[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
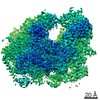
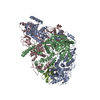
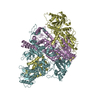
Yorodumi- EMDB-20017: Structure of the rice hyperosmolality-gated ion channel OSCA1.2 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20017 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the rice hyperosmolality-gated ion channel OSCA1.2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | rice hyperosmolality-gated ion channel OSCA1.2 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel osmolality gated /  TRANSPORT PROTEIN TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcalcium-activated cation channel activity / membrane => GO:0016020 /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Japanese rice) Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Japanese rice) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Maity K / Heumann JM | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019Title: Cryo-EM structure of OSCA1.2 from elucidates the mechanical basis of potential membrane hyperosmolality gating. Authors: Koustav Maity / John M Heumann / Aaron P McGrath / Noah J Kopcho / Po-Kai Hsu / Chang-Wook Lee / James H Mapes / Denisse Garza / Srinivasan Krishnan / Garry P Morgan / Kevin J Hendargo / ...Authors: Koustav Maity / John M Heumann / Aaron P McGrath / Noah J Kopcho / Po-Kai Hsu / Chang-Wook Lee / James H Mapes / Denisse Garza / Srinivasan Krishnan / Garry P Morgan / Kevin J Hendargo / Thomas Klose / Steven D Rees / Arturo Medrano-Soto / Milton H Saier / Miguel Piñeros / Elizabeth A Komives / Julian I Schroeder / Geoffrey Chang / Michael H B Stowell /  Abstract: Sensing and responding to environmental water deficiency and osmotic stresses are essential for the growth, development, and survival of plants. Recently, an osmolality-sensing ion channel called ...Sensing and responding to environmental water deficiency and osmotic stresses are essential for the growth, development, and survival of plants. Recently, an osmolality-sensing ion channel called OSCA1 was discovered that functions in sensing hyperosmolality in Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure and function of an OSCA1 homolog from rice (; OsOSCA1.2), leading to a model of how it could mediate hyperosmolality sensing and transport pathway gating. The structure reveals a dimer; the molecular architecture of each subunit consists of 11 transmembrane (TM) helices and a cytosolic soluble domain that has homology to RNA recognition proteins. The TM domain is structurally related to the TMEM16 family of calcium-dependent ion channels and lipid scramblases. The cytosolic soluble domain possesses a distinct structural feature in the form of extended intracellular helical arms that are parallel to the plasma membrane. These helical arms are well positioned to potentially sense lateral tension on the inner leaflet of the lipid bilayer caused by changes in turgor pressure. Computational dynamic analysis suggests how this domain couples to the TM portion of the molecule to open a transport pathway. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDXMS) experimentally confirms the conformational dynamics of these coupled domains. These studies provide a framework to understand the structural basis of proposed hyperosmolality sensing in a staple crop plant, extend our knowledge of the anoctamin superfamily important for plants and fungi, and provide a structural mechanism for potentially translating membrane stress to transport regulation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20017.map.gz emd_20017.map.gz | 49.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20017-v30.xml emd-20017-v30.xml emd-20017.xml emd-20017.xml | 15.3 KB 15.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20017.png emd_20017.png | 183.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20017.cif.gz emd-20017.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20017 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20017 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20017 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20017 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6oceMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20017.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20017.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | rice hyperosmolality-gated ion channel OSCA1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.38 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : OSCA1.2 dimer
| Entire | Name: OSCA1.2 dimer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: OSCA1.2 dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: OSCA1.2 dimer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Japanese rice) Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Japanese rice) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 180 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: stress-gated cation channel 1.2
| Macromolecule | Name: stress-gated cation channel 1.2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Japanese rice) Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Japanese rice) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 88.876383 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Komagataella pastoris (fungus) Komagataella pastoris (fungus) |
| Sequence | String: MATVSDIGLS AAINVSMAVA FLLVFAFLRL QPINDRVYFP KWYLRGMRDS PVSSGAAVQK VVNLNMRSYL KFLSWMPAAL KMPEDELIN HAGLDSAVYL RIYLTGIKIF VPISILASLV LFPVNWTNDT LDSMKVVHSK IDKLSISNIP YGSNRFVTHL V MAYAVTFW ...String: MATVSDIGLS AAINVSMAVA FLLVFAFLRL QPINDRVYFP KWYLRGMRDS PVSSGAAVQK VVNLNMRSYL KFLSWMPAAL KMPEDELIN HAGLDSAVYL RIYLTGIKIF VPISILASLV LFPVNWTNDT LDSMKVVHSK IDKLSISNIP YGSNRFVTHL V MAYAVTFW TCYVLFREYE IITTMRLRFL ASEKRRPDQF TVLVRNIPPD PDESISELVE HFFLVNHPDH YLRHQVVYNA NK LADLVEK KKKLQNWLDY YQLKYERNPS KRPTTKTGFL GCFGSEVDAI EYYKAEIEKI GKEEADERQK IMKDPQSAVP AAF VSFRSR WGAAVCAQTQ QTSNPTVWIT EWAPEPRDVY WNNLSIPFVS LTVRRLIVAV AFFFLNFFYV IPIAFVQSLA SLEG IEKAL PFLKPLIKID VIKSFIQGFL PGIALKVFLI LLPTILMFMS KFEGLISQSS LERRSASKYY IFLFFNVFLG SIVTG SALD QLKAYIHQSA NEIPRTIGVA IPMRATFFIT YVMVDGWTGV AGEILRLRAL IIFHLKNFFL VKTEKDREEA MDPGSI CFD WCEPRIQLYF LLGLVYAVVT PLLLPFILVF FGLAYVVYRH QIINVYNQQY ESGAQFWPSV HGRIIIALIV SQLLLIG LL STKGFEETTP VLVVLPVLTF WFYKYCKNRF EPAFVRNPLQ EAMRKDTLER AREPTFDLKA YLANAYLHPV FKGREEED N MSISEDVGME EVIVPTKRQS RRNTPAQSKY EGSDTLSLPE TVHERIKPQL EGS UniProtKB: Os05g0594700 protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Details: unspecified | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.2 mm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.2 mm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Specialist optics | Phase plate: VOLTA PHASE PLATE / Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-40 / Number grids imaged: 5 / Number real images: 2408 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 55.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Particle selection | Number selected: 169655 |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final 3D classification | Number classes: 1 |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION |
| Final reconstruction | Number classes used: 1 / Applied symmetry - Point group: C2 (2 fold cyclic ) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 64096 ) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 64096 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 400 |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6oce: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller