+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
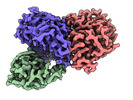
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of CDK2-cyclin A in complex with CDC25A | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | cell-cycle / CDK / phosphatase / cancer / CELL CYCLE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of G2/MI transition of meiotic cell cycle / cell cycle G1/S phase transition / mitotic cell cycle phase transition / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / Polo-like kinase mediated events / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex ...positive regulation of G2/MI transition of meiotic cell cycle / cell cycle G1/S phase transition / mitotic cell cycle phase transition / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / Polo-like kinase mediated events / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex / cyclin E1-CDK2 complex / cyclin A2-CDK2 complex / positive regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / G2 Phase / cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / Y chromosome / Phosphorylation of proteins involved in G1/S transition by active Cyclin E:Cdk2 complexes / positive regulation of heterochromatin formation / p53-Dependent G1 DNA Damage Response / X chromosome / PTK6 Regulates Cell Cycle / regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / regulation of DNA replication / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / centriole replication / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / centrosome duplication / phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / G0 and Early G1 / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / cellular response to nitric oxide / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / cyclin-dependent kinase / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Cajal body / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / condensed chromosome / regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / post-translational protein modification / cyclin binding / protein-tyrosine-phosphatase / protein tyrosine phosphatase activity / positive regulation of DNA replication / male germ cell nucleus / meiotic cell cycle / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / response to radiation / potassium ion transport / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / Meiotic recombination / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / Orc1 removal from chromatin / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / cellular response to UV / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / cellular senescence / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / nuclear envelope / protein-folding chaperone binding / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / regulation of gene expression / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / transcription regulator complex / Ras protein signal transduction / DNA replication / cell population proliferation / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / endosome / chromatin remodeling / protein phosphorylation / protein domain specific binding / cell division / protein serine kinase activity / DNA repair / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / centrosome / DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / protein kinase binding / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / magnesium ion binding / signal transduction Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
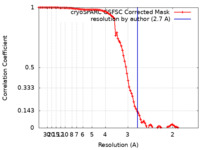
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Rowland RJ / Noble MEM / Endicott JA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structure of the CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A complex. Authors: Rhianna J Rowland / Svitlana Korolchuk / Marco Salamina / Natalie J Tatum / James R Ault / Sam Hart / Johan P Turkenburg / James N Blaza / Martin E M Noble / Jane A Endicott /  Abstract: The cell division cycle 25 phosphatases CDC25A, B and C regulate cell cycle transitions by dephosphorylating residues in the conserved glycine-rich loop of CDKs to activate their activity. Here, we ...The cell division cycle 25 phosphatases CDC25A, B and C regulate cell cycle transitions by dephosphorylating residues in the conserved glycine-rich loop of CDKs to activate their activity. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of CDK2-cyclin A in complex with CDC25A at 2.7 Å resolution, providing a detailed structural analysis of the overall complex architecture and key protein-protein interactions that underpin this 86 kDa complex. We further identify a CDC25A C-terminal helix that is critical for complex formation. Sequence conservation analysis suggests CDK1/2-cyclin A, CDK1-cyclin B and CDK2/3-cyclin E are suitable binding partners for CDC25A, whilst CDK4/6-cyclin D complexes appear unlikely substrates. A comparative structural analysis of CDK-containing complexes also confirms the functional importance of the conserved CDK1/2 GDSEID motif. This structure improves our understanding of the roles of CDC25 phosphatases in CDK regulation and may inform the development of CDC25-targeting anticancer strategies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_19408.map.gz emd_19408.map.gz | 85.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-19408-v30.xml emd-19408-v30.xml emd-19408.xml emd-19408.xml | 21.6 KB 21.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
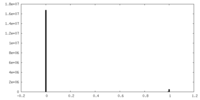
