[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-17985: Cryo-EM structure of DHS-ERK2 complex with 1:3 stoichiometry refi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 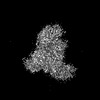 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of DHS-ERK2 complex with 1:3 stoichiometry refined in C1 symmetry | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Main map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | hypusination / transferase / protein-protein interaction / ERK1/2 kinase-independent function / TRANSLATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdeoxyhypusine synthase / peptidyl-lysine modification to peptidyl-hypusine / Hypusine synthesis from eIF5A-lysine / deoxyhypusine synthase activity / spermidine metabolic process / spermidine catabolic process / phospho-PLA2 pathway / Signaling by MAPK mutants / RAF-independent MAPK1/3 activation / Suppression of apoptosis ...deoxyhypusine synthase / peptidyl-lysine modification to peptidyl-hypusine / Hypusine synthesis from eIF5A-lysine / deoxyhypusine synthase activity / spermidine metabolic process / spermidine catabolic process / phospho-PLA2 pathway / Signaling by MAPK mutants / RAF-independent MAPK1/3 activation / Suppression of apoptosis / Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK / Signaling by Activin / cardiac neural crest cell development involved in heart development / caveolin-mediated endocytosis / cytosine metabolic process / response to epidermal growth factor / ERKs are inactivated / Signaling by MAP2K mutants / Signaling by NODAL / RSK activation / Golgi Cisternae Pericentriolar Stack Reorganization / positive regulation of macrophage proliferation / Regulation of the apoptosome activity / outer ear morphogenesis / regulation of cellular pH / regulation of Golgi inheritance / Signaling by LTK in cancer / ERBB signaling pathway / labyrinthine layer blood vessel development / mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation / trachea formation / Negative feedback regulation of MAPK pathway / regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport / regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade / IFNG signaling activates MAPKs / Frs2-mediated activation / positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis / ERBB2-ERBB3 signaling pathway / lung morphogenesis / response to exogenous dsRNA / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / ERK/MAPK targets / regulation of cytoskeleton organization / face development / androgen receptor signaling pathway / pseudopodium / RUNX2 regulates osteoblast differentiation / : / positive regulation of telomere capping / Recycling pathway of L1 / MAPK1 (ERK2) activation / Bergmann glial cell differentiation / thyroid gland development / negative regulation of cell differentiation / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / MAP kinase activity / RHO GTPases Activate NADPH Oxidases / regulation of ossification / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / Estrogen-dependent nuclear events downstream of ESR-membrane signaling / mitogen-activated protein kinase / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / phosphatase binding / Signal attenuation / Estrogen-stimulated signaling through PRKCZ / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / progesterone receptor signaling pathway / Schwann cell development / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / Growth hormone receptor signaling / lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of T cell proliferation / stress-activated MAPK cascade / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / phosphotyrosine residue binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / cellular response to cadmium ion / myelination / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / cellular response to amino acid starvation / NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth / ESR-mediated signaling / RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat kinase activity / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / thymus development / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / Signal transduction by L1 / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription / long-term synaptic potentiation / response to nicotine / peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / Negative regulation of FGFR2 signaling / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / Negative regulation of FGFR3 signaling / FCERI mediated MAPK activation / B cell receptor signaling pathway / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / Negative regulation of FGFR4 signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR1 signaling Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.67 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kochanowski P / Biela AP / Grudnik P | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Poland, 1 items Poland, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2024 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2024Title: ERK1/2 interaction with DHPS regulates eIF5A deoxyhypusination independently of ERK kinase activity. Authors: Andrew E Becker / Paweł Kochanowski / Pui-Kei Wu / Elżbieta Wątor / Wenjing Chen / Koushik Guchhait / Artur P Biela / Przemysław Grudnik / Jong-In Park /   Abstract: This study explores a non-kinase effect of extracellular regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) on the interaction between deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS) and its substrate, eukaryotic translation initiation ...This study explores a non-kinase effect of extracellular regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) on the interaction between deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS) and its substrate, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A). We report that Raf/MEK/ERK activation decreases the DHPS-ERK1/2 interaction while increasing DHPS-eIF5A association in cells. We determined the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the DHPS-ERK2 complex at 3.5 Å to show that ERK2 hinders substrate entrance to the DHPS active site, subsequently inhibiting deoxyhypusination in vitro. In cells, impairing the ERK2 activation loop, but not the catalytic site, prolongs the DHPS-ERK2 interaction irrespective of Raf/MEK signaling. The ERK2 Ser-Pro-Ser motif, but not the common docking or F-site recognition sites, also regulates this complex. These data suggest that ERK1/2 dynamically regulate the DHPS-eIF5A interaction in response to Raf/MEK activity, regardless of its kinase function. In contrast, ERK1/2 kinase activity is necessary to regulate the expression of DHPS and eIF5A. These findings highlight an ERK1/2-mediated dual kinase-dependent and -independent regulation of deoxyhypusination. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_17985.map.gz emd_17985.map.gz | 97.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-17985-v30.xml emd-17985-v30.xml emd-17985.xml emd-17985.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_17985_fsc.xml emd_17985_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_17985.png emd_17985.png | 126.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-17985.cif.gz emd-17985.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_17985_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17985_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17985_half_map_2.map.gz emd_17985_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.6 MB 95.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17985 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17985 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17985 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17985 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_17985_validation.pdf.gz emd_17985_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_17985_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_17985_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_17985_validation.xml.gz emd_17985_validation.xml.gz | 18.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_17985_validation.cif.gz emd_17985_validation.cif.gz | 23.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17985 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17985 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17985 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17985 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 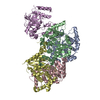 8pvuC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_17985.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_17985.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Main map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
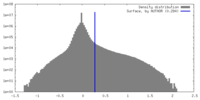
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_17985_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_17985_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of DHS-ERK2 with 1:3 stoichiometry
| Entire | Name: Complex of DHS-ERK2 with 1:3 stoichiometry |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of DHS-ERK2 with 1:3 stoichiometry
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of DHS-ERK2 with 1:3 stoichiometry / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: mitogen-activated protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMAAAAAAGA GPEMVRGQVF DVGPRYTNLS YIGEGAYGMV CSAYDNVNKV RVAIKKISPF EHQTYCQRTL REIKILLRFR HENIIGINDI IRAPTIEQMK DVYIVQDLME TDLYKLLKTQ HLSNDHICYF LYQILRGLKY IHSANVLHRD LKPSNLLLNT TCDLKICDFG ...String: SMAAAAAAGA GPEMVRGQVF DVGPRYTNLS YIGEGAYGMV CSAYDNVNKV RVAIKKISPF EHQTYCQRTL REIKILLRFR HENIIGINDI IRAPTIEQMK DVYIVQDLME TDLYKLLKTQ HLSNDHICYF LYQILRGLKY IHSANVLHRD LKPSNLLLNT TCDLKICDFG LARVADPDHD HTGFLTEYVA TRWYRAPEIM LNSKGYTKSI DIWSVGCILA EMLSNRPIFP GKHYLDQLNH ILGILGSPSQ EDLNCIINLK ARNYLLSLPH KNKVPWNRLF PNADSKALDL LDKMLTFNPH KRIEVEQALA HPYLEQYYDP SDEPIAEAPF KFDMELDDLP KEKLKELIFE ETARFQPGYR S UniProtKB: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: mitogen-activated protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMAAAAAAGA GPEMVRGQVF DVGPRYTNLS YIGEGAYGMV CSAYDNVNKV RVAIKKISPF EHQTYCQRTL REIKILLRFR HENIIGINDI IRAPTIEQMK DVYIVQDLME TDLYKLLKTQ HLSNDHICYF LYQILRGLKY IHSANVLHRD LKPSNLLLNT TCDLKICDFG ...String: SMAAAAAAGA GPEMVRGQVF DVGPRYTNLS YIGEGAYGMV CSAYDNVNKV RVAIKKISPF EHQTYCQRTL REIKILLRFR HENIIGINDI IRAPTIEQMK DVYIVQDLME TDLYKLLKTQ HLSNDHICYF LYQILRGLKY IHSANVLHRD LKPSNLLLNT TCDLKICDFG LARVADPDHD HTGFLTEYVA TRWYRAPEIM LNSKGYTKSI DIWSVGCILA EMLSNRPIFP GKHYLDQLNH ILGILGSPSQ EDLNCIINLK ARNYLLSLPH KNKVPWNRLF PNADSKALDL LDKMLTFNPH KRIEVEQALA HPYLEQYYDP SDEPIAEAPF KFDMELDDLP KEKLKELIFE ETARFQPGYR S UniProtKB: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: mitogen-activated protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMAAAAAAGA GPEMVRGQVF DVGPRYTNLS YIGEGAYGMV CSAYDNVNKV RVAIKKISPF EHQTYCQRTL REIKILLRFR HENIIGINDI IRAPTIEQMK DVYIVQDLME TDLYKLLKTQ HLSNDHICYF LYQILRGLKY IHSANVLHRD LKPSNLLLNT TCDLKICDFG ...String: SMAAAAAAGA GPEMVRGQVF DVGPRYTNLS YIGEGAYGMV CSAYDNVNKV RVAIKKISPF EHQTYCQRTL REIKILLRFR HENIIGINDI IRAPTIEQMK DVYIVQDLME TDLYKLLKTQ HLSNDHICYF LYQILRGLKY IHSANVLHRD LKPSNLLLNT TCDLKICDFG LARVADPDHD HTGFLTEYVA TRWYRAPEIM LNSKGYTKSI DIWSVGCILA EMLSNRPIFP GKHYLDQLNH ILGILGSPSQ EDLNCIINLK ARNYLLSLPH KNKVPWNRLF PNADSKALDL LDKMLTFNPH KRIEVEQALA HPYLEQYYDP SDEPIAEAPF KFDMELDDLP KEKLKELIFE ETARFQPGYR S UniProtKB: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Deoxyhypusine synthase
| Macromolecule | Name: Deoxyhypusine synthase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: deoxyhypusine synthase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL ...String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL LVPNENYCKF EDWLMPILDQ MVMEQNTEGV KWTPSKMIAR LGKEINNPES VYYWAQKNHI PVFSPALTDG SLGDMIFFHS YKNPGLVLDI VEDLRLINTQ AIFAKCTGMI ILGGGVVKHH IANANLMRNG ADYAVYINTA QEFDGSDSGA RPDEAVSWGK IRVDAQPVKV YADASLVFPL LVAETFAQKM DAFMHEKNED UniProtKB: Deoxyhypusine synthase |
-Macromolecule #5: Deoxyhypusine synthase
| Macromolecule | Name: Deoxyhypusine synthase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: deoxyhypusine synthase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL ...String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL LVPNENYCKF EDWLMPILDQ MVMEQNTEGV KWTPSKMIAR LGKEINNPES VYYWAQKNHI PVFSPALTDG SLGDMIFFHS YKNPGLVLDI VEDLRLINTQ AIFAKCTGMI ILGGGVVKHH IANANLMRNG ADYAVYINTA QEFDGSDSGA RPDEAVSWGK IRVDAQPVKV YADASLVFPL LVAETFAQKM DAFMHEKNED UniProtKB: Deoxyhypusine synthase |
-Macromolecule #6: Deoxyhypusine synthase
| Macromolecule | Name: Deoxyhypusine synthase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: deoxyhypusine synthase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL ...String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL LVPNENYCKF EDWLMPILDQ MVMEQNTEGV KWTPSKMIAR LGKEINNPES VYYWAQKNHI PVFSPALTDG SLGDMIFFHS YKNPGLVLDI VEDLRLINTQ AIFAKCTGMI ILGGGVVKHH IANANLMRNG ADYAVYINTA QEFDGSDSGA RPDEAVSWGK IRVDAQPVKV YADASLVFPL LVAETFAQKM DAFMHEKNED UniProtKB: Deoxyhypusine synthase |
-Macromolecule #7: Deoxyhypusine synthase
| Macromolecule | Name: Deoxyhypusine synthase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: deoxyhypusine synthase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL ...String: SMEGSLEREA PAGALAAVLK HSSTLPPEST QVRGYDFNRG VNYRALLEAF GTTGFQATNF GRAVQQVNAM IEKKLEPLSQ DEDQHADLTQ SRRPLTSCTI FLGYTSNLIS SGIRETIRYL VQHNMVDVLV TTAGGVEEDL IKCLAPTYLG EFSLRGKELR ENGINRIGNL LVPNENYCKF EDWLMPILDQ MVMEQNTEGV KWTPSKMIAR LGKEINNPES VYYWAQKNHI PVFSPALTDG SLGDMIFFHS YKNPGLVLDI VEDLRLINTQ AIFAKCTGMI ILGGGVVKHH IANANLMRNG ADYAVYINTA QEFDGSDSGA RPDEAVSWGK IRVDAQPVKV YADASLVFPL LVAETFAQKM DAFMHEKNED UniProtKB: Deoxyhypusine synthase |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.35 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 / Details: 50mM Tris-HCl, 200mM NaCl, 3mM 2-mercaptoethanol |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 70 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 278 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: blot time: 2 s, blot force: 0. |
| Details | Complex was stabilized with bis(sulfosuccinimidyl)suberate |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 6930 / Average electron dose: 40.16 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













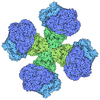



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)