+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM co-structure of AcrB with CU244 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump /  TRANSLOCASE TRANSLOCASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationxenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the cell outer membrane /  efflux pump complex / periplasmic side of plasma membrane / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / efflux pump complex / periplasmic side of plasma membrane / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.44 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.44 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Su CC | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2023 Journal: mBio / Year: 2023Title: Bacterial efflux pump modulators prevent bacterial growth in macrophages and under broth conditions that mimic the host environment. Authors: Samual C Allgood / Chih-Chia Su / Amy L Crooks / Christian T Meyer / Bojun Zhou / Meredith D Betterton / Michael R Barbachyn / Edward W Yu / Corrella S Detweiler /  Abstract: New approaches for combating microbial infections are needed. One strategy for disrupting pathogenesis involves developing compounds that interfere with bacterial virulence. A critical molecular ...New approaches for combating microbial infections are needed. One strategy for disrupting pathogenesis involves developing compounds that interfere with bacterial virulence. A critical molecular determinant of virulence for Gram-negative bacteria are efflux pumps of the resistance-nodulation-division family, which includes AcrAB-TolC. We previously identified small molecules that bind AcrB, inhibit AcrAB-TolC, and do not appear to damage membranes. These efflux pump modulators (EPMs) were discovered in an in-cell screening platform called SAFIRE (Screen for Anti-infectives using Fluorescence microscopy of IntracellulaR Enterobacteriaceae). SAFIRE identifies compounds that disrupt the growth of a Gram-negative human pathogen, serotype Typhimurium (. Typhimurium), in macrophages. We used medicinal chemistry to iteratively design ~200 EPM35 analogs and test them for activity in SAFIRE, generating compounds with nanomolar potency. Analogs were demonstrated to bind AcrB in a substrate binding pocket by cryo-electron microscopy. Despite having amphipathic structures, the EPM analogs do not disrupt membrane voltage, as monitored by FtsZ localization to the cell septum. The EPM analogs had little effect on bacterial growth in standard Mueller Hinton Broth. However, under broth conditions that mimic the micro-environment of the macrophage phagosome, is required for growth, the EPM analogs are bacteriostatic, and the EPM analogs increase the potency of antibiotics. These data suggest that under macrophage-like conditions, the EPM analogs prevent the export of a toxic bacterial metabolite(s) through AcrAB-TolC. Thus, compounds that bind AcrB could disrupt infection by specifically interfering with the export of bacterial toxic metabolites, host defense factors, and/or antibiotics.IMPORTANCEBacterial efflux pumps are critical for resistance to antibiotics and for virulence. We previously identified small molecules that inhibit efflux pumps (efflux pump modulators, EPMs) and prevent pathogen replication in host cells. Here, we used medicinal chemistry to increase the activity of the EPMs against pathogens in cells into the nanomolar range. We show by cryo-electron microscopy that these EPMs bind an efflux pump subunit. In broth culture, the EPMs increase the potency (activity), but not the efficacy (maximum effect), of antibiotics. We also found that bacterial exposure to the EPMs appear to enable the accumulation of a toxic metabolite that would otherwise be exported by efflux pumps. Thus, inhibitors of bacterial efflux pumps could interfere with infection not only by potentiating antibiotics, but also by allowing toxic waste products to accumulate within bacteria, providing an explanation for why efflux pumps are needed for virulence in the absence of antibiotics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44506.map.gz emd_44506.map.gz | 230.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44506-v30.xml emd-44506-v30.xml emd-44506.xml emd-44506.xml | 17.6 KB 17.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_44506.png emd_44506.png | 72.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44506.cif.gz emd-44506.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44506_additional_1.map.gz emd_44506_additional_1.map.gz emd_44506_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44506_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44506_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44506_half_map_2.map.gz | 123.6 MB 226.7 MB 226.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44506 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44506 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44506 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44506 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9bftMC  9bfhC  9bfmC  9bfnC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44506.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44506.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
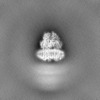
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
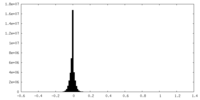
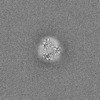
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_44506_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
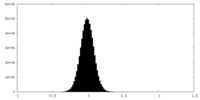
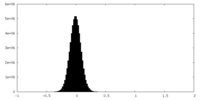
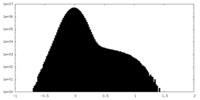
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44506_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
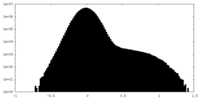
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44506_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : H6PD
| Entire | Name: H6PD |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: H6PD
| Supramolecule | Name: H6PD / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB
| Macromolecule | Name: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 113.66518 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MPNFFIDRPI FAWVIAIIIM LAGGLAILKL PVAQYPTIAP PAVTISASYP GADAKTVQDT VTQVIEQNMN GIDNLMYMSS NSDSTGTVQ ITLTFESGTD ADIAQVQVQN KLQLAMPLLP QEVQQQGVSV EKSSSSFLMV VGVINTDGTM TQEDISDYVA A NMKDAISR ...String: MPNFFIDRPI FAWVIAIIIM LAGGLAILKL PVAQYPTIAP PAVTISASYP GADAKTVQDT VTQVIEQNMN GIDNLMYMSS NSDSTGTVQ ITLTFESGTD ADIAQVQVQN KLQLAMPLLP QEVQQQGVSV EKSSSSFLMV VGVINTDGTM TQEDISDYVA A NMKDAISR TSGVGDVQLF GSQYAMRIWM NPNELNKFQL TPVDVITAIK AQNAQVAAGQ LGGTPPVKGQ QLNASIIAQT RL TSTEEFG KILLKVNQDG SRVLLRDVAK IELGGENYDI IAEFNGQPAS GLGIKLATGA NALDTAAAIR AELAKMEPFF PSG LKIVYP YDTTPFVKIS IHEVVKTLVE AIILVFLVMY LFLQNFRATL IPTIAVPVVL LGTFAVLAAF GFSINTLTMF GMVL AIGLL VDDAIVVVEN VERVMAEEGL PPKEATRKSM GQIQGALVGI AMVLSAVFVP MAFFGGSTGA IYRQFSITIV SAMAL SVLV ALILTPALCA TMLKPIAKGD HGEGKKGFFG WFNRMFEKST HHYTDSVGGI LRSTGRYLVL YLIIVVGMAY LFVRLP SSF LPDEDQGVFM TMVQLPAGAT QERTQKVLNE VTHYYLTKEK NNVESVFAVN GFGFAGRGQN TGIAFVSLKD WADRPGE EN KVEAITMRAT RAFSQIKDAM VFAFNLPAIV ELGTATGFDF ELIDQAGLGH EKLTQARNQL LAEAAKHPDM LTSVRPNG L EDTPQFKIDI DQEKAQALGV SINDINTTLG AAWGGSYVND FIDRGRVKKV YVMSEAKYRM LPDDIGDWYV RAADGQMVP FSAFSSSRWE YGSPRLERYN GLPSMEILGQ AAPGKSTGEA MELMEQLASK LPTGVGYDWT GMSYQERLSG NQAPSLYAIS LIVVFLCLA ALYESWSIPF SVMLVVPLGV IGALLAATFR GLTNDVYFQV GLLTTIGLSA KNAILIVEFA KDLMDKEGKG L IEATLDAV RMRLRPILMT SLAFILGVMP LVISTGAGSG AQNAVGTGVM GGMVTATVLA IFFVPVFFVV VRRRFSRKNE DI EHSHTVD HH UniProtKB: Multidrug efflux pump subunit AcrB |
-Macromolecule #2: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: 3PE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 748.065 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-3PE: |
-Macromolecule #3: (2S)-1-{[(1R,5R)-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-6-yl]amino}-3-(3,5-dich...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-1-{[(1R,5R)-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-6-yl]amino}-3-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)propan-2-ol type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: A1AOF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 317.211 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | This is from a heterogeneous and impure protein sample. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 29.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL / In silico model: ab initio reconstruction by cryosparc |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.44 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 162048 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9bft: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)