLLE KRQLVIPSRG ETIYAKGSFQ MFATSSMKTK ILGQRLWQIL DLTYQPDECV EVVSTLYPVL SIICPTLYSV YKDIFDLFSQ RSFLATSKIY RRLCLRDFYK FIKRVAFLYH KFMIPSDHVV ISQELQDAVF KEAIDMFGAF IPSRDGFDLV VRNVAIELNI PPEKALQLRY SIPVFQNLEH NINIGRCSLK KLSTIRSCST NSYAFTSSSL GLLEQLAAGV QTNEPLLLVG ETGTGKTTTI QLLAGLLGQK VTVINMSQQT ESSDMLGGYK PINASTLGLP LHERFIDIFE QTFSSKKNAK FISMASTSAR RFRWKTCLKI WKEACKLSKT VLDGQQPLPN PQKRQKRLSN QVELRNQWAK FEKEVEDFEK VLTGGSNGFM FSFVEGALVK AVRSGHWVLL DEINLASLET LEPIGQLLSS YESGILLSER GDITPITPHK NFRLFGCMNP STDVGKRELE PSFRSRFTEI YVHSPDQNLD DLLSIIQKYI GSLCIGNEHV IREVAELYQV AKSLSLDGSL VDGAGQRPHY TVRTLSRTLS YVTEIAPIYG LRRSLYEGFC MSFLTLLDHT SESLLYNHVV RFTLGELNRD QQNAILKQIP KVPDHSSYIA FCHYWLRRGS FPVEEQEHYI ITPFVQKNLL NIARACSTRM FPILIQGPTS SGKTSMIEYV AKKTGHKFVR INNHEHTDLQ EYIGTYVTDD NGSLSFREGV LVEALRNGYW IVLDELNLAP TDVLEALNRL LDDNRELFIP ETQVLVKPHP EFMLFATQNP PGVYAGRKHL SRAFRNRFLE IHFDDIPENE LETILHKRCK IAPSYAAKIV QVFRELSLRR QTTRIFEQKN SFATLRDLFR WAFREAVGYQ QLAENGYMLL AERARDQKDK LAVQEVIEKV MKVKIDTDGI YNLDSMEIFQ DMSLKEGPLS KVVWTRPMIR LFCLVWRCLL AKEPVLLVGD TGCGKTTVCQ ILAECLHKEL HIINAHQDTE NGDIIGAQRP VRNRSAVNYS LHSQLCEKFN VQESLDSIDD LIEKFEKLSS SEKNDNLSNL IERQIIKYRS LFEWHDGALV TAMKQGDFFL LDEISLADDS VLERLNSVLE LSRTLTLVEH SNAAVSLTAK DGFAFFATMN PGGDYGKKEL SPALRNRFTE IWVPPMVDTE DILKIVEGKL HNNKIELARP LVEYAKWHAN EYLYTDVISI RDVLSAVEFI NACEILDLNL VLFNAVSMVF IDALGSFTTF SLSNNLASLH AERQRCFAKL NELAGSNIMA SKSADISIKF SDSSFFIGDF GIPLGDSVES DSTYSLHTDT TLMNASKVLR ALQVLKPILL EGSPGVGKTS LITALARETG HQLVRINLSD QTDLMDLFGS DVPVEGGEGG QFAWRDAPFL AAMRNGHWVL LDELNLASQS VLEGLNACLD HRNEAYIPEL DKVFKAHPNF RVFAAQNPQH QGGGRKGLPR SFINRFSVVY VEALKEKDMI EIAACNYHQV NEDWRLKIIK FMFRLQDNIE KDISFGSFGS PWEFNLRDTL RWLQLLNDAP KYTCVSPADY LEVMVLHRMR TVEDRVRTCE LFKEVFDIDY EPRTIGFSLS SQCFKVGHSL LVRDVERQKT LLDSQNILQS QLPVLESVIT CINKKWPCIL VGDTATGKTC ILRLLAAIAG AKIKEMAVNS DTDTMDLIGE YEQIDISRKA SELFTDLSQQ LLNIVIKYRN FDNIFRETSL YTLTTTSFKT HSQAFTLLQK VVDQLDQLKI HETLVHSLGD IHEKARKLLA EFSASPAGRF EWFDGYLLKA VEEGHWFVLD NANLCSPAVL DRLNSLLEHK GVLIVNEKTT EDGHPKTIKP HPNFRLFLTV NPVYGELSRA MRNRGVEIFL LKEALTEIDK KQMSLLEPAP ISSAVDTLAS NISYIKYVFE TMGKIEIDGN YMYIAHAIIL ALFSPRQLKL LRKVLLTNPQ FSLSIKADAE LLLTLKNLVQ KIYCADYFNH MDLKASRFMD IYEYPVQLRE VVGLIQTIND FQSVILTSHL ELPETYASGL LFVSAHEILD LTEEVNRLAV STSNSTYLLK SASAVYHNVS SFKGSTPSLW NLLNQFSKFL IEIASANSNI VYKLSYDVIR HFLKLVVLWK NIYVWTNVPD CDISRFYCYT KMLGEWMFTL TEKTKLLESF LPKDSLEKFS ELQNLSTGLH MQAIWDKWHA FVPRTYDQWS LWNTVDKLLT QYVNANIPSI SMETTACEVV GTSLSLLNKV LVENEVGDIY SYLKILGKGV NELKSSKQVI LPENLVNLFN CLASLDLLHI FIKYTTSSFF LTDDFVRFIR VCFHSRISGN LLTLLHGISF DSTKAVAPVL TYFDFCSLTT GNILGRIALA FTSIDENANL ESANIFEHAR LALLQHFMDH SSLLAEDSST KMNLILLQRY AVIISIFLDQ GKCEKANDLI TKLSLPYEEL AENFVSILEA CKAFLVANSE FISYTYTERF IHSLRFLKDS WLSSNQQKML KNQGMAYIYF ASGMLLVYVP DKPFDPALLP LLTVESLRHY LESLYKESQI LEIAESLNSG KVNSVMRRLV STEISNTPNI DSSFSTVYRS LNESIVPLYS ELEFFMKSVV LNQYIFELAM RLSKESNIAV VEEAKSFVTK WKAYIERIRE AYPQFVDVYE LILSFISFMI YGIELLMFEA KRRLDERSQI LSTLILTLVD PSSFARSLSF DDVSNLIEQI KVLDLNDSIR FEIYLFLASR LCSEKQHSSD THSLANSFVL LANEFYIHNA KIKQKELEEI EEKNRLYRQR EFNFDKNDYL KVFINYDDEV EPEVEPEVVI ERKRFLQLQF AFWSLYNEIY SEKMNVIPLE QLMNTGSYLA KKIKVKNPDM IASSGFDIVS VVLMMGVKST NERQYWTPPV YNFYSDPNPS KAIEVRDLIK IVESRAISLI KNWPENFVLR GLKDAIDAIL NLSPFSPIAE YLSKLERVFH LLSEWEKLAS REYSLANEMD LIKKKIIDWR KFELSNWNNL LKLEEYKLSE RVYPRLYSIL QFIILKPFFE NSKFTKQNLC ESASIIVQFI TDLTVGEFQL CLKCLLSFSQ HAASLRICHG IDAMLLNIYH YFEQFLSKVS EAIHTQKQSL ENSIKERILL MSWKDTNVYA LKESAKKSHA ELFKVLHRYR EVLRQPVSSY LSQKHDWDSL LDTENNSAMW VAKKVNLSPS YIEKMDTEIM KLVPVRFSNT PTTLRLMWTL FANVEKPGST FTNMVSNLIT DARELMKLTP ETINDDNLSE IKHLKSRKHL LLTETFKTLK AFGLQYRVKA GIEENLSNLR NLLAVIPTFP VTSLSIEKVD RSLMKSLDFI PKFQTLAGHQ HNDLSVPEVQ KGVGLFNSML SLQLGERAQL VEFTNELLAL KNVYSEVGVN GSPLESFNNS SFNEVSSLGY DHDFENRAQA VSMLCQIYAI VIQKHSSISP TASFQSIGHE LSRFADLLSN KLFPSSIPLY ASADKVSSIR DQQKGINDLI EYCRKKRTEL PELSYCFKHL VSLQSLKSIS RTQVDLTNDE FLNLMNFVLN LFDSLLSSIE TATKNMRTFK ELAETSSFIE MSSCFSKVLR AFNLKFQSMK LSSLKEKLRS SSVDKMSCQL LMLFLPVCEQ FINLAESVLD YFINVHNSNL DSLSKISTLF FMVANNGFCS PDLPQEGKSN SGELESG |
-Macromolecule #2: SNAP-tagged MIDAS domain of Mdn1
| Macromolecule | Name: SNAP-tagged MIDAS domain of Mdn1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GMDKDCEMKR TTLDSPLGKL ELSGCEQGLH EIKLLGKGTS AADAVEVPAP AAVLGGPEPL MQATAWLNAY FHQPEAIEEF PVPALHHPVF QQESFTRQVL WKLLKVVKFG EVISYQQLAA LAGNPAATAA VKTALSGNPV PILIPCHRVV SSSGAVGGYE GGLAVKEWLL ...String: GMDKDCEMKR TTLDSPLGKL ELSGCEQGLH EIKLLGKGTS AADAVEVPAP AAVLGGPEPL MQATAWLNAY FHQPEAIEEF PVPALHHPVF QQESFTRQVL WKLLKVVKFG EVISYQQLAA LAGNPAATAA VKTALSGNPV PILIPCHRVV SSSGAVGGYE GGLAVKEWLL AHEGHRLGKP GLGKLAAAGE DTLPTEFGSI NQSEKVFELS EDEDIEDELP DYNVKITNLP AAMPIDEARD LWNKHEDSTK QLSIELCEQL RLILEPTLAT KMQGDFRTGK RLNMKRIIPY IASQFKKDKI WMRRVKPSKR TYQVMISIDD SKSMSESGST VLALETLALV TKALSLLEVG QIAVMKFGEQ PELLHPFDKQ FSSESGVQMF SHFTFEQSNT NVLALADASM KCFNYANTAS HHRSNSDIRQ LEIIISDGIC EDHDSIRKLL RRAQEEKVMI VFVILDNVNT QKKSSILDIK KVYYDTKEDG TMDLKIQPYI DEFAFDYYLV VRNIEELPQL LSSALRQWFQ QMSNT |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: uranyl formate |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI/PHILIPS CM10 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: OTHER / Average electron dose: 1.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 100 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



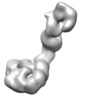




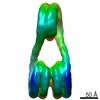

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)