[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7p6s: Crystal structure of the FimH-binding decoy module of human glyco... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7p6s | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
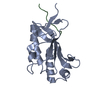
| Title | Crystal structure of the FimH-binding decoy module of human glycoprotein 2 (GP2) (crystal form II) | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Isoform Alpha of Pancreatic secretory granule membrane major glycoprotein GP2 | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  ANTIMICROBIAL PROTEIN / ANTIMICROBIAL PROTEIN /  Extracellular matrix / Extracellular matrix /  glycoprotein / glycoprotein /  N-glycan / N-glycan /  structural protein / decoy module / D10C domain / D8C sequence / structural protein / decoy module / D10C domain / D8C sequence /  pancreas / intestine / pancreas / intestine /  mucosal immunity / FimH / mucosal immunity / FimH /  AlphaFold AlphaFold | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationantigen transcytosis by M cells in mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue / zymogen granule membrane / Post-translational modification: synthesis of GPI-anchored proteins / neutrophil migration /  antigen binding / antigen binding /  endosome / endosome /  membrane raft / apical plasma membrane / external side of plasma membrane / membrane raft / apical plasma membrane / external side of plasma membrane /  innate immune response ...antigen transcytosis by M cells in mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue / zymogen granule membrane / Post-translational modification: synthesis of GPI-anchored proteins / neutrophil migration / innate immune response ...antigen transcytosis by M cells in mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue / zymogen granule membrane / Post-translational modification: synthesis of GPI-anchored proteins / neutrophil migration /  antigen binding / antigen binding /  endosome / endosome /  membrane raft / apical plasma membrane / external side of plasma membrane / membrane raft / apical plasma membrane / external side of plasma membrane /  innate immune response / innate immune response /  cell surface / cell surface /  extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.35 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.35 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Stsiapanava, A. / Tunyasuvunakool, K. / Jumper, J. / de Sanctis, D. / Jovine, L. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 3items Sweden, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the decoy module of human glycoprotein 2 and uromodulin and its interaction with bacterial adhesin FimH. Authors: Alena Stsiapanava / Chenrui Xu / Shunsuke Nishio / Ling Han / Nao Yamakawa / Marta Carroni / Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool / John Jumper / Daniele de Sanctis / Bin Wu / Luca Jovine /     Abstract: Glycoprotein 2 (GP2) and uromodulin (UMOD) filaments protect against gastrointestinal and urinary tract infections by acting as decoys for bacterial fimbrial lectin FimH. By combining AlphaFold2 ...Glycoprotein 2 (GP2) and uromodulin (UMOD) filaments protect against gastrointestinal and urinary tract infections by acting as decoys for bacterial fimbrial lectin FimH. By combining AlphaFold2 predictions with X-ray crystallography and cryo-EM, we show that these proteins contain a bipartite decoy module whose new fold presents the high-mannose glycan recognized by FimH. The structure rationalizes UMOD mutations associated with kidney diseases and visualizes a key epitope implicated in cast nephropathy. #1: Journal: Biochim.Biophys.Acta / Year: 1978 Title: Glycoprotein synthesis in the adult rat pancreas. IV. Subcellular distribution of membrane glycoproteins. Authors: Ronzio, R.A. / Kronquist, K.E. / Lewis, D.S. / MacDonald, R.J. / Mohrlok, S.H. / O'Donnell Jr., J.J. #2: Journal: Biochim.Biophys.Acta / Year: 2000 Title: Molecular cloning and sequences of cDNAs encoding alpha (large) and beta (small) isoforms of human pancreatic zymogen granule membrane-associated protein GP2. Authors: Fukuoka, S. #3: Journal: Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun. / Year: 2004 Title: GP2/THP gene family of self-binding, GPI-anchored proteins forms a cluster at chromosome 7F1 region in mouse genome. Authors: Kobayashi, K. / Yanagihara, K. / Ishiguro, K. / Fukuoka, S. #4: Journal: FEBS Lett / Year: 2004 Title: Identification and characterization of D8C, a novel domain present in liver-specific LZP, uromodulin and glycoprotein 2, mutated in familial juvenile hyperuricaemic nephropathy. Authors: Huirong Yang / Chaoqun Wu / Shouyuan Zhao / Jinhu Guo /  Abstract: Present work reported a novel domain--D8C (domain with conserved eight cysteines in liver-specific ZP domain-containing protein, glycoprotein 2 (GP-2) and uromodulin (UMOD)), present in liver- ...Present work reported a novel domain--D8C (domain with conserved eight cysteines in liver-specific ZP domain-containing protein, glycoprotein 2 (GP-2) and uromodulin (UMOD)), present in liver-specific LZP, UMOD, GP-2 and some uncharacterized proteins, most of which are membrane proteins, extracellular proteins or nuclear membrane proteins. D8C contains eight well-conserved cysteine residues, which were predicted to form four pairs of disulfide bridges. D8C is composed mainly of beta-strands. Mutation in the D8C at Cys217 in human UMOD is associated with familial juvenile hyperuricaemic nephropathy, which might be due to the disruption of the disulfide bridge. Identification of D8C would further the understandings of related proteins. #5: Journal: BMC Gastroenterol / Year: 2009 Title: The pancreatic zymogen granule membrane protein, GP2, binds Escherichia coli Type 1 fimbriae. Authors: Yu, S. / Lowe, A.W. #6: Journal: Nature / Year: 2009 Title: Uptake through glycoprotein 2 of FimH(+) bacteria by M cells initiates mucosal immune response. Authors: Hase, K. / Kawano, K. / Nochi, T. / Pontes, G.S. / Fukuda, S. / Ebisawa, M. / Kadokura, K. / Tobe, T. / Fujimura, Y. / Kawano, S. / Yabashi, A. / Waguri, S. / Nakato, G. / Kimura, S. / ...Authors: Hase, K. / Kawano, K. / Nochi, T. / Pontes, G.S. / Fukuda, S. / Ebisawa, M. / Kadokura, K. / Tobe, T. / Fujimura, Y. / Kawano, S. / Yabashi, A. / Waguri, S. / Nakato, G. / Kimura, S. / Murakami, T. / Iimura, M. / Hamura, K. / Fukuoka, S. / Lowe, A.W. / Itoh, K. / Kiyono, H. / Ohno, H. #7: Journal: Gut / Year: 2009 Title: Identification of GP2, the major zymogen granule membrane glycoprotein, as the autoantigen of pancreatic antibodies in Crohn's disease. Authors: Roggenbuck, D. / Hausdorf, G. / Martinez-Gamboa, L. / Reinhold, D. / Buttner, T. / Jungblut, P.R. / Porstmann, T. / Laass, M.W. / Henker, J. / Buning, C. / Feist, E. / Conrad, K. #8: Journal: Clin.Chim.Acta / Year: 2012 Title: Autoantibodies to GP2, the major zymogen granule membrane glycoprotein, in patients with gluten-sensitive enteropathy: a possible serological trap. Authors: Bonaci-Nikolic, B. / Spuran, M. / Andrejevic, S. / Nikolic, M. #9: Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Title: Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Authors: John Jumper / Richard Evans / Alexander Pritzel / Tim Green / Michael Figurnov / Olaf Ronneberger / Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool / Russ Bates / Augustin Žídek / Anna Potapenko / Alex Bridgland ...Authors: John Jumper / Richard Evans / Alexander Pritzel / Tim Green / Michael Figurnov / Olaf Ronneberger / Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool / Russ Bates / Augustin Žídek / Anna Potapenko / Alex Bridgland / Clemens Meyer / Simon A A Kohl / Andrew J Ballard / Andrew Cowie / Bernardino Romera-Paredes / Stanislav Nikolov / Rishub Jain / Jonas Adler / Trevor Back / Stig Petersen / David Reiman / Ellen Clancy / Michal Zielinski / Martin Steinegger / Michalina Pacholska / Tamas Berghammer / Sebastian Bodenstein / David Silver / Oriol Vinyals / Andrew W Senior / Koray Kavukcuoglu / Pushmeet Kohli / Demis Hassabis /   Abstract: Proteins are essential to life, and understanding their structure can facilitate a mechanistic understanding of their function. Through an enormous experimental effort, the structures of around ...Proteins are essential to life, and understanding their structure can facilitate a mechanistic understanding of their function. Through an enormous experimental effort, the structures of around 100,000 unique proteins have been determined, but this represents a small fraction of the billions of known protein sequences. Structural coverage is bottlenecked by the months to years of painstaking effort required to determine a single protein structure. Accurate computational approaches are needed to address this gap and to enable large-scale structural bioinformatics. Predicting the three-dimensional structure that a protein will adopt based solely on its amino acid sequence-the structure prediction component of the 'protein folding problem'-has been an important open research problem for more than 50 years. Despite recent progress, existing methods fall far short of atomic accuracy, especially when no homologous structure is available. Here we provide the first computational method that can regularly predict protein structures with atomic accuracy even in cases in which no similar structure is known. We validated an entirely redesigned version of our neural network-based model, AlphaFold, in the challenging 14th Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP14), demonstrating accuracy competitive with experimental structures in a majority of cases and greatly outperforming other methods. Underpinning the latest version of AlphaFold is a novel machine learning approach that incorporates physical and biological knowledge about protein structure, leveraging multi-sequence alignments, into the design of the deep learning algorithm. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7p6s.cif.gz 7p6s.cif.gz | 80.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7p6s.ent.gz pdb7p6s.ent.gz | 54.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7p6s.json.gz 7p6s.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p6/7p6s https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p6/7p6s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p6/7p6s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p6/7p6s | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 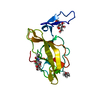
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 17910.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GP2 / Plasmid: pLJ6 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F GnTI- / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GP2 / Plasmid: pLJ6 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F GnTI- / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P55259 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P55259 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Sugar |  N-Acetylglucosamine N-Acetylglucosamine#3: Chemical | ChemComp-9JE / |  Pentane-1,5-diol Pentane-1,5-diol#4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |  Water WaterHas ligand of interest | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.42 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 49.27 % / Description: Plate |
|---|---|
Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 8.5 Details: 20% (v/v) 1,5-pentanediol, 10% (w/v) PEG 8K, 0.1 M GlyGly/AMPD pH 8.5, 0.5 mM YCl3, 0.5 mM ErCl3, 0.5 mM TbCl3, 0.5 mM YbCl3, 20 mM Na-HEPES pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: ID30B / Wavelength: 0.976254 Å / Beamline: ID30B / Wavelength: 0.976254 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Apr 18, 2021 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 0.976254 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 0.976254 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.35→49.12 Å / Num. obs: 38991 / % possible obs: 99.7 % / Redundancy: 6 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 13.25 Å2 / CC1/2: 1 / CC star: 1 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.153 / Rpim(I) all: 0.067 / Rrim(I) all: 0.167 / Net I/σ(I): 7 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.35→1.39 Å / Redundancy: 4.7 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 2.318 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 0.7 / Num. unique obs: 2960 / CC1/2: 0.4 / CC star: 0.75 / Rpim(I) all: 1.18 / Rrim(I) all: 2.612 / % possible all: 98.2 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: Partially refined model of crystal form I of the same protein (PDB D_1292117104) Resolution: 1.35→49.12 Å / SU ML: 0.1991 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 27.0674 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 18.48 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.35→49.12 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj