+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8g57 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
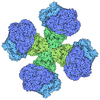
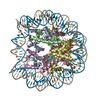
| Title | Structure of nucleosome-bound Sirtuin 6 deacetylase | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE/DNA /  Nucleosome / Nucleosome /  Sirt6 / Sirt6 /  aging / aging /  DNA damage / DNA damage /  repair / repair /  deacetylation / diacylation / apo / deacetylation / diacylation / apo /  chromatin / chromatin /  heterochromatin / heterochromatin /  GENE REGULATION / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex GENE REGULATION / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationNAD-dependent histone H3K56 deacetylase activity / NAD-dependent histone H3K18 deacetylase activity / ketone biosynthetic process / NAD-dependent histone H3K9 deacetylase activity / protein delipidation / regulation of lipid catabolic process / NAD+- protein-lysine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD-dependent protein demyristoylase activity / NAD-dependent protein depalmitoylase activity /  chromosome, subtelomeric region ...NAD-dependent histone H3K56 deacetylase activity / NAD-dependent histone H3K18 deacetylase activity / ketone biosynthetic process / NAD-dependent histone H3K9 deacetylase activity / protein delipidation / regulation of lipid catabolic process / NAD+- protein-lysine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD-dependent protein demyristoylase activity / NAD-dependent protein depalmitoylase activity / chromosome, subtelomeric region ...NAD-dependent histone H3K56 deacetylase activity / NAD-dependent histone H3K18 deacetylase activity / ketone biosynthetic process / NAD-dependent histone H3K9 deacetylase activity / protein delipidation / regulation of lipid catabolic process / NAD+- protein-lysine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD-dependent protein demyristoylase activity / NAD-dependent protein depalmitoylase activity /  chromosome, subtelomeric region / pericentric heterochromatin formation / NAD+-protein-arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / positive regulation of protein localization to chromatin / DNA damage sensor activity / positive regulation of stem cell differentiation / positive regulation of blood vessel branching / retrotransposon silencing / NAD-dependent protein lysine deacetylase activity / protein localization to site of double-strand break / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase / NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity / positive regulation of chondrocyte proliferation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance / protein deacetylation / negative regulation of glucose import / TORC2 complex binding / chromosome, subtelomeric region / pericentric heterochromatin formation / NAD+-protein-arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / positive regulation of protein localization to chromatin / DNA damage sensor activity / positive regulation of stem cell differentiation / positive regulation of blood vessel branching / retrotransposon silencing / NAD-dependent protein lysine deacetylase activity / protein localization to site of double-strand break / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase / NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity / positive regulation of chondrocyte proliferation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance / protein deacetylation / negative regulation of glucose import / TORC2 complex binding /  lncRNA binding / negative regulation of glycolytic process / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / negative regulation of protein import into nucleus / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of stem cell proliferation / lncRNA binding / negative regulation of glycolytic process / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / negative regulation of protein import into nucleus / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of stem cell proliferation /  regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / site of DNA damage / NAD+-protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / negative regulation of cellular senescence / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / regulation of lipid metabolic process / regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / site of DNA damage / NAD+-protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / negative regulation of cellular senescence / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / regulation of lipid metabolic process /  NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity /  Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases / Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases /  nucleosome binding / nucleosome binding /  NAD+ binding / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of fat cell differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / pericentric heterochromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / response to UV / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / NAD+ binding / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of fat cell differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / pericentric heterochromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / response to UV / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere /  Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening /  nucleotidyltransferase activity / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / nucleotidyltransferase activity / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication /  DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / HCMV Late Events / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / HCMV Late Events / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression /  innate immune response in mucosa / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / determination of adult lifespan / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / innate immune response in mucosa / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / determination of adult lifespan / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) /  lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex /  base-excision repair / circadian regulation of gene expression / protein destabilization / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / base-excision repair / circadian regulation of gene expression / protein destabilization / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression /  regulation of circadian rhythm / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / positive regulation of insulin secretion / Metalloprotease DUBs / chromatin DNA binding regulation of circadian rhythm / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / positive regulation of insulin secretion / Metalloprotease DUBs / chromatin DNA bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.07 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.07 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chio, U.S. / Rechiche, O. / Bryll, A.R. / Zhu, J. / Feldman, J.L. / Peterson, C.L. / Tan, S. / Armache, J.