[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDBW7: N-terminal and chromo-ATPase-DBD domains of chromo domain-contain... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDBW7 |
|---|---|
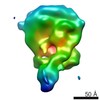
 Sample Sample | N-terminal and chromo-ATPase-DBD domains of chromo domain-containing protein 1 (Chd1: 1-1305)
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnucleolar chromatin / regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome organization /  rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion ...nucleolar chromatin / regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome organization / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion ...nucleolar chromatin / regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome organization /  rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / methylated histone binding / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / methylated histone binding /  helicase activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / helicase activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / chromatin DNA binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / chromatin DNA binding /  histone binding / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / histone binding / transcription cis-regulatory region binding /  chromatin remodeling / chromatin remodeling /  chromatin binding / chromatin binding /  chromatin / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  nucleus nucleusSimilarity search - Function |
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2017 Journal: Elife / Year: 2017Title: Structural reorganization of the chromatin remodeling enzyme Chd1 upon engagement with nucleosomes. Authors: Ramasubramanian Sundaramoorthy / Amanda L Hughes / Vijender Singh / Nicola Wiechens / Daniel P Ryan / Hassane El-Mkami / Maxim Petoukhov / Dmitri I Svergun / Barbara Treutlein / Salina Quack ...Authors: Ramasubramanian Sundaramoorthy / Amanda L Hughes / Vijender Singh / Nicola Wiechens / Daniel P Ryan / Hassane El-Mkami / Maxim Petoukhov / Dmitri I Svergun / Barbara Treutlein / Salina Quack / Monika Fischer / Jens Michaelis / Bettina Böttcher / David G Norman / Tom Owen-Hughes /   Abstract: The yeast Chd1 protein acts to position nucleosomes across genomes. Here, we model the structure of the Chd1 protein in solution and when bound to nucleosomes. In the apo state, the DNA-binding ...The yeast Chd1 protein acts to position nucleosomes across genomes. Here, we model the structure of the Chd1 protein in solution and when bound to nucleosomes. In the apo state, the DNA-binding domain contacts the edge of the nucleosome while in the presence of the non-hydrolyzable ATP analog, ADP-beryllium fluoride, we observe additional interactions between the ATPase domain and the adjacent DNA gyre 1.5 helical turns from the dyad axis of symmetry. Binding in this conformation involves unravelling the outer turn of nucleosomal DNA and requires substantial reorientation of the DNA-binding domain with respect to the ATPase domains. The orientation of the DNA-binding domain is mediated by sequences in the N-terminus and mutations to this part of the protein have positive and negative effects on Chd1 activity. These observations indicate that the unfavorable alignment of C-terminal DNA-binding region in solution contributes to an auto-inhibited state. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Models
| Model #917 |  Type: dummy / Software: GASBOR (2.3i) / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Symmetry  : C1 / Chi-square value: 1.90 / P-value: 0.000020 : C1 / Chi-square value: 1.90 / P-value: 0.000020 Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: N-terminal and chromo-ATPase-DBD domains of chromo domain-containing protein 1 (Chd1: 1-1305) Specimen concentration: 0.50-4.00 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 50mM Hepes 150mM NaCl / pH: 7.5 |
| Entity #519 | Name: Chd1 / Type: protein / Description: chromodomain helicase DNA binding domain / Formula weight: 150.014 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Saccharomyces cerevisiae / References: UniProt: P32657 / Type: protein / Description: chromodomain helicase DNA binding domain / Formula weight: 150.014 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Saccharomyces cerevisiae / References: UniProt: P32657Sequence: MAAKDISTEV LQNPELYGLR RSHRAAAHQQ NYFNDSDDED DEDNIKQSRR KRMTTIEDDE DEFEDEEGEE DSGEDEDEED FEEDDDYYGS PIKQNRSKPK SRTKSKSKSK PKSQSEKQST VKIPTRFSNR QNKTVNYNID YSDDDLLESE DDYGSEEALS EENVHEASAN ...Sequence: MAAKDISTEV LQNPELYGLR RSHRAAAHQQ NYFNDSDDED DEDNIKQSRR KRMTTIEDDE DEFEDEEGEE DSGEDEDEED FEEDDDYYGS PIKQNRSKPK SRTKSKSKSK PKSQSEKQST VKIPTRFSNR QNKTVNYNID YSDDDLLESE DDYGSEEALS EENVHEASAN PQPEDFHGID IVINHRLKTS LEEGKVLEKT VPDLNNCKEN YEFLIKWTDE SHLHNTWETY ESIGQVRGLK RLDNYCKQFI IEDQQVRLDP YVTAEDIEIM DMERERRLDE FEEFHVPERI IDSQRASLED GTSQLQYLVK WRRLNYDEAT WENATDIVKL APEQVKHFQN RENSKILPQY SSNYTSQRPR FEKLSVQPPF IKGGELRDFQ LTGINWMAFL WSKGDNGILA DEMGLGKTVQ TVAFISWLIF ARRQNGPHII VVPLSTMPAW LDTFEKWAPD LNCICYMGNQ KSRDTIREYE FYTNPRAKGK KTMKFNVLLT TYEYILKDRA ELGSIKWQFM AVDEAHRLKN AESSLYESLN SFKVANRMLI TGTPLQNNIK ELAALVNFLM PGRFTIDQEI DFENQDEEQE EYIHDLHRRI QPFILRRLKK DVEKSLPSKT ERILRVELSD VQTEYYKNIL TKNYSALTAG AKGGHFSLLN IMNELKKASN HPYLFDNAEE RVLQKFGDGK MTRENVLRGL IMSSGKMVLL DQLLTRLKKD GHRVLIFSQM VRMLDILGDY LSIKGINFQR LDGTVPSAQR RISIDHFNSP DSNDFVFLLS TRAGGLGINL MTADTVVIFD SDWNPQADLQ AMARAHRIGQ KNHVMVYRLV SKDTVEEEVL ERARKKMILE YAIISLGVTD GNKYTKKNEP NAGELSAILK FGAGNMFTAT DNQKKLEDLN LDDVLNHAED HVTTPDLGES HLGGEEFLKQ FEVTDYKADI DWDDIIPEEE LKKLQDEEQK RKDEEYVKEQ LEMMNRRDNA LKKIKNSVNG DGTAANSDSD DDSTSRSSRR RARANDMDSI GESEVRALYK AILKFGNLKE ILDELIADGT LPVKSFEKYG ETYDEMMEAA KDCVHEEEKN RKEILEKLEK HATAYRAKLK SGEIKAENQP KDNPLTRLSL KKREKKAVLF NFKGVKSLNA ESLLSRVEDL KYLKNLINSN YKDDPLKFSL GNNTPKPVQN WSSNWTKEED EKLLIGVFKY GYGSWTQIRD DPFLGITDKI FLNEVHNPVA KKSASSSDTT PTPSKKGKGI TGSSKKVPGA IHLGRRVDYL LSFLRGGLNT KSPSADIGSK KLPTGPSKKR QRKPANHSKS MTPEI |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name:  DORIS III X33 DORIS III X33  / City: Hamburg / 国: Germany / City: Hamburg / 国: Germany  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron Synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.154 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 5 mm Synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.154 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 5 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus 2M | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

 SASDBW7
SASDBW7