+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7sd0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
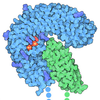
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the SHOC2:PP1C:MRAS complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN /  Phosphatase / Phosphatase /  leucine rich repeat / RAF / leucine rich repeat / RAF /  complex complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to growth hormone stimulus / protein phosphatase type 1 complex / negative regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / nerve growth factor signaling pathway /  protein phosphatase 1 binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / GTP-dependent protein binding / protein phosphatase 1 binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / GTP-dependent protein binding /  lamin binding ...cellular response to growth hormone stimulus / protein phosphatase type 1 complex / negative regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / nerve growth factor signaling pathway / lamin binding ...cellular response to growth hormone stimulus / protein phosphatase type 1 complex / negative regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / nerve growth factor signaling pathway /  protein phosphatase 1 binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / GTP-dependent protein binding / protein phosphatase 1 binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / GTP-dependent protein binding /  lamin binding / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / lamin binding / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction /  microtubule organizing center / myosin phosphatase activity / microtubule organizing center / myosin phosphatase activity /  protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity / glycogen metabolic process / protein-serine/threonine phosphatase / entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod / Triglyceride catabolism / protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity / glycogen metabolic process / protein-serine/threonine phosphatase / entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod / Triglyceride catabolism /  phosphatase activity / phosphatase activity /  phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / phosphoprotein phosphatase activity /  cleavage furrow / blastocyst development / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / positive regulation of neuron differentiation / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / protein dephosphorylation / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / cleavage furrow / blastocyst development / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / positive regulation of neuron differentiation / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / protein dephosphorylation / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling /  small monomeric GTPase / G protein activity / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / RAF activation / circadian regulation of gene expression / small monomeric GTPase / G protein activity / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / RAF activation / circadian regulation of gene expression /  regulation of circadian rhythm / neuron differentiation / regulation of circadian rhythm / neuron differentiation /  kinetochore / positive regulation of neuron projection development / Separation of Sister Chromatids / GDP binding / kinetochore / positive regulation of neuron projection development / Separation of Sister Chromatids / GDP binding /  MAPK cascade / MAPK cascade /  Circadian Clock / presynapse / midbody / actin cytoskeleton organization / Circadian Clock / presynapse / midbody / actin cytoskeleton organization /  spermatogenesis / spermatogenesis /  protein phosphatase binding / Ras protein signal transduction / mitochondrial outer membrane / protein phosphatase binding / Ras protein signal transduction / mitochondrial outer membrane /  dendritic spine / nuclear speck / dendritic spine / nuclear speck /  cell cycle / cell cycle /  cell division / protein domain specific binding / cell division / protein domain specific binding /  focal adhesion / focal adhesion /  GTPase activity / glutamatergic synapse / protein-containing complex binding / GTP binding / GTPase activity / glutamatergic synapse / protein-containing complex binding / GTP binding /  nucleolus / nucleolus /  protein kinase binding / protein kinase binding /  signal transduction / protein-containing complex / signal transduction / protein-containing complex /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  RNA binding / RNA binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.95 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.95 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Liau, N.P.D. / Johnson, M.C. / Hymowitz, S.G. / Sudhamsu, J. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Authors: Nicholas P D Liau / Matthew C Johnson / Saeed Izadi / Luca Gerosa / Michal Hammel / John M Bruning / Timothy J Wendorff / Wilson Phung / Sarah G Hymowitz / Jawahar Sudhamsu /  Abstract: The RAS-RAF pathway is one of the most commonly dysregulated in human cancers. Despite decades of study, understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying dimerization and activation of the kinase ...The RAS-RAF pathway is one of the most commonly dysregulated in human cancers. Despite decades of study, understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying dimerization and activation of the kinase RAF remains limited. Recent structures of inactive RAF monomer and active RAF dimer bound to 14-3-3 have revealed the mechanisms by which 14-3-3 stabilizes both RAF conformations via specific phosphoserine residues. Prior to RAF dimerization, the protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit (PP1C) must dephosphorylate the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) of RAF to relieve inhibition by 14-3-3, although PP1C in isolation lacks intrinsic substrate selectivity. SHOC2 is as an essential scaffolding protein that engages both PP1C and RAS to dephosphorylate RAF NTpS, but the structure of SHOC2 and the architecture of the presumptive SHOC2-PP1C-RAS complex remain unknown. Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of the SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS complex to an overall resolution of 3 Å, revealing a tripartite molecular architecture in which a crescent-shaped SHOC2 acts as a cradle and brings together PP1C and MRAS. Our work demonstrates the GTP dependence of multiple RAS isoforms for complex formation, delineates the RAS-isoform preference for complex assembly, and uncovers how the SHOC2 scaffold and RAS collectively drive specificity of PP1C for RAF NTpS. Our data indicate that disease-relevant mutations affect complex assembly, reveal the simultaneous requirement of two RAS molecules for RAF activation, and establish rational avenues for discovery of new classes of inhibitors to target this pathway. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7sd0.cif.gz 7sd0.cif.gz | 237.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7sd0.ent.gz pdb7sd0.ent.gz | 176 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7sd0.json.gz 7sd0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sd/7sd0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sd/7sd0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sd/7sd0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sd/7sd0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25044MC  7sd1C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
| Other databases |
|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein |  / Protein soc-2 homolog / Protein sur-8 homolog / Protein soc-2 homolog / Protein sur-8 homologMass: 65156.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SHOC2, KIAA0862 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SHOC2, KIAA0862 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q9UQ13 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q9UQ13 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 24028.621 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MRAS, RRAS3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MRAS, RRAS3 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: O14807, Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: O14807,  small monomeric GTPase small monomeric GTPase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 37174.906 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1CC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1CC / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)References: UniProt: P36873, protein-serine/threonine phosphatase |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 4 molecules 



| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-GCP / |
|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #6: Chemical |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.19 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K Details: Used the "perpetually hydrated" method of applying graphene oxide. (Cheung et al., 2018) |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 64 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.1-4122_final: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3996056 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.95 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 323910 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj