+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7td6 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | aRML prion fibril | |||||||||
 Components Components | Major prion protein | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / infectious prion /  amyloid / parallel in-register amyloid / parallel in-register | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInsertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process /  lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity /  glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport ...Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process / glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport ...Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process /  lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity /  glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / cupric ion binding / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / response to copper ion / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / cuprous ion binding / activation of protein kinase activity / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / response to amyloid-beta / negative regulation of type II interferon production / : / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / response to cadmium ion / side of membrane / glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / cupric ion binding / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / response to copper ion / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / cuprous ion binding / activation of protein kinase activity / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / response to amyloid-beta / negative regulation of type II interferon production / : / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / response to cadmium ion / side of membrane /  inclusion body / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to copper ion / neuron projection maintenance / molecular condensate scaffold activity / inclusion body / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to copper ion / neuron projection maintenance / molecular condensate scaffold activity /  tubulin binding / protein sequestering activity / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / molecular function activator activity / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / protein destabilization / protein homooligomerization / negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity / tubulin binding / protein sequestering activity / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / molecular function activator activity / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / protein destabilization / protein homooligomerization / negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity /  terminal bouton / cellular response to amyloid-beta / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / terminal bouton / cellular response to amyloid-beta / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process /  regulation of protein localization / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / regulation of protein localization / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus /  signaling receptor activity / signaling receptor activity /  amyloid-beta binding / protein-folding chaperone binding / amyloid-beta binding / protein-folding chaperone binding /  microtubule binding / microtubule binding /  nuclear membrane / response to oxidative stress / nuclear membrane / response to oxidative stress /  protease binding / mitochondrial outer membrane / transmembrane transporter binding / protease binding / mitochondrial outer membrane / transmembrane transporter binding /  postsynaptic density / learning or memory / molecular adaptor activity / copper ion binding / postsynaptic density / learning or memory / molecular adaptor activity / copper ion binding /  membrane raft / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / membrane raft / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle /  dendrite / protein-containing complex binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / dendrite / protein-containing complex binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process /  Golgi apparatus / Golgi apparatus /  cell surface / cell surface /  endoplasmic reticulum / endoplasmic reticulum /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hoyt, F. / Standke, H.G. / Artikis, E. / Caughey, B. / Kraus, A. | |||||||||
| Funding support | 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM structure of anchorless RML prion reveals variations in shared motifs between distinct strains. Authors: Forrest Hoyt / Heidi G Standke / Efrosini Artikis / Cindi L Schwartz / Bryan Hansen / Kunpeng Li / Andrew G Hughson / Matteo Manca / Olivia R Thomas / Gregory J Raymond / Brent Race / Gerald ...Authors: Forrest Hoyt / Heidi G Standke / Efrosini Artikis / Cindi L Schwartz / Bryan Hansen / Kunpeng Li / Andrew G Hughson / Matteo Manca / Olivia R Thomas / Gregory J Raymond / Brent Race / Gerald S Baron / Byron Caughey / Allison Kraus /  Abstract: Little is known about the structural basis of prion strains. Here we provide a high (3.0 Å) resolution cryo-electron microscopy-based structure of infectious brain-derived fibrils of the mouse ...Little is known about the structural basis of prion strains. Here we provide a high (3.0 Å) resolution cryo-electron microscopy-based structure of infectious brain-derived fibrils of the mouse anchorless RML scrapie strain which, like the recently determined hamster 263K strain, has a parallel in-register β-sheet-based core. Several structural motifs are shared between these ex vivo prion strains, including an amino-proximal steric zipper and three β-arches. However, detailed comparisons reveal variations in these shared structural topologies and other features. Unlike 263K and wildtype RML prions, the anchorless RML prions lack glycophosphatidylinositol anchors and are severely deficient in N-linked glycans. Nonetheless, the similarity of our anchorless RML structure to one reported for wildtype RML prion fibrils in an accompanying paper indicates that these post-translational modifications do not substantially alter the amyloid core conformation. This work demonstrates both common and divergent structural features of prion strains at the near-atomic level. #1:  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: High-resolution structure and strain comparison of infectious mammalian prions. Authors: Allison Kraus / Forrest Hoyt / Cindi L Schwartz / Bryan Hansen / Efrosini Artikis / Andrew G Hughson / Gregory J Raymond / Brent Race / Gerald S Baron / Byron Caughey /  Abstract: Within the extensive range of self-propagating pathologic protein aggregates of mammals, prions are the most clearly infectious (e.g., ∼10 lethal doses per milligram). The structures of such lethal ...Within the extensive range of self-propagating pathologic protein aggregates of mammals, prions are the most clearly infectious (e.g., ∼10 lethal doses per milligram). The structures of such lethal assemblies of PrP molecules have been poorly understood. Here we report a near-atomic core structure of a brain-derived, fully infectious prion (263K strain). Cryo-electron microscopy showed amyloid fibrils assembled with parallel in-register intermolecular β sheets. Each monomer provides one rung of the ordered fibril core, with N-linked glycans and glycolipid anchors projecting outward. Thus, single monomers form the templating surface for incoming monomers at fibril ends, where prion growth occurs. Comparison to another prion strain (aRML) revealed major differences in fibril morphology but, like 263K, an asymmetric fibril cross-section without paired protofilaments. These findings provide structural insights into prion propagation, strains, species barriers, and membrane pathogenesis. This structure also helps frame considerations of factors influencing the relative transmissibility of other pathologic amyloids. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7td6.cif.gz 7td6.cif.gz | 135.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7td6.ent.gz pdb7td6.ent.gz | 104.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7td6.json.gz 7td6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/td/7td6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/td/7td6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/td/7td6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/td/7td6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25824MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 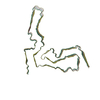
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments:
NCS oper:
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 28008.393 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: proteinase-K resistant aRML prion fibril ordered core encompasses residues 93-230 Source: (natural)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / References: UniProt: P04925 Mus musculus (house mouse) / References: UniProt: P04925 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: aRML prion / Type: COMPLEX / Details: anchorless RML prion fibril / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Tissue: brain-derived Mus musculus (house mouse) / Tissue: brain-derived |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES / Details: purified aRML prion fibrils : YES / Details: purified aRML prion fibrils |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 135939 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 15857 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 102.8 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints NCS |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj

