+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | S. aureus GS(12)-Q-GlnR peptide | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened (B factor 62A^2) | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | glutamine synthetase repressor dodecamer /  BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN /  LIGASE LIGASE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information glutamine synthetase / glutamine biosynthetic process / glutamine synthetase / glutamine biosynthetic process /  glutamine synthetase activity / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / glutamine synthetase activity / DNA-binding transcription factor activity /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.15 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.15 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Travis BA / Peck J | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Molecular dissection of the glutamine synthetase-GlnR nitrogen regulatory circuitry in Gram-positive bacteria. Authors: Brady A Travis / Jared V Peck / Raul Salinas / Brandon Dopkins / Nicholas Lent / Viet D Nguyen / Mario J Borgnia / Richard G Brennan / Maria A Schumacher /  Abstract: How bacteria sense and respond to nitrogen levels are central questions in microbial physiology. In Gram-positive bacteria, nitrogen homeostasis is controlled by an operon encoding glutamine ...How bacteria sense and respond to nitrogen levels are central questions in microbial physiology. In Gram-positive bacteria, nitrogen homeostasis is controlled by an operon encoding glutamine synthetase (GS), a dodecameric machine that assimilates ammonium into glutamine, and the GlnR repressor. GlnR detects nitrogen excess indirectly by binding glutamine-feedback-inhibited-GS (FBI-GS), which activates its transcription-repression function. The molecular mechanisms behind this regulatory circuitry, however, are unknown. Here we describe biochemical and structural analyses of GS and FBI-GS-GlnR complexes from pathogenic and non-pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria. The structures show FBI-GS binds the GlnR C-terminal domain within its active-site cavity, juxtaposing two GlnR monomers to form a DNA-binding-competent GlnR dimer. The FBI-GS-GlnR interaction stabilizes the inactive GS conformation. Strikingly, this interaction also favors a remarkable dodecamer to tetradecamer transition in some GS, breaking the paradigm that all bacterial GS are dodecamers. These data thus unveil unique structural mechanisms of transcription and enzymatic regulation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25863.map.gz emd_25863.map.gz | 230.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25863-v30.xml emd-25863-v30.xml emd-25863.xml emd-25863.xml | 14.8 KB 14.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_25863.png emd_25863.png | 119.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25863.cif.gz emd-25863.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_25863_additional_1.map.gz emd_25863_additional_1.map.gz | 123.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25863 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25863 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25863 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25863 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7tf6MC  7tdpC  7tdvC  7teaC  7tecC  7tenC  7tf7C  7tf9C  7tfaC  7tfbC  7tfcC  7tfdC  7tfeC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25863.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25863.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened (B factor 62A^2) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.88 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_25863_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
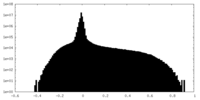
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
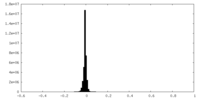
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Dodecameric GS complex with glutamine and GlnR C-tail peptides
| Entire | Name: Dodecameric GS complex with glutamine and GlnR C-tail peptides |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Dodecameric GS complex with glutamine and GlnR C-tail peptides
| Supramolecule | Name: Dodecameric GS complex with glutamine and GlnR C-tail peptides type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamine synthetase
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamine synthetase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  glutamine synthetase glutamine synthetase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 51.19684 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: GSHMPKRTFT KEDIRKFAEE ENVRYLRLQF TDILGTIKNV EVPVSQLEKV LDNEMMFDGS SIEGFVRIEE SDMYLHPDLD TWVIFPWTA GQGKVARLIC DVYKTDGTPF EGDPRANLKR VLKEMEDLGF TDFNLGPEPE FFLFKLDEKG EPTLELNDDG G YFDLAPTD ...String: GSHMPKRTFT KEDIRKFAEE ENVRYLRLQF TDILGTIKNV EVPVSQLEKV LDNEMMFDGS SIEGFVRIEE SDMYLHPDLD TWVIFPWTA GQGKVARLIC DVYKTDGTPF EGDPRANLKR VLKEMEDLGF TDFNLGPEPE FFLFKLDEKG EPTLELNDDG G YFDLAPTD LGENCRRDIV LELEDMGFDI EASHHEVAPG QHEIDFKYAD AVTACDNIQT FKLVVKTIAR KHNLHATFMP KP LFGVNGS GMHFNVSLFK GKENAFFDPN TEMGLTETAY QFTAGVLKNA RGFTAVCNPL VNSYKRLVPG YEAPCYIAWS GKN RSPLIR VPSSRGLSTR IEVRSVDPAA NPYMALAAIL EAGLDGIKNK LKVPEPVNQN IYEMNREERE AVGIQDLPST LYTA LKAMR ENEVIKKALG NHIYNQFINS KSIEWDYYRT QVSEWERDQY MKQY UniProtKB:  Glutamine synthetase Glutamine synthetase |
-Macromolecule #2: Peptide from Glutamine synthetase repressor
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptide from Glutamine synthetase repressor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.289485 KDa |
| Sequence | String: PINRGDLSRF I UniProtKB:  Glutamine synthetase Glutamine synthetase |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 24 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: GLUTAMINE
| Macromolecule | Name: GLUTAMINE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: GLN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 146.144 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GLN: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.75 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.5 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 3.2) |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 3.2) |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: D6 (2x6 fold dihedral ) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.15 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 3.2) / Number images used: 222918 ) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.15 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 3.2) / Number images used: 222918 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7tf6: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z
Z Y
Y X
X