+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
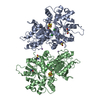
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7exb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | DfgA-DfgB complex apo 2.4 angstrom | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  LYASE / C-deglycosylation / sugar phosphate isomerase/epimerase LYASE / C-deglycosylation / sugar phosphate isomerase/epimerase | ||||||
| Function / homology | Domain of unknown function DUF6379 / Domain of unknown function (DUF6379) / Xylose isomerase-like, TIM barrel domain / Xylose isomerase-like TIM barrel / Xylose isomerase-like superfamily /  isomerase activity / isomerase activity /  : / DUF6379 domain-containing protein / Sugar phosphate isomerase/epimerase : / DUF6379 domain-containing protein / Sugar phosphate isomerase/epimerase Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  [Eubacterium] cellulosolvens 6 (bacteria) [Eubacterium] cellulosolvens 6 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.4 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Mori, T. / Senda, M. / Senda, T. / Abe, I. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: C-Glycoside metabolism in the gut and in nature: Identification, characterization, structural analyses and distribution of C-C bond-cleaving enzymes. Authors: Takahiro Mori / Takuto Kumano / Haibing He / Satomi Watanabe / Miki Senda / Toshio Moriya / Naruhiko Adachi / Sanae Hori / Yuzu Terashita / Masato Kawasaki / Yoshiteru Hashimoto / Takayoshi ...Authors: Takahiro Mori / Takuto Kumano / Haibing He / Satomi Watanabe / Miki Senda / Toshio Moriya / Naruhiko Adachi / Sanae Hori / Yuzu Terashita / Masato Kawasaki / Yoshiteru Hashimoto / Takayoshi Awakawa / Toshiya Senda / Ikuro Abe / Michihiko Kobayashi /  Abstract: C-Glycosides, in which a sugar moiety is linked via a carbon-carbon (C-C) bond to a non-sugar moiety (aglycone), are found in our food and medicine. The C-C bond is cleaved by intestinal microbes and ...C-Glycosides, in which a sugar moiety is linked via a carbon-carbon (C-C) bond to a non-sugar moiety (aglycone), are found in our food and medicine. The C-C bond is cleaved by intestinal microbes and the resulting aglycones exert various bioactivities. Although the enzymes responsible for the reactions have been identified, their catalytic mechanisms and the generality of the reactions in nature remain to be explored. Here, we present the identification and structural basis for the activation of xenobiotic C-glycosides by heterocomplex C-deglycosylation enzymes from intestinal and soil bacteria. They are found to be metal-dependent enzymes exhibiting broad substrate specificity toward C-glycosides. X-ray crystallographic and cryo-electron microscopic analyses, as well as structure-based mutagenesis, reveal the structural details of these enzymes and the detailed catalytic mechanisms of their remarkable C-C bond cleavage reactions. Furthermore, bioinformatic and biochemical analyses suggest that the C-deglycosylation enzymes are widely distributed in the gut, soil, and marine bacteria. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7exb.cif.gz 7exb.cif.gz | 136.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7exb.ent.gz pdb7exb.ent.gz | 84 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7exb.json.gz 7exb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/7exb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/7exb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/7exb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/7exb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7bvrC  7bvsSC  7drdC  7dreC  7exzC S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 33764.246 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  [Eubacterium] cellulosolvens 6 (bacteria) [Eubacterium] cellulosolvens 6 (bacteria)Gene: EubceDRAFT1_2664 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: I5AX50 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: I5AX50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 18458.150 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  [Eubacterium] cellulosolvens 6 (bacteria) [Eubacterium] cellulosolvens 6 (bacteria)Gene: EubceDRAFT1_2663 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: I5AX49 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: I5AX49 | ||||
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MN / | ||||
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 /  Sulfate Sulfate#5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |  Water WaterHas ligand of interest | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 6.06 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 79.7 % |
|---|---|
Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / Details: 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH8.5), 1190 mM (NH4)2SO4 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Photon Factory Photon Factory  / Beamline: BL-17A / Wavelength: 1.88 Å / Beamline: BL-17A / Wavelength: 1.88 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: May 19, 2021 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 1.88 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 1.88 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.4→47.1 Å / Num. obs: 51290 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 36.9 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 43.75 Å2 / CC1/2: 1 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.14 / Net I/σ(I): 27.4 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.4→2.47 Å / Redundancy: 22.8 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.417 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.8 / Num. unique obs: 4359 / CC1/2: 0.83 / % possible all: 99.9 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 7BVS Resolution: 2.4→47.1 Å / SU ML: 0.2941 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 20.4611 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 42.02 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.4→47.1 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



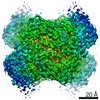
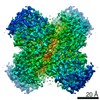









 PDBj
PDBj