[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-16563: 80S S. cerevisiae ribosome with ligands in hybrid-1 pre-transloca... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | 80S S. cerevisiae ribosome with ligands in hybrid-1 pre-translocation (PRE-H1) complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Eukaryote / ribosome / translocation / elongation | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of translational fidelity / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Protein methylation / ribosomal subunit / mTORC1-mediated signalling / Protein hydroxylation / ribosome-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay ...negative regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of translational fidelity / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Protein methylation / ribosomal subunit / mTORC1-mediated signalling / Protein hydroxylation / ribosome-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay / pre-mRNA 5'-splice site binding / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Translation initiation complex formation / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / nonfunctional rRNA decay / cleavage in ITS2 between 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / response to cycloheximide / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / mRNA destabilization / negative regulation of translational frameshifting / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / preribosome, large subunit precursor / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / translational elongation / regulation of amino acid metabolic process / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / 90S preribosome / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / regulation of translational fidelity / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / protein-RNA complex assembly / maturation of LSU-rRNA / translational termination / translation regulator activity / rescue of stalled ribosome / cellular response to amino acid starvation / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / protein kinase C binding / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / small-subunit processome / translational initiation / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / macroautophagy / maintenance of translational fidelity / modification-dependent protein catabolic process / protein tag activity / rRNA processing / cytoplasmic stress granule / ribosome biogenesis / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / 5S rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / protein ubiquitination / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / translation / negative regulation of gene expression / response to antibiotic / mRNA binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / nucleolus / mitochondrion / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / metal ion binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
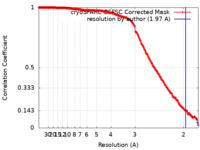
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Milicevic N / Jenner L / Myasnikov A / Yusupov M / Yusupova G | |||||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1 items France, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: mRNA reading frame maintenance during eukaryotic ribosome translocation. Authors: Nemanja Milicevic / Lasse Jenner / Alexander Myasnikov / Marat Yusupov / Gulnara Yusupova /   Abstract: One of the most critical steps of protein synthesis is coupled translocation of messenger RNA (mRNA) and transfer RNAs (tRNAs) required to advance the mRNA reading frame by one codon. In ...One of the most critical steps of protein synthesis is coupled translocation of messenger RNA (mRNA) and transfer RNAs (tRNAs) required to advance the mRNA reading frame by one codon. In eukaryotes, translocation is accelerated and its fidelity is maintained by elongation factor 2 (eEF2). At present, only a few snapshots of eukaryotic ribosome translocation have been reported. Here we report ten high-resolution cryogenic-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of the elongating eukaryotic ribosome bound to the full translocation module consisting of mRNA, peptidyl-tRNA and deacylated tRNA, seven of which also contained ribosome-bound, naturally modified eEF2. This study recapitulates mRNA-tRNA-growing peptide module progression through the ribosome, from the earliest states of eEF2 translocase accommodation until the very late stages of the process, and shows an intricate network of interactions preventing the slippage of the translational reading frame. We demonstrate how the accuracy of eukaryotic translocation relies on eukaryote-specific elements of the 80S ribosome, eEF2 and tRNAs. Our findings shed light on the mechanism of translation arrest by the anti-fungal eEF2-binding inhibitor, sordarin. We also propose that the sterically constrained environment imposed by diphthamide, a conserved eukaryotic posttranslational modification in eEF2, not only stabilizes correct Watson-Crick codon-anticodon interactions but may also uncover erroneous peptidyl-tRNA, and therefore contribute to higher accuracy of protein synthesis in eukaryotes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16563.map.gz emd_16563.map.gz | 416.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16563-v30.xml emd-16563-v30.xml emd-16563.xml emd-16563.xml | 101.7 KB 101.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16563_fsc.xml emd_16563_fsc.xml | 19.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16563.png emd_16563.png | 37.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16563.cif.gz emd-16563.cif.gz | 20.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16563_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16563_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16563_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16563_half_map_2.map.gz | 764.3 MB 764.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16563 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16563 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_16563_validation.pdf.gz emd_16563_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_16563_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_16563_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_16563_validation.xml.gz emd_16563_validation.xml.gz | 28.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_16563_validation.cif.gz emd_16563_validation.cif.gz | 38.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16563 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16563 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8ccsMC  8cdlC  8cdrC  8cehC  8cf5C  8cg8C  8cgnC  8civC  8ckuC  8cmjC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16563.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16563.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.9 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
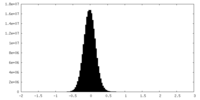
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_16563_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
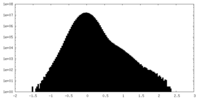
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_16563_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Elongating Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome in complex with ...
+Supramolecule #1: Elongating Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome in complex with ...
+Macromolecule #1: 40S ribosomal protein S24-A
+Macromolecule #2: 40S ribosomal protein S25-A
+Macromolecule #3: 40S ribosomal protein S26
+Macromolecule #4: 40S ribosomal protein S27-A
+Macromolecule #5: 40S ribosomal protein S28-A
+Macromolecule #6: HLJ1_G0030400.mRNA.1.CDS.1
+Macromolecule #7: 40S ribosomal protein S30-A
+Macromolecule #8: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-like protein
+Macromolecule #9: Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S31
+Macromolecule #10: 60S ribosomal protein L16-A
+Macromolecule #12: 60S ribosomal protein L17-A
+Macromolecule #15: 60S ribosomal protein L18-A
+Macromolecule #18: 60S ribosomal protein L19-A
+Macromolecule #19: 60S acidic ribosomal protein P0
+Macromolecule #21: 60S ribosomal protein L20-A
+Macromolecule #22: 60S ribosomal protein L2-A
+Macromolecule #23: 60S ribosomal protein L12-A
+Macromolecule #24: 60S ribosomal protein L21-A
+Macromolecule #25: 60S ribosomal protein L3
+Macromolecule #26: 60S ribosomal protein L22-A
+Macromolecule #27: 60S ribosomal protein L4-A
+Macromolecule #28: 60S ribosomal protein L23-A
+Macromolecule #29: 60S ribosomal protein L5
+Macromolecule #30: 60S ribosomal protein L24-A
+Macromolecule #31: 60S ribosomal protein L6-A
+Macromolecule #32: 60S ribosomal protein L25
+Macromolecule #33: 60S ribosomal protein L7-A
+Macromolecule #34: 60S ribosomal protein L26-A
+Macromolecule #35: 60S ribosomal protein L8-A
+Macromolecule #36: 60S ribosomal protein L27-A
+Macromolecule #37: 60S ribosomal protein L9-A
+Macromolecule #38: 60S ribosomal protein L28
+Macromolecule #39: 60S ribosomal protein L10
+Macromolecule #40: 60S ribosomal protein L29
+Macromolecule #41: 60S ribosomal protein L11-A
+Macromolecule #42: 60S ribosomal protein L30
+Macromolecule #43: 60S ribosomal protein L13-A
+Macromolecule #44: 60S ribosomal protein L31-A
+Macromolecule #45: 60S ribosomal protein L14-A
+Macromolecule #46: di-peptide
+Macromolecule #47: 60S ribosomal protein L32
+Macromolecule #48: 60S ribosomal protein L15-A
+Macromolecule #49: 60S ribosomal protein L33-A
+Macromolecule #50: 60S ribosomal protein L34-A
+Macromolecule #51: 60S ribosomal protein L35-A
+Macromolecule #52: 60S ribosomal protein L36-A
+Macromolecule #53: 60S ribosomal protein L37-A
+Macromolecule #54: 60S ribosomal protein L38
+Macromolecule #55: 60S ribosomal protein L39
+Macromolecule #56: Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40
+Macromolecule #57: 60S ribosomal protein L41-A
+Macromolecule #58: 60S ribosomal protein L42-A
+Macromolecule #59: 60S ribosomal protein L43-A
+Macromolecule #61: 40S ribosomal protein S0-A
+Macromolecule #62: 40S ribosomal protein S1-A
+Macromolecule #63: 40S ribosomal protein S2
+Macromolecule #64: RPS3 isoform 1
+Macromolecule #65: 40S ribosomal protein S4-A
+Macromolecule #66: 40S ribosomal protein S5
+Macromolecule #67: 40S ribosomal protein S6-A
+Macromolecule #68: 40S ribosomal protein S7-A
+Macromolecule #69: 40S ribosomal protein S8-B
+Macromolecule #70: 40S ribosomal protein S9-A
+Macromolecule #71: 40S ribosomal protein S10-A
+Macromolecule #72: 40S ribosomal protein S11-A
+Macromolecule #73: 40S ribosomal protein S13
+Macromolecule #74: 40S ribosomal protein S14-A
+Macromolecule #75: 40S ribosomal protein S15
+Macromolecule #76: 40S ribosomal protein S16-A
+Macromolecule #77: 40S ribosomal protein S17-A
+Macromolecule #78: 40S ribosomal protein S18-A
+Macromolecule #79: 40S ribosomal protein S19-A
+Macromolecule #80: 40S ribosomal protein S20
+Macromolecule #81: 40S ribosomal protein S21-A
+Macromolecule #82: 40S ribosomal protein S22-A
+Macromolecule #83: 40S ribosomal protein S23-A
+Macromolecule #11: 25S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #13: 5S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #14: Transfer RNA Phe
+Macromolecule #16: 5.8S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #17: Transfer RNA fMet
+Macromolecule #20: Messenger RNA
+Macromolecule #60: 18S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #84: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #85: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #86: POTASSIUM ION
+Macromolecule #87: SPERMIDINE
+Macromolecule #88: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.4 µm / Nominal magnification: 270000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)