[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDCL9: Catalytic domain (AC) of B. Pertussis Adenylate Cyclase Toxin (Cy... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDCL9 |
|---|---|
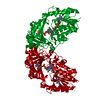
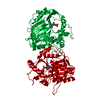
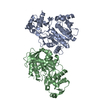
 Sample Sample | Catalytic domain (AC) of B. Pertussis Adenylate Cyclase Toxin (CyaA) in complex with calmodulin
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcalcium- and calmodulin-responsive adenylate cyclase activity /  hemolysis in another organism / hemolysis in another organism /  : / : /  adenylate cyclase / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / cAMP biosynthetic process / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / adenylate cyclase / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / cAMP biosynthetic process / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding /  adenylate cyclase activity / channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis ...calcium- and calmodulin-responsive adenylate cyclase activity / adenylate cyclase activity / channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis ...calcium- and calmodulin-responsive adenylate cyclase activity /  hemolysis in another organism / hemolysis in another organism /  : / : /  adenylate cyclase / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / cAMP biosynthetic process / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / adenylate cyclase / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / cAMP biosynthetic process / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding /  adenylate cyclase activity / channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / response to corticosterone / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / adenylate cyclase activity / channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / response to corticosterone / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation /  nitric-oxide synthase binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / nitric-oxide synthase binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity /  adenylate cyclase binding / adenylate cyclase binding /  catalytic complex / detection of calcium ion / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of DNA binding / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / enzyme regulator activity / catalytic complex / detection of calcium ion / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of DNA binding / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / enzyme regulator activity /  voltage-gated potassium channel complex / voltage-gated potassium channel complex /  phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of protein dephosphorylation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of protein dephosphorylation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling /  titin binding / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / response to amphetamine / titin binding / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / response to amphetamine /  calcium channel complex / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / substantia nigra development / adenylate cyclase activator activity / calcium channel complex / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / substantia nigra development / adenylate cyclase activator activity /  regulation of heart rate / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of heart rate / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity /  sarcomere / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / sarcomere / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation /  regulation of cytokinesis / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / regulation of cytokinesis / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity /  mitochondrial membrane / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / synaptic vesicle membrane / mitochondrial membrane / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / synaptic vesicle membrane /  spindle pole / response to calcium ion / calcium-dependent protein binding / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / disordered domain specific binding / spindle pole / response to calcium ion / calcium-dependent protein binding / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / disordered domain specific binding /  myelin sheath / myelin sheath /  toxin activity / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / toxin activity / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration /  growth cone / vesicle / transmembrane transporter binding / growth cone / vesicle / transmembrane transporter binding /  calmodulin binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / protein domain specific binding / calmodulin binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / protein domain specific binding /  centrosome / centrosome /  calcium ion binding / calcium ion binding /  protein kinase binding / host cell plasma membrane / protein-containing complex / extracellular region / protein kinase binding / host cell plasma membrane / protein-containing complex / extracellular region /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  membrane / membrane /  nucleus / nucleus /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function |
| Biological species |   Bordetella pertussis (strain Tohama I / ATCC BAA-589 / NCTC 13251) (bacteria) Bordetella pertussis (strain Tohama I / ATCC BAA-589 / NCTC 13251) (bacteria)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2017 Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2017Title: Calmodulin fishing with a structurally disordered bait triggers CyaA catalysis. Authors: Darragh P O'Brien / Dominique Durand / Alexis Voegele / Véronique Hourdel / Marilyne Davi / Julia Chamot-Rooke / Patrice Vachette / Sébastien Brier / Daniel Ladant / Alexandre Chenal /  Abstract: Once translocated into the cytosol of target cells, the catalytic domain (AC) of the adenylate cyclase toxin (CyaA), a major virulence factor of Bordetella pertussis, is potently activated by binding ...Once translocated into the cytosol of target cells, the catalytic domain (AC) of the adenylate cyclase toxin (CyaA), a major virulence factor of Bordetella pertussis, is potently activated by binding calmodulin (CaM) to produce supraphysiological levels of cAMP, inducing cell death. Using a combination of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS), and synchrotron radiation circular dichroism (SR-CD), we show that, in the absence of CaM, AC exhibits significant structural disorder, and a 75-residue-long stretch within AC undergoes a disorder-to-order transition upon CaM binding. Beyond this local folding, CaM binding induces long-range allosteric effects that stabilize the distant catalytic site, whilst preserving catalytic loop flexibility. We propose that the high enzymatic activity of AC is due to a tight balance between the CaM-induced decrease of structural flexibility around the catalytic site and the preservation of catalytic loop flexibility, allowing for fast substrate binding and product release. The CaM-induced dampening of AC conformational disorder is likely relevant to other CaM-activated enzymes. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDCL9 SASDCL9 |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
| Model #1694 |  Type: mix / Software: (08) / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Chi-square value: 1.956  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #1696 |  Type: atomic / Software: (2.1) / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Chi-square value: 1.410 / P-value: 0.000713  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Catalytic domain (AC) of B. Pertussis Adenylate Cyclase Toxin (CyaA) in complex with calmodulin Entity id: 904 / 905 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 20 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 4 mM CaCl2 / pH: 7.4 |
| Entity #904 | Name: AC domain from CyaA / Type: protein / Description: Bifunctional hemolysin/adenylate cyclase / Formula weight: 39.38 / Num. of mol.: 1 Source: Bordetella pertussis (strain Tohama I / ATCC BAA-589 / NCTC 13251) References: UniProt: P0DKX7 Sequence: MQQSHQAGYA NAADRESGIP AAVLDGIKAV AKEKNATLMF RLVNPHSTSL IAEGVATKGL GVHAKSSDWG LQAGYIPVNP NLSKLFGRAP EVIARADNDV NSSLAHGHTA VDLTLSKERL DYLRQAGLVT GMADGVVASN HAGYEQFEFR VKETSDGRYA VQYRRKGGDD ...Sequence: MQQSHQAGYA NAADRESGIP AAVLDGIKAV AKEKNATLMF RLVNPHSTSL IAEGVATKGL GVHAKSSDWG LQAGYIPVNP NLSKLFGRAP EVIARADNDV NSSLAHGHTA VDLTLSKERL DYLRQAGLVT GMADGVVASN HAGYEQFEFR VKETSDGRYA VQYRRKGGDD FEAVKVIGNA AGIPLTADID MFAIMPHLSN FRDSARSSVT SGDSVTDYLA RTRRAASEAT GGLDRERIDL LWKIARAGAR SAVGTEARRQ FRYDGDMNIG VITDFELEVR NALNRRAHAV GAQDVVQHGT EQNNPFPEAD EKIFVVSATG ESQMLTRGQL KEYIGQQRGE GYVFYENRAY GVAGKSLFDD GLGA |
| Entity #905 | Name: CaM / Type: protein / Description: Calmodulin / Formula weight: 16.837 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P62158 / Formula weight: 16.837 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P62158Sequence: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREAF RVFDKDGNGY ISAAELRHVM TNLGEKLTDE EVDEMIREAD IDGDGQVNYE EFVQMMTAK |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: SOLEIL SWING  / City: Saint-Aubin / 国: France / City: Saint-Aubin / 国: France  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron Synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.987 mm Synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.987 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: AVIEX / Type: CCD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan | Measurement date: Jun 19, 2015 / Storage temperature: 10 °C / Cell temperature: 15 °C / Exposure time: 1.5 sec. / Number of frames: 250 / Unit: 1/A /
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result | Comments: The scattered intensities were displayed on an absolute scale (cm-1) using the scattering of water. Frames were examined individually and 20 identical frames were averaged and further ...Comments: The scattered intensities were displayed on an absolute scale (cm-1) using the scattering of water. Frames were examined individually and 20 identical frames were averaged and further processed. The corresponding concentration was 0.82 g/L. Three independent determinations of the molecular mass were obtained from the value of I(0)/c, where c is the protein concentration, and using the programs SAXSMow2 and ScÅtter3 available at the URLs http://saxs.ifsc.usp.br/ and https://bl1231.als.lbl.gov/scatter/, respectively. The average value is The average value is MWexperimental=56.3 kDa. AC-CAM complex: Top panel: Comparison of the experimental data (blue dots) with the calculated scattering pattern (red line) of the BUNCH model shown on the right. chi2=1.96. Each CaM domain were handled as rigid bodies while the program searches an optimal conformation of the inter-domain helix of CaM. Bottom panel: Typical ensemble of conformations describing the AC:CaM complex, obtained using the program EOM and displayed after superimposition of the AC moiety of each conformation. chi2=1.41. The corresponding scattering curve is shown in red superimposed over experimental data (blue dots).
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller