[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
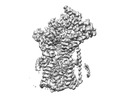
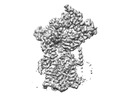
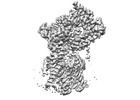
Yorodumi- PDB-8dnz: Cryo-EM structure of the human Sec61 complex inhibited by apratoxin F -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8dnz | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human Sec61 complex inhibited by apratoxin F | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN TRANSPORT/INHIBITOR /  translocon / translocon /  inhibitor / inhibitor /  protein translocation / protein translocation /  PROTEIN TRANSPORT / PROTEIN TRANSPORT-INHIBITOR complex PROTEIN TRANSPORT / PROTEIN TRANSPORT-INHIBITOR complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationendoplasmic reticulum Sec complex / endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment / pronephric nephron development / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / protein targeting to ER / protein insertion into ER membrane /  post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation ...endoplasmic reticulum Sec complex / endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment / pronephric nephron development / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / protein targeting to ER / protein insertion into ER membrane / post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation ...endoplasmic reticulum Sec complex / endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment / pronephric nephron development / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Ssh1 translocon complex / Sec61 translocon complex / protein targeting to ER / protein insertion into ER membrane /  post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation /  signal sequence binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / signal sequence binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane /  post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / endoplasmic reticulum organization / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol / post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / endoplasmic reticulum organization / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol /  epidermal growth factor binding / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein transmembrane transporter activity / : / epidermal growth factor binding / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein transmembrane transporter activity / : /  calcium channel activity / calcium channel activity /  ribosome binding / ER-Phagosome pathway / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / ribosome binding / ER-Phagosome pathway / endoplasmic reticulum membrane /  endoplasmic reticulum / endoplasmic reticulum /  RNA binding / RNA binding /  membrane / membrane /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Lyngbya bouillonii (bacteria) Lyngbya bouillonii (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.57 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.57 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Park, E. / Itskanov, S. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2023Title: A common mechanism of Sec61 translocon inhibition by small molecules. Authors: Samuel Itskanov / Laurie Wang / Tina Junne / Rumi Sherriff / Li Xiao / Nicolas Blanchard / Wei Q Shi / Craig Forsyth / Dominic Hoepfner / Martin Spiess / Eunyong Park /    Abstract: The Sec61 complex forms a protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane that is required for secretion of soluble proteins and production of many membrane proteins. Several natural ...The Sec61 complex forms a protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane that is required for secretion of soluble proteins and production of many membrane proteins. Several natural and synthetic small molecules specifically inhibit Sec61, generating cellular effects that are useful for therapeutic purposes, but their inhibitory mechanisms remain unclear. Here we present near-atomic-resolution structures of human Sec61 inhibited by a comprehensive panel of structurally distinct small molecules-cotransin, decatransin, apratoxin, ipomoeassin, mycolactone, cyclotriazadisulfonamide and eeyarestatin. All inhibitors bind to a common lipid-exposed pocket formed by the partially open lateral gate and plug domain of Sec61. Mutations conferring resistance to the inhibitors are clustered at this binding pocket. The structures indicate that Sec61 inhibitors stabilize the plug domain in a closed state, thereby preventing the protein-translocation pore from opening. Our study provides the atomic details of Sec61-inhibitor interactions and the structural framework for further pharmacological studies and drug design. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8dnz.cif.gz 8dnz.cif.gz | 116.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8dnz.ent.gz pdb8dnz.ent.gz | 84.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8dnz.json.gz 8dnz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dn/8dnz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dn/8dnz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dn/8dnz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dn/8dnz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27585MC 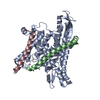 8dnvC  8dnwC  8dnxC  8dnyC  8do0C 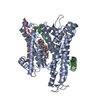 8do1C 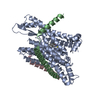 8do2C  8do3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Protein targeting Protein targetingMass: 7752.325 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SEC61G / Plasmid: pFastBac / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SEC61G / Plasmid: pFastBac / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P60059 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P60059 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  Protein targeting Protein targetingMass: 9987.456 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SEC61B / Plasmid: pFastBac / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SEC61B / Plasmid: pFastBac / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P60468 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P60468 |
| #3: Protein |  Protein targeting / Sec61 alpha-1 Protein targeting / Sec61 alpha-1Mass: 52202.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Mutation: V263L, D264E, K268R, A270T, R271K, Y272V, Y276I, N277G, T278I, L394F, E346D, Q348G, M401I, R402N, H404K, M409I, V410Y, H411R Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SEC61A1, SEC61A / Plasmid: pFastBac / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SEC61A1, SEC61A / Plasmid: pFastBac / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P61619 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P61619 |
| #4: Protein/peptide | Mass: 848.144 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Lyngbya bouillonii (bacteria) Lyngbya bouillonii (bacteria) |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: A human-yeast chimeric Sec complex treated with apratoxin F Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / Organelle Homo sapiens (human) / Organelle : endoplasmic reticulum : endoplasmic reticulum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / Strain: Sf9 / Plasmid Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / Strain: Sf9 / Plasmid : pFastBac : pFastBac | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: Reconsitituted into a peptidisc. Monodisperse peak from a Superose 6 column. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: blot for 4 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 910463 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.57 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 497555 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 63.51 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj





