+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7t62 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GPC2 HEP CT3 complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  IMMUNE SYSTEM / IMMUNE SYSTEM /  Glypican-3 complex Glypican-3 complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of protein localization to membrane / Defective B3GALT6 causes EDSP2 and SEMDJL1 / Defective B4GALT7 causes EDS, progeroid type / Defective B3GAT3 causes JDSSDHD / Defective EXT2 causes exostoses 2 / Defective EXT1 causes exostoses 1, TRPS2 and CHDS / A tetrasaccharide linker sequence is required for GAG synthesis / HS-GAG biosynthesis / HS-GAG degradation / smoothened signaling pathway ...regulation of protein localization to membrane / Defective B3GALT6 causes EDSP2 and SEMDJL1 / Defective B4GALT7 causes EDS, progeroid type / Defective B3GAT3 causes JDSSDHD / Defective EXT2 causes exostoses 2 / Defective EXT1 causes exostoses 1, TRPS2 and CHDS / A tetrasaccharide linker sequence is required for GAG synthesis / HS-GAG biosynthesis / HS-GAG degradation / smoothened signaling pathway /  regulation of signal transduction / Retinoid metabolism and transport / lysosomal lumen / positive regulation of neuron projection development / neuron differentiation / Golgi lumen / regulation of signal transduction / Retinoid metabolism and transport / lysosomal lumen / positive regulation of neuron projection development / neuron differentiation / Golgi lumen /  cell migration / collagen-containing extracellular matrix / Attachment and Entry / cell migration / collagen-containing extracellular matrix / Attachment and Entry /  synapse / synapse /  cell surface / cell surface /  endoplasmic reticulum / endoplasmic reticulum /  extracellular space / extracellular space /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  negative staining / Resolution: 21 Å negative staining / Resolution: 21 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhu, J. / Cachau, R. / De Val Alda, N. / Li, N. / Ho, M. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep Med / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Rep Med / Year: 2021Title: CAR T cells targeting tumor-associated exons of glypican 2 regress neuroblastoma in mice. Authors: Nan Li / Madeline B Torres / Madeline R Spetz / Ruixue Wang / Luyi Peng / Meijie Tian / Christopher M Dower / Rosa Nguyen / Ming Sun / Chin-Hsien Tai / Natalia de Val / Raul Cachau / Xiaolin ...Authors: Nan Li / Madeline B Torres / Madeline R Spetz / Ruixue Wang / Luyi Peng / Meijie Tian / Christopher M Dower / Rosa Nguyen / Ming Sun / Chin-Hsien Tai / Natalia de Val / Raul Cachau / Xiaolin Wu / Stephen M Hewitt / Rosandra N Kaplan / Javed Khan / Brad St Croix / Carol J Thiele / Mitchell Ho /  Abstract: Targeting solid tumors must overcome several major obstacles, in particular, the identification of elusive tumor-specific antigens. Here, we devise a strategy to help identify tumor-specific epitopes. ...Targeting solid tumors must overcome several major obstacles, in particular, the identification of elusive tumor-specific antigens. Here, we devise a strategy to help identify tumor-specific epitopes. Glypican 2 (GPC2) is overexpressed in neuroblastoma. Using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis, we show that exon 3 and exons 7-10 of GPC2 are expressed in cancer but are minimally expressed in normal tissues. Accordingly, we discover a monoclonal antibody (CT3) that binds exons 3 and 10 and visualize the complex structure of CT3 and GPC2 by electron microscopy. The potential of this approach is exemplified by designing CT3-derived chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells that regress neuroblastoma in mice. Genomic sequencing of T cells recovered from mice reveals the CAR integration sites that may contribute to CAR T cell proliferation and persistence. These studies demonstrate how RNA-seq data can be exploited to help identify tumor-associated exons that can be targeted by CAR T cell therapies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7t62.cif.gz 7t62.cif.gz | 310.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7t62.ent.gz pdb7t62.ent.gz | 258.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7t62.json.gz 7t62.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/7t62 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/7t62 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/7t62 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t6/7t62 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 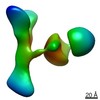 25708MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 61002.066 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GPC2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GPC2 / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8N158 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8N158 |
|---|---|
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 47359.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: GPC2 HET CT3 complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.01 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : YES / Vitrification applied : YES / Vitrification applied : NO : NO |
| EM staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: A 3 uL aliquot containing ~0.01 mg/mL of the samples was applied for 20 s onto a carbon-coated 200 Cu mesh grid (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Protochips, Inc.) that had been glow discharged ...Details: A 3 uL aliquot containing ~0.01 mg/mL of the samples was applied for 20 s onto a carbon-coated 200 Cu mesh grid (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Protochips, Inc.) that had been glow discharged at 30 mA for 30 s (Pelco easiGlow, Ted Pella, Inc.), then negatively stained with 0.7% (w/v) uranyl formate for 40 sec. Material: uranyl formate |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI 20 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source : LAB6 / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN : LAB6 / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 100000 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 100000 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI EAGLE (2k x 2k) / Num. of real images: 200 |
| Image scans | Width: 2048 / Height: 2048 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 21000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 21 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 21000 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj





