+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | a22L prion fibril | |||||||||
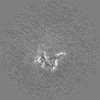
 Map data Map data | Post processed, real space averaged map of anchorless 22L prion fibril | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInsertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process /  lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity /  glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport ...Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process / glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport ...Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process /  lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / lamin binding / regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity /  glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / cupric ion binding / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / response to copper ion / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / cuprous ion binding / activation of protein kinase activity / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / response to amyloid-beta / : / negative regulation of type II interferon production / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / response to cadmium ion / side of membrane / glycosaminoglycan binding / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / ATP-dependent protein binding / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / cupric ion binding / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / response to copper ion / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / cuprous ion binding / activation of protein kinase activity / negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / response to amyloid-beta / : / negative regulation of type II interferon production / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / response to cadmium ion / side of membrane /  inclusion body / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to copper ion / neuron projection maintenance / molecular condensate scaffold activity / inclusion body / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to copper ion / neuron projection maintenance / molecular condensate scaffold activity /  tubulin binding / protein sequestering activity / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / molecular function activator activity / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / protein destabilization / protein homooligomerization / negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity / tubulin binding / protein sequestering activity / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / molecular function activator activity / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / protein destabilization / protein homooligomerization / negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity /  terminal bouton / cellular response to amyloid-beta / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / terminal bouton / cellular response to amyloid-beta / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process /  regulation of protein localization / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / regulation of protein localization / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus /  signaling receptor activity / signaling receptor activity /  amyloid-beta binding / protein-folding chaperone binding / amyloid-beta binding / protein-folding chaperone binding /  microtubule binding / microtubule binding /  nuclear membrane / response to oxidative stress / nuclear membrane / response to oxidative stress /  protease binding / mitochondrial outer membrane / transmembrane transporter binding / protease binding / mitochondrial outer membrane / transmembrane transporter binding /  postsynaptic density / learning or memory / molecular adaptor activity / postsynaptic density / learning or memory / molecular adaptor activity /  membrane raft / copper ion binding / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / membrane raft / copper ion binding / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle /  dendrite / protein-containing complex binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / dendrite / protein-containing complex binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process /  Golgi apparatus / Golgi apparatus /  cell surface / cell surface /  endoplasmic reticulum / endoplasmic reticulum /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Mus musculus (house mouse) /   house mouse (house mouse) house mouse (house mouse) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hoyt F / Caughey B | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2022 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM of prion strains from the same genotype of host identifies conformational determinants. Authors: Forrest Hoyt / Parvez Alam / Efrosini Artikis / Cindi L Schwartz / Andrew G Hughson / Brent Race / Chase Baune / Gregory J Raymond / Gerald S Baron / Allison Kraus / Byron Caughey /  Abstract: Prion strains in a given type of mammalian host are distinguished by differences in clinical presentation, neuropathological lesions, survival time, and characteristics of the infecting prion protein ...Prion strains in a given type of mammalian host are distinguished by differences in clinical presentation, neuropathological lesions, survival time, and characteristics of the infecting prion protein (PrP) assemblies. Near-atomic structures of prions from two host species with different PrP sequences have been determined but comparisons of distinct prion strains of the same amino acid sequence are needed to identify purely conformational determinants of prion strain characteristics. Here we report a 3.2 Å resolution cryogenic electron microscopy-based structure of the 22L prion strain purified from the brains of mice engineered to express only PrP lacking glycophosphatidylinositol anchors [anchorless (a) 22L]. Comparison of this near-atomic structure to our recently determined structure of the aRML strain propagated in the same inbred mouse reveals that these two mouse prion strains have distinct conformational templates for growth via incorporation of PrP molecules of the same sequence. Both a22L and aRML are assembled as stacks of PrP molecules forming parallel in-register intermolecular β-sheets and intervening loops, with single monomers spanning the ordered fibril core. Each monomer shares an N-terminal steric zipper, three major arches, and an overall V-shape, but the details of these and other conformational features differ markedly. Thus, variations in shared conformational motifs within a parallel in-register β-stack fibril architecture provide a structural basis for prion strain differentiation within a single host genotype. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28089.map.gz emd_28089.map.gz | 9.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28089-v30.xml emd-28089-v30.xml emd-28089.xml emd-28089.xml | 16.5 KB 16.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_28089_fsc.xml emd_28089_fsc.xml | 13.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_28089.png emd_28089.png | 65.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28089_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28089_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28089_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28089_half_map_2.map.gz | 171.9 MB 171.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28089 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28089 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28089 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28089 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8efuMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28089.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28089.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Post processed, real space averaged map of anchorless 22L prion fibril | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.045 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: EM half map for anchorless 22L prion fibril
| File | emd_28089_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | EM half map for anchorless 22L prion fibril | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
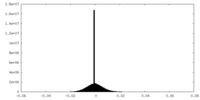
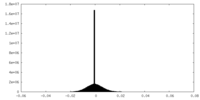
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: EM half map for anchorless 22L prion fibril
| File | emd_28089_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | EM half map for anchorless 22L prion fibril | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
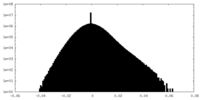
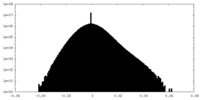
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : GPI anchorless underglycosylated 22L prion fibril
| Entire | Name: GPI anchorless underglycosylated 22L prion fibril |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: GPI anchorless underglycosylated 22L prion fibril
| Supramolecule | Name: GPI anchorless underglycosylated 22L prion fibril / type: complex / Chimera: Yes / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Organ: Brain Mus musculus (house mouse) / Organ: Brain |
-Macromolecule #1: Major prion protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Major prion protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   house mouse (house mouse) house mouse (house mouse) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.550348 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MANLGYWLLA LFVTMWTDVG LCKKRPKPGG WNTGGSRYPG QGSPGGNRYP PQGGTWGQPH GGGWGQPHGG SWGQPHGGSW GQPHGGGWG QGGGTHNQWN KPSKPKTNLK HVAGAAAAGA VVGGLGGYML GSAMSRPMIH FGNDWEDRYY RENMYRYPNQ V YYRPVDQY ...String: MANLGYWLLA LFVTMWTDVG LCKKRPKPGG WNTGGSRYPG QGSPGGNRYP PQGGTWGQPH GGGWGQPHGG SWGQPHGGSW GQPHGGGWG QGGGTHNQWN KPSKPKTNLK HVAGAAAAGA VVGGLGGYML GSAMSRPMIH FGNDWEDRYY RENMYRYPNQ V YYRPVDQY SNQNNFVHDC VNITIKQHTV TTTTKGENFT ETDVKMMERV VEQMCVTQYQ KESQAYYDGR RSS |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: Sample suspended in 20 mM Tris pH 7.4, 100 mM containing 0.02% amphipol 8-35 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 4449 / Average electron dose: 57.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8efu: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z
Z Y
Y X
X