+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7asd | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
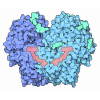
| Title | Structure of native royal jelly filaments | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL /  protein filament / protein filament /  lipoprotein / lipoprotein /  glycosylation / royal jelly / major royal jelly protein / honeybee glycosylation / royal jelly / major royal jelly protein / honeybee | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcaste determination, influence by environmental factors / defense response to fungus / killing of cells of another organism / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / extracellular region Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Apis mellifera (honey bee) Apis mellifera (honey bee) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mattei, S. / Ban, A. / Picenoni, A. / Leibundgut, M. / Glockshuber, R. / Boehringer, D. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Structure of native glycolipoprotein filaments in honeybee royal jelly. Authors: Simone Mattei / Arvid Ban / Armin Picenoni / Marc Leibundgut / Rudi Glockshuber / Daniel Boehringer /   Abstract: Royal jelly (RJ) is produced by honeybees (Apis mellifera) as nutrition during larval development. The high viscosity of RJ originates from high concentrations of long lipoprotein filaments that ...Royal jelly (RJ) is produced by honeybees (Apis mellifera) as nutrition during larval development. The high viscosity of RJ originates from high concentrations of long lipoprotein filaments that include the glycosylated major royal jelly protein 1 (MRJP1), the small protein apisimin and insect lipids. Using cryo-electron microscopy we reveal the architecture and the composition of RJ filaments, in which the MRJP1 forms the outer shell of the assembly, surrounding stacked apisimin tetramers harbouring tightly packed lipids in the centre. The structural data rationalize the pH-dependent disassembly of RJ filaments in the gut of the larvae. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7asd.cif.gz 7asd.cif.gz | 648.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7asd.ent.gz pdb7asd.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7asd.json.gz 7asd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7asd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7asd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7asd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/7asd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11892MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
| 2 | 
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 16 molecules AABACADAEAFAGAHAABBBCBDBEBFBGBHB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48934.898 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Apis mellifera (honey bee) / References: UniProt: O18330 Apis mellifera (honey bee) / References: UniProt: O18330#2: Protein | Mass: 7949.325 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Apis mellifera (honey bee) / Plasmid details: royal jelly / References: UniProt: Q8ISL8 Apis mellifera (honey bee) / Plasmid details: royal jelly / References: UniProt: Q8ISL8 |
|---|
-Sugars , 3 types, 24 molecules 
| #3: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose  / Mass: 424.401 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Mass: 424.401 Da / Num. of mol.: 8Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #4: Polysaccharide | beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta- ...beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose  / Mass: 586.542 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Mass: 586.542 Da / Num. of mol.: 8Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #6: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG /  N-Acetylglucosamine N-Acetylglucosamine |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 24 molecules 


| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-94R / ( #7: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 /  Sulfate Sulfate |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: native royal jelly filaments / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Apis mellifera (honey bee) Apis mellifera (honey bee) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 119050 X / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 119050 X / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.7 sec. / Electron dose: 82 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 64 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 54 Å / Axial symmetry: D2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 240483 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj