+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23986 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
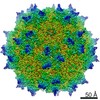
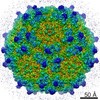
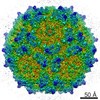
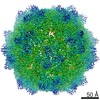
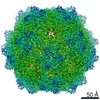
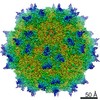
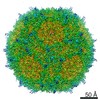
| Title | Structure of the adeno-associated virus 9 capsid at pH 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | AAV9 capsid at pH 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology | Phospholipase A2-like domain / Phospholipase A2-like domain / Parvovirus coat protein VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP1/VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP2 / Capsid/spike protein, ssDNA virus / T=1 icosahedral viral capsid / structural molecule activity /  Capsid protein VP1 Capsid protein VP1 Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |    Adeno-associated virus 9 Adeno-associated virus 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.67 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.67 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Penzes JJ / Chipman P / Bhattacharya N / Zeher A / Huang R / McKenna R / Agbandje-McKenna M | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2021 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2021Title: Adeno-associated Virus 9 Structural Rearrangements Induced by Endosomal Trafficking pH and Glycan Attachment. Authors: Judit J Penzes / Paul Chipman / Nilakshee Bhattacharya / Allison Zeher / Rick Huang / Robert McKenna / Mavis Agbandje-McKenna /  Abstract: Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are small nonenveloped single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses that are currently being developed as gene therapy biologics. After cell entry, AAVs traffic to the nucleus ...Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are small nonenveloped single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses that are currently being developed as gene therapy biologics. After cell entry, AAVs traffic to the nucleus using the endo-lysosomal pathway. The subsequent decrease in pH triggers conformational changes to the capsid that enable the externalization of the capsid protein (VP) N termini, including the unique domain of the minor capsid protein VP1 (VP1u), which permits the phospholipase activity required for the capsid lysosomal egress. Here, we report the AAV9 capsid structure, determined at the endosomal pHs (7.4, 6.0, 5.5, and 4.0), and terminal galactose-bound AAV9 capsids at pHs 7.4 and 5.5 using cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional image reconstruction. Taken together, these studies provide insight into AAV9 capsid conformational changes at the 5-fold pore during endosomal trafficking, in both the presence and absence of its cellular glycan receptor. We visualized, for the first time, that acidification induces the externalization of the VP3 and possibly VP2 N termini, presumably in prelude to the externalization of VP1u at pH 4.0, which is essential for lysosomal membrane disruption. In addition, the structural study of AAV9-galactose interactions demonstrates that AAV9 remains attached to its glycan receptor at the late endosome pH 5.5. This interaction significantly alters the conformational stability of the variable region I of the VPs, as well as the dynamics associated with VP N terminus externalization. There are 13 distinct Adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotypes that are structurally homologous and whose capsid proteins (VP1 to -3) are similar in amino acid sequence. However, AAV9 is one of the most commonly studied and is used as a gene therapy vector. This is partly because AAV9 is capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier and readily transduces a wide array of tissues, including the central nervous system. In this study, we provide AAV9 capsid structural insight during intracellular trafficking. Although the AAV capsid has been shown to externalize the N termini of its VPs, to enzymatically disrupt the lysosome membrane at low pH, there was no structural evidence to confirm this. By utilizing AAV9 as our model, we provide the first structural evidence that the externalization process occurs at the protein interface at the icosahedral 5-fold symmetry axis and can be triggered by lowering the pH. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23986.map.gz emd_23986.map.gz | 104.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23986-v30.xml emd-23986-v30.xml emd-23986.xml emd-23986.xml | 14.3 KB 14.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23986.png emd_23986.png | 153.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23986 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23986 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23986 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23986 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mtgMC  7mt0C  7mtpC  7mtwC  7mtzC  7muaC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23986.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 327.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23986.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 327.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | AAV9 capsid at pH 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.087 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Adeno-associated virus 9
| Entire | Name:    Adeno-associated virus 9 Adeno-associated virus 9 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Adeno-associated virus 9
| Supramolecule | Name: Adeno-associated virus 9 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / NCBI-ID: 235455 / Sci species name: Adeno-associated virus 9 / Virus type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE / Virus isolate: SEROTYPE / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: Yes |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Host system | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / Recombinant cell: Sf9 / Recombinant plasmid: pFastBac1-HM Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / Recombinant cell: Sf9 / Recombinant plasmid: pFastBac1-HM |
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 1 / Name: AAV9 virus like particle / Diameter: 240.0 Å / T number (triangulation number): 1 |
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein VP1
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein VP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 60 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Adeno-associated virus 9 Adeno-associated virus 9 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 58.474414 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) |
| Sequence | String: DGVGSSSGNW HCDSQWLGDR VITTSTRTWA LPTYNNHLYK QISNSTSGGS SNDNAYFGYS TPWGYFDFNR FHCHFSPRDW QRLINNNWG FRPKRLNFKL FNIQVKEVTD NNGVKTIANN LTSTVQVFTD SDYQLPYVLG SAHEGCLPPF PADVFMIPQY G YLTLNDGS ...String: DGVGSSSGNW HCDSQWLGDR VITTSTRTWA LPTYNNHLYK QISNSTSGGS SNDNAYFGYS TPWGYFDFNR FHCHFSPRDW QRLINNNWG FRPKRLNFKL FNIQVKEVTD NNGVKTIANN LTSTVQVFTD SDYQLPYVLG SAHEGCLPPF PADVFMIPQY G YLTLNDGS QAVGRSSFYC LEYFPSQMLR TGNNFQFSYE FENVPFHSSY AHSQSLDRLM NPLIDQYLYY LSKTINGSGQ NQ QTLKFSV AGPSNMAVQG RNYIPGPSYR QQRVSTTVTQ NNNSEFAWPG ASSWALNGRN SLMNPGPAMA SHKEGEDRFF PLS GSLIFG KQGTGRDNVD ADKVMITNEE EIKTTNPVAT ESYGQVATNH QSAQAQAQTG WVQNQGILPG MVWQDRDVYL QGPI WAKIP HTDGNFHPSP LMGGFGMKHP PPQILIKNTP VPADPPTAFN KDKLNSFITQ YSTGQVSVEI EWELQKENSK RWNPE IQYT SNYYKSNNVE FAVNTEGVYS EPRPIGTRYL TRNL |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: 1x Universal buffer of 20 mM HEPES, 20 mM MES, 20 mM sodium acetate, 0.15 M NaCl, 3.7 mM CaCl2 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source: OTHER |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: OTHER / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Software - Name: Auto3DEM (ver. 5.04.2) / Software - details: Autopp3X subroutine |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL In silico model: Ab initio random model based on 100 boxed particles |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.67 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: Auto3DEM (ver. 5.02.4) / Number images used: 107405 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller