+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8g46 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of DDB1deltaB-DDA1-DCAF16-BRD4(BD2)-MMH2 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  LIGASE / LIGASE /  E3 ligase / E3 ligase /  ubiquitin / degrader / targeted protein degradation ubiquitin / degrader / targeted protein degradation | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / UV-damage excision repair / biological process involved in interaction with symbiont / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / WD40-repeat domain binding / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex ...positive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / UV-damage excision repair / biological process involved in interaction with symbiont / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / WD40-repeat domain binding / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process / cullin family protein binding / RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain binding / negative regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / P-TEFb complex binding / viral release from host cell / negative regulation by host of viral transcription / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of viral genome replication / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / histone reader activity / RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat kinase activity / condensed nuclear chromosome / proteasomal protein catabolic process / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / nucleotide-excision repair / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II /  transcription coregulator activity / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / lysine-acetylated histone binding / Dual Incision in GG-NER / transcription coregulator activity / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / lysine-acetylated histone binding / Dual Incision in GG-NER /  regulation of circadian rhythm / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / regulation of circadian rhythm / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex /  Wnt signaling pathway / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / protein polyubiquitination / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / cellular response to UV / rhythmic process / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Wnt signaling pathway / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / protein polyubiquitination / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / cellular response to UV / rhythmic process / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process /  p53 binding / site of double-strand break / p53 binding / site of double-strand break /  chromosome / chromosome /  Neddylation / Neddylation /  regulation of inflammatory response / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Potential therapeutics for SARS / damaged DNA binding / regulation of inflammatory response / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Potential therapeutics for SARS / damaged DNA binding /  chromosome, telomeric region / chromosome, telomeric region /  transcription coactivator activity / protein ubiquitination / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / transcription coactivator activity / protein ubiquitination / transcription cis-regulatory region binding /  chromatin remodeling / chromatin remodeling /  DNA repair / apoptotic process / DNA damage response / DNA repair / apoptotic process / DNA damage response /  chromatin binding / protein-containing complex binding / chromatin binding / protein-containing complex binding /  nucleolus / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / nucleolus / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription /  enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular space / extracellular exosome /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ma, M.W. / Hunkeler, M. / Jin, C.Y. / Fischer, E.S. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023Title: Template-assisted covalent modification of DCAF16 underlies activity of BRD4 molecular glue degraders. Authors: Yen-Der Li / Michelle W Ma / Muhammad Murtaza Hassan / Moritz Hunkeler / Mingxing Teng / Kedar Puvar / Ryan Lumpkin / Brittany Sandoval / Cyrus Y Jin / Scott B Ficarro / Michelle Y Wang / ...Authors: Yen-Der Li / Michelle W Ma / Muhammad Murtaza Hassan / Moritz Hunkeler / Mingxing Teng / Kedar Puvar / Ryan Lumpkin / Brittany Sandoval / Cyrus Y Jin / Scott B Ficarro / Michelle Y Wang / Shawn Xu / Brian J Groendyke / Logan H Sigua / Isidoro Tavares / Charles Zou / Jonathan M Tsai / Paul M C Park / Hojong Yoon / Felix C Majewski / Jarrod A Marto / Jun Qi / Radosław P Nowak / Katherine A Donovan / Mikołaj Słabicki / Nathanael S Gray / Eric S Fischer / Benjamin L Ebert /   Abstract: Small molecules that induce protein-protein interactions to exert proximity-driven pharmacology such as targeted protein degradation are a powerful class of therapeutics. Molecular glues are of ...Small molecules that induce protein-protein interactions to exert proximity-driven pharmacology such as targeted protein degradation are a powerful class of therapeutics. Molecular glues are of particular interest given their favorable size and chemical properties and represent the only clinically approved degrader drugs. The discovery and development of molecular glues for novel targets, however, remains challenging. Covalent strategies could in principle facilitate molecular glue discovery by stabilizing the neo-protein interfaces. Here, we present structural and mechanistic studies that define a -labeling covalent molecular glue mechanism, which we term "template-assisted covalent modification". We found that a novel series of BRD4 molecular glue degraders act by recruiting the CUL4 ligase to the second bromodomain of BRD4 (BRD4). BRD4, in complex with DCAF16, serves as a structural template to facilitate covalent modification of DCAF16, which stabilizes the BRD4-degrader-DCAF16 ternary complex formation and facilitates BRD4 degradation. A 2.2 Å cryo-electron microscopy structure of the ternary complex demonstrates that DCAF16 and BRD4 have pre-existing structural complementarity which optimally orients the reactive moiety of the degrader for DCAF16 covalent modification. Systematic mutagenesis of both DCAF16 and BRD4 revealed that the loop conformation around BRD4, rather than specific side chains, is critical for stable interaction with DCAF16 and BD2 selectivity. Together our work establishes "template-assisted covalent modification" as a mechanism for covalent molecular glues, which opens a new path to proximity driven pharmacology. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8g46.cif.gz 8g46.cif.gz | 232.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8g46.ent.gz pdb8g46.ent.gz | 179 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8g46.json.gz 8g46.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g4/8g46 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g4/8g46 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g4/8g46 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g4/8g46 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 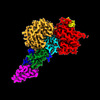 29714MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 4 molecules ABCE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 96425.586 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Fragment: UNP residues 1-395 + GNGNSG linker + UNP residues 706-1140 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDB1, XAP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDB1, XAP1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q16531 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q16531 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 24547.697 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DCAF16, C4orf30 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DCAF16, C4orf30 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NXF7 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NXF7 |
| #3: Protein |  BRD4 / Protein HUNK1 BRD4 / Protein HUNK1Mass: 14899.109 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BRD4, HUNK1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BRD4, HUNK1 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: O60885 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: O60885 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 12183.646 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDA1, C19orf58, PCIA1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDA1, C19orf58, PCIA1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BW61 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BW61 |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 112 molecules 




| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|---|
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-YK3 / |
| #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH /  Water Water |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ternary complex of cullin ring E3 ubiquitin ligase substrate receptor arm (DDB1deltaB-DDA1-DCAF16) in compound-induced complex with bromodomain 2 of BRD4 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.148 MDa / Experimental value: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain: Hi5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain: Hi5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: 50 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 200 mM NaCl, 2 mM TCEP, 0.011% LMNG | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.25 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: The ternary complex was incubated at RT for 30 min before polishing on through size exclusion chromatography. The purified DCAF16 complex was incubated with an extra 1.2x molar excess of ...Details: The ternary complex was incubated at RT for 30 min before polishing on through size exclusion chromatography. The purified DCAF16 complex was incubated with an extra 1.2x molar excess of purified BRD4BD2 for 30 minutes at 4 degree C before grid preparation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 20 mA / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R0./1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K / Details: detergent added directly before grid application |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.3 sec. / Electron dose: 50.27 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 17118 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: REFMAC / Version: 5.8.0352 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Details: in cryoSPARC / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 14452363 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1433050 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 3 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 74 / Protocol: OTHER / Details: refinement in both real and Fourier space | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 2.2→146.97 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.779 / SU B: 4.489 / SU ML: 0.105 / ESU R: 0.165 Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD WITH PHASES Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: PARAMETERS FOR MASK CACLULATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 73.259 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: 1 / Total: 8603 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj





