[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-13801: Local refinement structure of the C-domain of full-length, monome... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Local refinement structure of the C-domain of full-length, monomeric, soluble somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Globally-sharpened map from local refinement of the C-domain of full-length monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Zinc metalloprotease Dicarboxypeptidase Glycoprotein / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmononuclear cell proliferation / cell proliferation in bone marrow / bradykinin receptor binding / exopeptidase activity / regulation of angiotensin metabolic process / substance P catabolic process / peptidyl-dipeptidase A / tripeptidyl-peptidase activity / regulation of renal output by angiotensin / positive regulation of peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation ...mononuclear cell proliferation / cell proliferation in bone marrow / bradykinin receptor binding / exopeptidase activity / regulation of angiotensin metabolic process / substance P catabolic process / peptidyl-dipeptidase A / tripeptidyl-peptidase activity / regulation of renal output by angiotensin / positive regulation of peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation / negative regulation of calcium ion import / response to laminar fluid shear stress / negative regulation of gap junction assembly / metallodipeptidase activity / cellular response to aldosterone / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / angiogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis / response to thyroid hormone / negative regulation of D-glucose import / vasoconstriction / neutrophil mediated immunity / regulation of smooth muscle cell migration / regulation of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / hormone metabolic process / mitogen-activated protein kinase binding / embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching / chloride ion binding / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding / positive regulation of neurogenesis / arachidonate secretion / post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression / eating behavior / heterocyclic compound binding / peptide catabolic process / heart contraction / lung alveolus development / antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / positive regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / response to dexamethasone / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by renin-angiotensin / blood vessel remodeling / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / amyloid-beta metabolic process / regulation of vasoconstriction / peptidyl-dipeptidase activity / animal organ regeneration / angiotensin maturation / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / positive regulation of vasoconstriction / carboxypeptidase activity / sperm midpiece / blood vessel diameter maintenance / basal plasma membrane / kidney development / angiotensin-activated signaling pathway / female pregnancy / brush border membrane / response to nutrient levels / cellular response to glucose stimulus / regulation of synaptic plasticity / metalloendopeptidase activity / regulation of blood pressure / male gonad development / metallopeptidase activity / peptidase activity / actin binding / spermatogenesis / endopeptidase activity / response to lipopolysaccharide / lysosome / response to hypoxia / calmodulin binding / endosome / positive regulation of apoptotic process / response to xenobiotic stimulus / external side of plasma membrane / negative regulation of gene expression / proteolysis / extracellular space / zinc ion binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
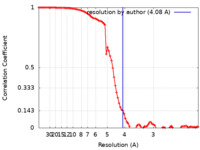
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.08 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lubbe L / Sewell BT / Sturrock ED | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2022 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM reveals mechanisms of angiotensin I-converting enzyme allostery and dimerization. Authors: Lizelle Lubbe / Bryan Trevor Sewell / Jeremy D Woodward / Edward D Sturrock /  Abstract: Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death worldwide. The somatic isoform of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (sACE) ...Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death worldwide. The somatic isoform of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (sACE) plays a critical role in blood pressure regulation, and ACE inhibitors are thus widely used to treat hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Our current understanding of sACE structure, dynamics, function, and inhibition has been limited because truncated, minimally glycosylated forms of sACE are typically used for X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamics simulations. Here, we report the first cryo-EM structures of full-length, glycosylated, soluble sACE (sACE ). Both monomeric and dimeric forms of the highly flexible apo enzyme were reconstructed from a single dataset. The N- and C-terminal domains of monomeric sACE were resolved at 3.7 and 4.1 Å, respectively, while the interacting N-terminal domains responsible for dimer formation were resolved at 3.8 Å. Mechanisms are proposed for intradomain hinging, cooperativity, and homodimerization. Furthermore, the observation that both domains were in the open conformation has implications for the design of sACE modulators. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13801.map.gz emd_13801.map.gz | 59.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13801-v30.xml emd-13801-v30.xml emd-13801.xml emd-13801.xml | 27.5 KB 27.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13801_fsc.xml emd_13801_fsc.xml | 8.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13801.png emd_13801.png | 69.8 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13801_msk_1.map emd_13801_msk_1.map emd_13801_msk_2.map emd_13801_msk_2.map | 64 MB 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13801.cif.gz emd-13801.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_13801_additional_1.map.gz emd_13801_additional_1.map.gz emd_13801_additional_2.map.gz emd_13801_additional_2.map.gz emd_13801_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13801_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13801_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13801_half_map_2.map.gz | 2.2 MB 59.4 MB 59.4 MB 59.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13801 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13801 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13801 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13801 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_13801_validation.pdf.gz emd_13801_validation.pdf.gz | 1002.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_13801_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_13801_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1002.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_13801_validation.xml.gz emd_13801_validation.xml.gz | 16.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_13801_validation.cif.gz emd_13801_validation.cif.gz | 20.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13801 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13801 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13801 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13801 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7q4cMC  7q3yC  7q49C  7q4dC  7q4eC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10980 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of monomeric and dimeric human somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme (apo form) EMPIAR-10980 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of monomeric and dimeric human somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme (apo form)Data size: 3.8 TB Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame cryo-EM micrographs of human somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme in the apo state [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13801.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13801.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Globally-sharpened map from local refinement of the C-domain of full-length monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
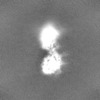
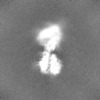
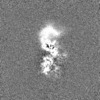
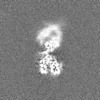
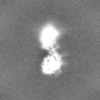
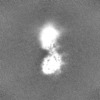
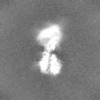
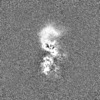
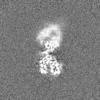
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
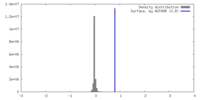
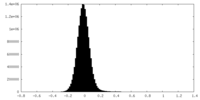
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_13801_msk_1.map emd_13801_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
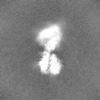
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
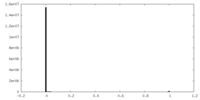
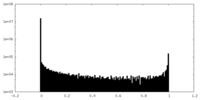
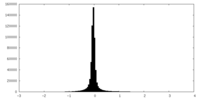
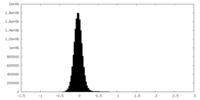
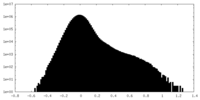
| Density Histograms |
-Mask #2
| File |  emd_13801_msk_2.map emd_13801_msk_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
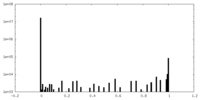
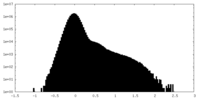
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Density-modified map (Phenix resolve cryo-EM) from local refinement...
| File | emd_13801_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Density-modified map (Phenix resolve cryo-EM) from local refinement of the C-domain of full-length monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Raw, unfiltered full map from local refinement of...
| File | emd_13801_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Raw, unfiltered full map from local refinement of the C-domain of full-length monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Raw, unfiltered half-map B from local refinement of...
| File | emd_13801_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Raw, unfiltered half-map B from local refinement of the C-domain of full-length monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Raw, unfiltered half-map A from local refinement of...
| File | emd_13801_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Raw, unfiltered half-map A from local refinement of the C-domain of full-length monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Full-length, soluble, monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting ...
| Entire | Name: Full-length, soluble, monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Full-length, soluble, monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Full-length, soluble, monomeric somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 139 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Angiotensin-converting enzyme
| Macromolecule | Name: Angiotensin-converting enzyme / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Soluble secreted form of human somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme terminating at Ser1211,Soluble secreted form of human somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme terminating at Ser1211 Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Glycosylases; Glycosidases, i.e. enzymes that hydrolyse O- and S-glycosyl compounds |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 139.614 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: LDPGLQPGNF SADEAGAQLF AQSYNSSAEQ VLFQSVAASW AHDTNITAEN ARRQEEAALL SQEFAEAWGQ KAKELYEPIW QNFTDPQLR RIIGAVRTLG SANLPLAKRQ QYNALLSNMS RIYSTAKVCL PNKTATCWSL DPDLTNILAS SRSYAMLLFA W EGWHNAAG ...String: LDPGLQPGNF SADEAGAQLF AQSYNSSAEQ VLFQSVAASW AHDTNITAEN ARRQEEAALL SQEFAEAWGQ KAKELYEPIW QNFTDPQLR RIIGAVRTLG SANLPLAKRQ QYNALLSNMS RIYSTAKVCL PNKTATCWSL DPDLTNILAS SRSYAMLLFA W EGWHNAAG IPLKPLYEDF TALSNEAYKQ DGFTDTGAYW RSWYNSPTFE DDLEHLYQQL EPLYLNLHAF VRRALHRRYG DR YINLRGP IPAHLLGDMW AQSWENIYDM VVPFPDKPNL DVTSTMLQQG WNATHMFRVA EEFFTSLELS PMPPEFWEGS MLE KPADGR EVVCHASAWD FYNRKDFRIK QCTRVTMDQL STVHHEMGHI QYYLQYKDLP VSLRRGANPG FHEAIGDVLA LSVS TPEHL HKIGLLDRVT NDTESDINYL LKMALEKIAF LPFGYLVDQW RWGVFSGRTP PSRYNFDWWY LRTKYQGICP PVTRN ETHF DAGAKFHVPN VTPYIRYFVS FVLQFQFHEA LCKEAGYEGP LHQCDIYRST KAGAKLRKVL QAGSSRPWQE VLKDMV GLD ALDAQPLLKY FQLVTQWLQE QNQQNGEVLG WPEYQWHPPL PDNYPEGIDL VTDEAEASKF VEEYDRTSQV VWNEYAE AN WNYNTNITTE TSKILLQKNM QIANHTLKYG TQARKFDVNQ LQNTTIKRII KKVQDLERAA LPAQELEEYN KILLDMET T YSVATVCHPN GSCLQLEPDL TNVMATSRKY EDLLWAWEGW RDKAGRAILQ FYPKYVELIN QAARLNGYVD AGDSWRSMY ETPSLEQDLE RLFQELQPLY LNLHAYVRRA LHRHYGAQHI NLEGPIPAHL LGNMWAQTWS NIYDLVVPFP SAPSMDTTEA MLKQGWTPR RMFKEADDFF TSLGLLPVPP EFWNKSMLEK PTDGREVVCH ASAWDFYNGK DFRIKQCTTV NLEDLVVAHH E MGHIQYFM QYKDLPVALR EGANPGFHEA IGDVLALSVS TPKHLHSLNL LSSEGGSDEH DINFLMKMAL DKIAFIPFSY LV DQWRWRV FDGSITKENY NQEWWSLRLK YQGLCPPVPR TQGDFDPGAK FHIPSSVPYI RYFVSFIIQF QFHEALCQAA GHT GPLHKC DIYQSKEAGQ RLATAMKLGF SRPWPEAMQL ITGQPNMSAS AMLSYFKPLL DWLRTENELH GEKLGWPQYN WTPN SARSE GPLPDS UniProtKB: Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
-Macromolecule #4: CHLORIDE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CHLORIDE ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.453 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: Solutions were prepared with deionized water | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Diluted protein (in buffer containing zinc chloride and sodium chloride) was incubated on ice for 30 minutes after which it was applied to the grid, incubated for 30 seconds, and blotted for ...Details: Diluted protein (in buffer containing zinc chloride and sodium chloride) was incubated on ice for 30 minutes after which it was applied to the grid, incubated for 30 seconds, and blotted for 3 seconds before plunging. | ||||||||||||
| Details | The protein was stored at 3.0mg/ml in 50mM HEPES (pH 7.5) and diluted immediately prior to grid preparation |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 11628 / Average exposure time: 3.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 43.0 e/Å2 Details: Images were recorded in super-resolution mode with 40 frames per image |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7q4c: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)