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_19408_fsc.xml emd_19408_fsc.xml | 9.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_19408.png emd_19408.png | 122.1 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_19408_msk_1.map emd_19408_msk_1.map | 91.1 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-19408.cif.gz emd-19408.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_19408_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19408_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19408_half_map_2.map.gz emd_19408_half_map_2.map.gz | 84.6 MB 84.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19408 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19408 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19408 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19408 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_19408_validation.pdf.gz emd_19408_validation.pdf.gz | 805.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_19408_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_19408_full_validation.pdf.gz | 805.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_19408_validation.xml.gz emd_19408_validation.xml.gz | 17.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_19408_validation.cif.gz emd_19408_validation.cif.gz | 22.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19408 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19408 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19408 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-19408 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8rozMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
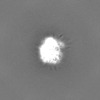
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_19408.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_19408.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.825 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
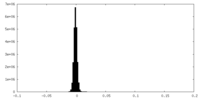
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
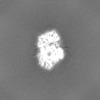
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_19408_msk_1.map emd_19408_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
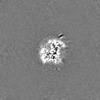
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_19408_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_19408_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Trimeric complex of CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A
| Entire | Name: Trimeric complex of CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Trimeric complex of CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A
| Supramolecule | Name: Trimeric complex of CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 86 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Human cyclin dependant protein kinase 2 (CDK2) phosphorylated at Tyr15 and Thr160 Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: cyclin-dependent kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 34.136449 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MENFQKVEKI GEGT(PTR)GVVYK ARNKLTGEVV ALKKIRLDTE TEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELNH PNIVKLLDVI HTENKL YLV FEFLHQDLKK FMDASALTGI PLPLIKSYLF QLLQGLAFCH SHRVLHRDLK PQNLLINTEG AIKLADFGLA RAFGVPV RT Y(TPO) ...String: MENFQKVEKI GEGT(PTR)GVVYK ARNKLTGEVV ALKKIRLDTE TEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELNH PNIVKLLDVI HTENKL YLV FEFLHQDLKK FMDASALTGI PLPLIKSYLF QLLQGLAFCH SHRVLHRDLK PQNLLINTEG AIKLADFGLA RAFGVPV RT Y(TPO)HEVVTLWY RAPEILLGCK YYSTAVDIWS LGCIFAEMVT RRALFPGDSE IDQLFRIFRT LGTPDEVVWP GVTS MPDYK PSFPKWARQD FSKVVPPLDE DGRSLLSQML HYDPNKRISA KAALAHPFFQ DVTKPVPHLR L UniProtKB: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Cyclin-A2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-A2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: Bovine cyclin A2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 30.119799 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGVNEVPDYH EDIHTYLREM EVKCKPKVGY MKKQPDITNS MRAILVDWLV EVGEEYKLQN ETLHLAVNYI DRFLSSMSVL RGKLQLVGT AAMLLASKFE EIYPPEVAEF VYITDDTYTK KQVLRMEHLV LKVLAFDLAA PTINQFLTQY FLHQQPANCK V ESLAMFLG ...String: MGVNEVPDYH EDIHTYLREM EVKCKPKVGY MKKQPDITNS MRAILVDWLV EVGEEYKLQN ETLHLAVNYI DRFLSSMSVL RGKLQLVGT AAMLLASKFE EIYPPEVAEF VYITDDTYTK KQVLRMEHLV LKVLAFDLAA PTINQFLTQY FLHQQPANCK V ESLAMFLG ELSLIDADPY LKYLPSVIAA AAFHLALYTV TGQSWPESLV QKTGYTLETL KPCLLDLHQT YLRAPQHAQQ SI REKYKNS KYHGVSLLNP PETLNV UniProtKB: Cyclin-A2 |
-Macromolecule #3: M-phase inducer phosphatase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: M-phase inducer phosphatase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 Details: M-phase inducer phosphatase 1 (CDC25A) catalytic domain Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: protein-tyrosine-phosphatase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.533123 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMVIGDFSKG YLFHTVAGKH QDLKYISPEI MASVLNGKFA NLIKEFVIID CRYPYEYEGG HIKGAVNLHM EEEVEDFLLK KPIVPTDGK RVIVVFHSEF SSERGPRMCR YVRERDRLGN EYPKLHYPEL YVLKGGYKEF FMKCQSYCEP PSYRPMHHED F KEDLKKFR TKSRTWAGEK SKREMYSRLK KL UniProtKB: M-phase inducer phosphatase 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.8 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: 50 mM HEPES, 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, pH 7.4 | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.026000000000000002 kPa Details: Grids were glow discharged for 1min at 20 mAmp/0.26 mBar | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 1.92 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 150000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | Chain - Source name: Other / Chain - Initial model type: in silico model / Details: ModelAngelo |
|---|---|
| Details | A model was generated using ModelAngelo. Initial local fitting was performed in ChimerX followed by real space refinement in Phenix and manual fitting in coot. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 144 |
| Output model |  PDB-8roz: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)