+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7qvc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | TMEM106B filaments with Fold I from Alzheimer's disease (case 1) | ||||||
 Components Components | Transmembrane protein 106B Transmembrane protein Transmembrane protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL /  Amyloid / Amyloid /  neurodegeneration / neurodegeneration /  filament / filament /  TMEM106B TMEM106B | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information lysosomal protein catabolic process / regulation of lysosome organization / lysosomal lumen acidification / lysosome localization / positive regulation of dendrite development / dendrite morphogenesis / lysosomal transport / lysosome organization / neuron cellular homeostasis / late endosome membrane ... lysosomal protein catabolic process / regulation of lysosome organization / lysosomal lumen acidification / lysosome localization / positive regulation of dendrite development / dendrite morphogenesis / lysosomal transport / lysosome organization / neuron cellular homeostasis / late endosome membrane ... lysosomal protein catabolic process / regulation of lysosome organization / lysosomal lumen acidification / lysosome localization / positive regulation of dendrite development / dendrite morphogenesis / lysosomal transport / lysosome organization / neuron cellular homeostasis / late endosome membrane / lysosomal protein catabolic process / regulation of lysosome organization / lysosomal lumen acidification / lysosome localization / positive regulation of dendrite development / dendrite morphogenesis / lysosomal transport / lysosome organization / neuron cellular homeostasis / late endosome membrane /  ATPase binding / ATPase binding /  lysosome / lysosome /  endosome / lysosomal membrane / endosome / lysosomal membrane /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.64 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.64 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lovestam, S. / Schweighauser, M. / Scheres, S.H.W. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Age-dependent formation of TMEM106B amyloid filaments in human brains. Authors: Manuel Schweighauser / Diana Arseni / Mehtap Bacioglu / Melissa Huang / Sofia Lövestam / Yang Shi / Yang Yang / Wenjuan Zhang / Abhay Kotecha / Holly J Garringer / Ruben Vidal / Grace I ...Authors: Manuel Schweighauser / Diana Arseni / Mehtap Bacioglu / Melissa Huang / Sofia Lövestam / Yang Shi / Yang Yang / Wenjuan Zhang / Abhay Kotecha / Holly J Garringer / Ruben Vidal / Grace I Hallinan / Kathy L Newell / Airi Tarutani / Shigeo Murayama / Masayuki Miyazaki / Yuko Saito / Mari Yoshida / Kazuko Hasegawa / Tammaryn Lashley / Tamas Revesz / Gabor G Kovacs / John van Swieten / Masaki Takao / Masato Hasegawa / Bernardino Ghetti / Maria Grazia Spillantini / Benjamin Ryskeldi-Falcon / Alexey G Murzin / Michel Goedert / Sjors H W Scheres /       Abstract: Many age-dependent neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, are characterized by abundant inclusions of amyloid filaments. Filamentous inclusions of the proteins tau, amyloid- ...Many age-dependent neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, are characterized by abundant inclusions of amyloid filaments. Filamentous inclusions of the proteins tau, amyloid-β, α-synuclein and transactive response DNA-binding protein (TARDBP; also known as TDP-43) are the most common. Here we used structure determination by cryogenic electron microscopy to show that residues 120-254 of the lysosomal type II transmembrane protein 106B (TMEM106B) also form amyloid filaments in human brains. We determined the structures of TMEM106B filaments from a number of brain regions of 22 individuals with abundant amyloid deposits, including those resulting from sporadic and inherited tauopathies, amyloid-β amyloidoses, synucleinopathies and TDP-43 proteinopathies, as well as from the frontal cortex of 3 individuals with normal neurology and no or only a few amyloid deposits. We observed three TMEM106B folds, with no clear relationships between folds and diseases. TMEM106B filaments correlated with the presence of a 29-kDa sarkosyl-insoluble fragment and globular cytoplasmic inclusions, as detected by an antibody specific to the carboxy-terminal region of TMEM106B. The identification of TMEM106B filaments in the brains of older, but not younger, individuals with normal neurology indicates that they form in an age-dependent manner. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7qvc.cif.gz 7qvc.cif.gz | 83.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7qvc.ent.gz pdb7qvc.ent.gz | 65.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7qvc.json.gz 7qvc.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qvc https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qvc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qvc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qvc | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 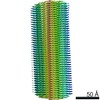 14174MC  7qvfC  7qwgC  7qwlC  7qwmC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Transmembrane protein Transmembrane proteinMass: 31142.295 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NUM4 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NUM4Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: TMEM106B / Type: TISSUE / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL / Type: TISSUE / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -0.42 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 4.81 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | |||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.64 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 47414 / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj
