[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
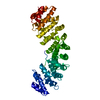
Yorodumi- PDB-1pjm: Mouse Importin alpha-bipartite NLS from human retinoblastoma prot... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1pjm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
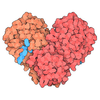
| Title | Mouse Importin alpha-bipartite NLS from human retinoblastoma protein Complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  PROTEIN TRANSPORT / IMPORTIN ALPHA/KARYOPHERIN ALPHA / NUCLEAR LOCALIZATION SEQUENCE (NLS) RECOGNITION / BIPARTITE NLS / PROTEIN TRANSPORT / IMPORTIN ALPHA/KARYOPHERIN ALPHA / NUCLEAR LOCALIZATION SEQUENCE (NLS) RECOGNITION / BIPARTITE NLS /  HUMAN RETINOBLASTOMA PROTEIN HUMAN RETINOBLASTOMA PROTEIN | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDefective translocation of RB1 mutants to the nucleus / enucleate erythrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of collagen fibril organization / negative regulation of tau-protein kinase activity / Rb-E2F complex /  regulation of lipid kinase activity / negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation / maintenance of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation / chromatin lock complex ...Defective translocation of RB1 mutants to the nucleus / enucleate erythrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of collagen fibril organization / negative regulation of tau-protein kinase activity / Rb-E2F complex / regulation of lipid kinase activity / negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation / maintenance of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation / chromatin lock complex ...Defective translocation of RB1 mutants to the nucleus / enucleate erythrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of collagen fibril organization / negative regulation of tau-protein kinase activity / Rb-E2F complex /  regulation of lipid kinase activity / negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation / maintenance of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation / chromatin lock complex / sister chromatid biorientation / Inhibition of replication initiation of damaged DNA by RB1/E2F1 / positive regulation of extracellular matrix organization / Sensing of DNA Double Strand Breaks / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / regulation of centromere complex assembly / positive regulation of macrophage differentiation / entry of viral genome into host nucleus through nuclear pore complex via importin / tissue homeostasis / glial cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of viral life cycle / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / importin-alpha family protein binding / negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process / positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / neuron maturation / NLS-dependent protein nuclear import complex / postsynapse to nucleus signaling pathway / digestive tract development / aortic valve morphogenesis / myoblast differentiation / Replication of the SARS-CoV-1 genome / regulation of lipid kinase activity / negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation / maintenance of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation / chromatin lock complex / sister chromatid biorientation / Inhibition of replication initiation of damaged DNA by RB1/E2F1 / positive regulation of extracellular matrix organization / Sensing of DNA Double Strand Breaks / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / regulation of centromere complex assembly / positive regulation of macrophage differentiation / entry of viral genome into host nucleus through nuclear pore complex via importin / tissue homeostasis / glial cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of viral life cycle / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / importin-alpha family protein binding / negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process / positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / neuron maturation / NLS-dependent protein nuclear import complex / postsynapse to nucleus signaling pathway / digestive tract development / aortic valve morphogenesis / myoblast differentiation / Replication of the SARS-CoV-1 genome /  SWI/SNF complex / negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / nuclear import signal receptor activity / SWI/SNF complex / negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / nuclear import signal receptor activity /  nuclear localization sequence binding / negative regulation of glial cell proliferation / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / smoothened signaling pathway / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Phosphorylation of proteins involved in G1/S transition by active Cyclin E:Cdk2 complexes / hepatocyte apoptotic process / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / RUNX2 regulates osteoblast differentiation / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / negative regulation of cell cycle / chromosome organization / glial cell proliferation / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / chondrocyte differentiation / heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / nuclear localization sequence binding / negative regulation of glial cell proliferation / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / smoothened signaling pathway / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Phosphorylation of proteins involved in G1/S transition by active Cyclin E:Cdk2 complexes / hepatocyte apoptotic process / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / RUNX2 regulates osteoblast differentiation / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / negative regulation of cell cycle / chromosome organization / glial cell proliferation / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / chondrocyte differentiation / heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry /  host cell / striated muscle cell differentiation / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / epithelial cell proliferation / host cell / striated muscle cell differentiation / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / epithelial cell proliferation /  phosphoprotein binding / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / negative regulation of protein kinase activity / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / Oncogene Induced Senescence / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell growth / negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity / PML body / phosphoprotein binding / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / negative regulation of protein kinase activity / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / Oncogene Induced Senescence / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell growth / negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity / PML body /  kinase binding / negative regulation of inflammatory response / cytoplasmic stress granule / spindle / protein import into nucleus / cellular response to insulin stimulus / transcription corepressor activity / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / neuron projection development / negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / disordered domain specific binding / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / Replication of the SARS-CoV-2 genome / kinase binding / negative regulation of inflammatory response / cytoplasmic stress granule / spindle / protein import into nucleus / cellular response to insulin stimulus / transcription corepressor activity / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / neuron projection development / negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / disordered domain specific binding / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / Replication of the SARS-CoV-2 genome /  spermatogenesis / neuron apoptotic process / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / Ras protein signal transduction / transcription by RNA polymerase II / spermatogenesis / neuron apoptotic process / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / Ras protein signal transduction / transcription by RNA polymerase II /  postsynaptic density / molecular adaptor activity / postsynaptic density / molecular adaptor activity /  cell differentiation / cell differentiation /  regulation of cell cycle / regulation of cell cycle /  chromatin remodeling / chromatin remodeling /  cell division / negative regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / glutamatergic synapse cell division / negative regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / glutamatergic synapseSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  FOURIER SYNTHESIS / Resolution: 2.5 Å FOURIER SYNTHESIS / Resolution: 2.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Fontes, M.R.M. / Teh, T. / Jans, D. / Brinkworth, R.I. / Kobe, B. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 2003 Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 2003Title: Structural basis for the specificity of bipartite nuclear localization sequence binding by importin-alpha Authors: Fontes, M.R.M. / Teh, T. / Jans, D. / Brinkworth, R.I. / Kobe, B. #1:  Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2000 Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2000Title: Structural basis of recognition of monopartite and bipartite nuclear localization sequences by mammalian importin-alpha Authors: Fontes, M.R.M. / Teh, T. / Kobe, B. #2:  Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 2001 Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 2001Title: Biophysical Characterization of Interactions Involving Impostin-alpha during Nuclear Import Authors: Catimel, B. / Teh, T. / Fontes, M.R.M. / Jennings, I.G. / Jans, D. / Howlett, G.J. / Nice, E.C. / Kobe, B. #3:  Journal: Nat.Struct.Biol. / Year: 1999 Journal: Nat.Struct.Biol. / Year: 1999Title: Autoinhibition by an internal nuclear localization signal reveled by the crystal structure of mammalian importin alpha Authors: Kobe, B. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1pjm.cif.gz 1pjm.cif.gz | 101.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1pjm.ent.gz pdb1pjm.ent.gz | 75.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1pjm.json.gz 1pjm.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pj/1pjm https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pj/1pjm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pj/1pjm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pj/1pjm | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1pjnC  1ialS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2129.530 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Fragment: NLS (nuclear localization signal) bipartite peptide Source method: obtained synthetically Details: THE PEPTIDE WAS CHEMICALLY SYNTHESIZED. THE SEQUENCE OF THIS PEPTIDE IS NATURALLY FOUND IN HUMAN RETINOBLASTOMA PROTEIN References: UniProt: P06400 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  Importin α / Karyopherin alpha-2 subunit Importin α / Karyopherin alpha-2 subunitMass: 49886.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: NLS binding domain (70-529) Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Gene: KPNA2 OR RCH1 / Plasmid: PET30A / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Gene: KPNA2 OR RCH1 / Plasmid: PET30A / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P52293 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P52293 |
| #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH /  Water Water |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.42 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 64.01 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6 Details: Sodium Citrate, DTT, pH 6.0, VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 293K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Method: vapor diffusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU RU200 / Wavelength: 1.5418 Å ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU RU200 / Wavelength: 1.5418 Å |
| Detector | Type: MARRESEARCH / Detector: IMAGE PLATE / Date: Aug 10, 2000 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: Mirrors / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 1.5418 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 1.5418 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.5→99 Å / Num. all: 25382 / Num. obs: 25382 / % possible obs: 96 % / Observed criterion σ(I): -3 / Redundancy: 9.8 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 53.2 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.073 / Net I/σ(I): 19 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.5→2.59 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.403 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.8 / % possible all: 98.3 |
| Reflection | *PLUS % possible obs: 96 % / Num. measured all: 249870 |
| Reflection shell | *PLUS % possible obs: 98.3 % |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  FOURIER SYNTHESIS FOURIER SYNTHESISStarting model: PDB ENTRY: 1ial Resolution: 2.5→29.57 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.007 / Isotropic thermal model: RESTRAINED / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: FLAT MODEL / Bsol: 38.52 Å2 / ksol: 0.363607 e/Å3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 46.2 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.5→29.57 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.5→2.66 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.021 / Total num. of bins used: 6
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xplor file |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.5 Å / Lowest resolution: 30 Å / % reflection Rfree: 5 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.5 Å / Rfactor Rfree: 0.292 / Rfactor Rwork: 0.263 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 PDBj
PDBj