-P. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM structure of the human Sirtuin 6-nucleosome complex. Authors: Un Seng Chio / Othman Rechiche / Alysia R Bryll / Jiang Zhu / Erik M Leith / Jessica L Feldman / Craig L Peterson / Song Tan / Jean-Paul Armache /  Abstract: Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is a multifaceted protein deacetylase/deacylase and a major target for small-molecule modulators of longevity and cancer. In the context of chromatin, SIRT6 removes acetyl groups ...Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is a multifaceted protein deacetylase/deacylase and a major target for small-molecule modulators of longevity and cancer. In the context of chromatin, SIRT6 removes acetyl groups from histone H3 in nucleosomes, but the molecular basis for its nucleosomal substrate preference is unknown. Our cryo-electron microscopy structure of human SIRT6 in complex with the nucleosome shows that the catalytic domain of SIRT6 pries DNA from the nucleosomal entry-exit site and exposes the histone H3 N-terminal helix, while the SIRT6 zinc-binding domain binds to the histone acidic patch using an arginine anchor. In addition, SIRT6 forms an inhibitory interaction with the C-terminal tail of histone H2A. The structure provides insights into how SIRT6 can deacetylate both H3 K9 and H3 K56. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8g57.cif.gz 8g57.cif.gz | 339.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8g57.ent.gz pdb8g57.ent.gz | 260.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8g57.json.gz 8g57.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g5/8g57 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g5/8g57 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g5/8g57 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g5/8g57 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29735MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 9 molecules KAEBFCGDH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 39708.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SIRT6, SIR2L6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SIRT6, SIR2L6 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)References: UniProt: Q8N6T7,  Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups, protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase, Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups, protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase,  Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  Mass: 15004.579 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Gene: LOC121398065 / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Gene: LOC121398065 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: A0A310TTQ1 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: A0A310TTQ1#3: Protein |  Mass: 9704.396 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799#4: Protein | Mass: 14034.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC4, H2AFM, HIST1H2AB, H2AC8, H2AFA, HIST1H2AE / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC4, H2AFM, HIST1H2AB, H2AC8, H2AFA, HIST1H2AE / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P04908 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P04908#5: Protein | Mass: 13804.045 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC11, H2BFR, HIST1H2BJ / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC11, H2BFR, HIST1H2BJ / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P06899 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P06899 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #6: DNA chain |  DNA DNAMass: 46541.637 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain |  DNA DNAMass: 46061.348 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Sirt6 deacetylase bound to a nucleosome assembled with 172-bp 601 Widom DNA Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 300 kDa/nm / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 12.5 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 60 mM KCl, 1.5% glycerol, 1 mM DTT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: SIRT6 deacetylase bound to asymmetrical nucleosome with 172 DNA base-pairs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Glass slides were wrapped with fresh parafilm. Tweezers were washed with ethanol, dried, and then used to pick grids from a grid box. Grids were carefully examined and placed on the parafilm- ...Details: Glass slides were wrapped with fresh parafilm. Tweezers were washed with ethanol, dried, and then used to pick grids from a grid box. Grids were carefully examined and placed on the parafilm-covered slides. These slides were then placed into the PelCO easyGLOW glow discharger, and treated there. Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Calibrated magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2200 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Calibrated magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2200 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 75 K / Temperature (min): 64 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 3.3 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 11872 Details: Data was collected in Super Resolution mode, thus the image size is 11520 (width) x 8184 (height) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV / Phase plate: OTHER |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Details: CTF was estimated using Patch CTF estimation (multi), and was applied during the refinement Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 12821862 / Details: Particles were selected using Blob Picker | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.07 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 71603 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 79 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL Details: UCSF Chimera was used for manual fitting of the models; It was then used for optimizing the fit by using option Fit in Map. Then Coot was used to analyze the fits, build and adjust the ...Details: UCSF Chimera was used for manual fitting of the models; It was then used for optimizing the fit by using option Fit in Map. Then Coot was used to analyze the fits, build and adjust the models into the existing densities, and refine parts of the model. Once the model has been built, validated and adjusted, we used phenix.real_space_refine to fix and improve the fit into the densities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj