+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7bw6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
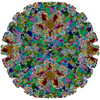
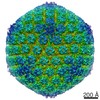
| Title | Varicella-zoster virus capsid | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS / A-capsid VIRUS / A-capsid | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationT=16 icosahedral viral capsid /  viral capsid assembly / viral process / viral capsid assembly / viral process /  viral capsid / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / viral capsid / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity /  DNA binding DNA bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, P.Y. / Qi, J.X. / Liu, C.C. / Sun, J.Q. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM structure of the varicella-zoster virus A-capsid. Authors: Junqing Sun / Congcong Liu / Ruchao Peng / Fu-Kun Zhang / Zhou Tong / Sheng Liu / Yi Shi / Zhennan Zhao / Wen-Bo Zeng / George Fu Gao / Hong-Jie Shen / Xiaoming Yang / Minhua Luo / Jianxun Qi / Peiyi Wang /  Abstract: Varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the Alphaherpesvirinae subfamily, causes severe diseases in humans of all ages. The viral capsids play critical roles in herpesvirus infection, making them ...Varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the Alphaherpesvirinae subfamily, causes severe diseases in humans of all ages. The viral capsids play critical roles in herpesvirus infection, making them potential antiviral targets. Here, we present the 3.7-Å-resolution structure of the VZV A-capsid and define the molecular determinants underpinning the assembly of this complicated viral machinery. Overall, the VZV capsid has a similar architecture to that of other known herpesviruses. The major capsid protein (MCP) assembles into pentons and hexons, forming extensive intra- and inter-capsomer interaction networks that are further secured by the small capsid protein (SCP) and the heterotriplex. The structure reveals a pocket beneath the floor of MCP that could potentially be targeted by antiviral inhibitors. In addition, we identified two alphaherpesvirus-specific structural features in SCP and Tri1 proteins. These observations highlight the divergence of different herpesviruses and provide an important basis for developing antiviral drugs. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7bw6.cif.gz 7bw6.cif.gz | 4.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7bw6.ent.gz pdb7bw6.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7bw6.json.gz 7bw6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bw6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bw6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bw6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bw/7bw6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  30228MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5
|
| 4 | x 6
|
| 5 | 
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral )) )) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 155145.359 Da / Num. of mol.: 16 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus)References: UniProt: Q6QCL5 #2: Protein | Mass: 24440.119 Da / Num. of mol.: 15 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus)References: UniProt: Q6QCN2 #3: Protein | Mass: 34421.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus)References: UniProt: Q6QCL4 #4: Protein | Mass: 54028.180 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) Human herpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus)References: UniProt: Q6QCN5 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human alphaherpesvirus 3 Varicella zoster virus / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL Varicella zoster virus / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (Varicella-zoster virus) |
| Details of virus | Empty: YES / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: OTHER / Type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Homemade |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: blot for 2 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated magnification: 59000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 386.3 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 5116 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated magnification: 59000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 386.3 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 5116 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 93 K / Temperature (min): 81 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 26979 |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 94640 Details: Images were low-pass to 15 angstrom to facilitated particle picking. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 311236 / Num. of class averages: 5 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 101.55 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj

