[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7p5z: Structure of a DNA-loaded MCM double hexamer engaged with the Dbf... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7p5z | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
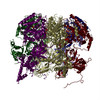
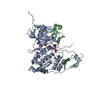
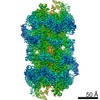
| Title | Structure of a DNA-loaded MCM double hexamer engaged with the Dbf4-dependent kinase | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  REPLICATION / REPLICATION /  Kinase / Mcm2-7 helicase / Kinase / Mcm2-7 helicase /  nucleoprotein complex / nucleoprotein complex /  DNA replication DNA replication | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation involved in reciprocal meiotic recombination / positive regulation of DNA replication initiation / positive regulation of kinetochore assembly / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation / negative regulation of exit from mitosis / Dbf4-dependent protein kinase complex / positive regulation of meiosis I / regulation of cell cycle phase transition / positive regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication ...positive regulation of spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation involved in reciprocal meiotic recombination / positive regulation of DNA replication initiation / positive regulation of kinetochore assembly / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation / negative regulation of exit from mitosis / Dbf4-dependent protein kinase complex / positive regulation of meiosis I / regulation of cell cycle phase transition / positive regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / MCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / nuclear DNA replication / MCM complex binding / mitotic DNA replication preinitiation complex assembly / premeiotic DNA replication / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / mitotic DNA replication / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / CMG complex / nuclear pre-replicative complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / MCM complex / DNA replication preinitiation complex / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / protein-containing complex localization / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / replication fork protection complex / mitotic DNA replication initiation / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / DNA unwinding involved in DNA replication / nuclear replication fork /  DNA replication origin binding / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / DNA replication origin binding / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation /  chromosome, centromeric region / DNA replication initiation / heterochromatin formation / chromosome, centromeric region / DNA replication initiation / heterochromatin formation /  DNA helicase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / DNA helicase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity /  helicase activity / helicase activity /  chromosome segregation / chromosome segregation /  single-stranded DNA binding / single-stranded DNA binding /  DNA helicase / DNA helicase /  chromosome, telomeric region / chromosome, telomeric region /  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation /  cell division / cell division /  phosphorylation / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / phosphorylation / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity /  centrosome / DNA damage response / centrosome / DNA damage response /  chromatin binding / chromatin binding /  chromatin / chromatin /  signal transduction / signal transduction /  ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast)  Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Greiwe, J.F. / Miller, T.C.R. / Martino, F. / Costa, A. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022Title: Structural mechanism for the selective phosphorylation of DNA-loaded MCM double hexamers by the Dbf4-dependent kinase. Authors: Julia F Greiwe / Thomas C R Miller / Julia Locke / Fabrizio Martino / Steven Howell / Anne Schreiber / Andrea Nans / John F X Diffley / Alessandro Costa /    Abstract: Loading of the eukaryotic replicative helicase onto replication origins involves two MCM hexamers forming a double hexamer (DH) around duplex DNA. During S phase, helicase activation requires MCM ...Loading of the eukaryotic replicative helicase onto replication origins involves two MCM hexamers forming a double hexamer (DH) around duplex DNA. During S phase, helicase activation requires MCM phosphorylation by Dbf4-dependent kinase (DDK), comprising Cdc7 and Dbf4. DDK selectively phosphorylates loaded DHs, but how such fidelity is achieved is unknown. Here, we determine the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DDK in the act of phosphorylating a DH. DDK docks onto one MCM ring and phosphorylates the opposed ring. Truncation of the Dbf4 docking domain abrogates DH phosphorylation, yet Cdc7 kinase activity is unaffected. Late origin firing is blocked in response to DNA damage via Dbf4 phosphorylation by the Rad53 checkpoint kinase. DDK phosphorylation by Rad53 impairs DH phosphorylation by blockage of DDK binding to DHs, and also interferes with the Cdc7 active site. Our results explain the structural basis and regulation of the selective phosphorylation of DNA-loaded MCM DHs, which supports bidirectional replication. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7p5z.cif.gz 7p5z.cif.gz | 2.8 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7p5z.ent.gz pdb7p5z.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7p5z.json.gz 7p5z.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/7p5z https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/7p5z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/7p5z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p5/7p5z | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 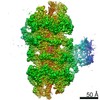 13211MC 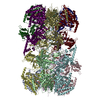 7p30C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA replication licensing factor ... , 5 types, 10 molecules 2A3B4C6E7F
| #1: Protein | Mass: 98911.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM2, YBL023C, YBL0438 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P29469, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P29469,  DNA helicase DNA helicase#2: Protein | Mass: 111720.242 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM3, YEL032W, SYGP-ORF23 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P24279, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P24279,  DNA helicase DNA helicase#3: Protein | Mass: 105138.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM4, CDC54, HCD21, YPR019W, YP9531.13 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P30665, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P30665,  DNA helicase DNA helicase#5: Protein | Mass: 113110.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM6, YGL201C / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P53091, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P53091,  DNA helicase DNA helicase#6: Protein | Mass: 95049.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM7, CDC47, YBR202W, YBR1441 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P38132, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P38132,  DNA helicase DNA helicase |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 4 molecules 5D1G
| #4: Protein |  / Cell division control protein 46 / Cell division control protein 46Mass: 86505.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM5, CDC46, YLR274W, L9328.1 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P29496, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P29496,  DNA helicase DNA helicase#7: Protein | | Mass: 58391.129 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: CDC7, OAF2, YDL017W, D2855 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast)References: UniProt: P06243,  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase#8: Protein | | Mass: 84503.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: DBF4, DNA52, YDR052C, D4205, YD9609.07C / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P32325 Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / References: UniProt: P32325 |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules XY
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 16326.441 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) |
|---|---|
| #10: DNA chain | Mass: 16335.457 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 31 molecules 






| #11: Chemical |  Adenosine triphosphate Adenosine triphosphate#12: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #13: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #14: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP /  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphate |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: DNA-loaded MCM double hexamer engaged with the dimeric Dbf4-dependent kinase Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#10 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: The entire MCM loading and phosphorylation reaction was applied to the EM grid. |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Details: blotted for 3 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4100 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4100 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 9 sec. / Electron dose: 51.3 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 18135 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 30 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 149876 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 134.24 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj