+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ttb | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the PP2A:B55-ARPP19 complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN /  HYDROLASE / Protein Phosphatase 2A:B55 holoenzyme / ARPP19 inhibitor / HYDROLASE / Protein Phosphatase 2A:B55 holoenzyme / ARPP19 inhibitor /  cell cycle regulation cell cycle regulation | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information phosphatase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of protein dephosphorylation / meiotic spindle elongation / Integration of energy metabolism / PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of key metabolic factors / phosphatase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of protein dephosphorylation / meiotic spindle elongation / Integration of energy metabolism / PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of key metabolic factors /  regulation of microtubule binding / MASTL Facilitates Mitotic Progression / mitotic sister chromatid separation / regulation of meiotic cell cycle process involved in oocyte maturation / protein phosphatase type 2A complex ... regulation of microtubule binding / MASTL Facilitates Mitotic Progression / mitotic sister chromatid separation / regulation of meiotic cell cycle process involved in oocyte maturation / protein phosphatase type 2A complex ... phosphatase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of protein dephosphorylation / meiotic spindle elongation / Integration of energy metabolism / PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of key metabolic factors / phosphatase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of protein dephosphorylation / meiotic spindle elongation / Integration of energy metabolism / PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of key metabolic factors /  regulation of microtubule binding / MASTL Facilitates Mitotic Progression / mitotic sister chromatid separation / regulation of meiotic cell cycle process involved in oocyte maturation / protein phosphatase type 2A complex / meiotic sister chromatid cohesion, centromeric / peptidyl-serine dephosphorylation / peptidyl-threonine dephosphorylation / regulation of microtubule binding / MASTL Facilitates Mitotic Progression / mitotic sister chromatid separation / regulation of meiotic cell cycle process involved in oocyte maturation / protein phosphatase type 2A complex / meiotic sister chromatid cohesion, centromeric / peptidyl-serine dephosphorylation / peptidyl-threonine dephosphorylation /  : / positive regulation of microtubule binding / negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein / Regulation of glycolysis by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate metabolism / Inhibition of replication initiation of damaged DNA by RB1/E2F1 / female meiotic nuclear division / protein antigen binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / ceramide metabolic process / : / positive regulation of microtubule binding / negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein / Regulation of glycolysis by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate metabolism / Inhibition of replication initiation of damaged DNA by RB1/E2F1 / female meiotic nuclear division / protein antigen binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / ceramide metabolic process /  GABA receptor binding / negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / APC truncation mutants have impaired AXIN binding / AXIN missense mutants destabilize the destruction complex / Truncations of AMER1 destabilize the destruction complex / Initiation of Nuclear Envelope (NE) Reformation / ERKs are inactivated / response to morphine / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / Beta-catenin phosphorylation cascade / Signaling by GSK3beta mutants / CTNNB1 S33 mutants aren't phosphorylated / CTNNB1 S37 mutants aren't phosphorylated / CTNNB1 S45 mutants aren't phosphorylated / CTNNB1 T41 mutants aren't phosphorylated / GABA receptor binding / negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / APC truncation mutants have impaired AXIN binding / AXIN missense mutants destabilize the destruction complex / Truncations of AMER1 destabilize the destruction complex / Initiation of Nuclear Envelope (NE) Reformation / ERKs are inactivated / response to morphine / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / Beta-catenin phosphorylation cascade / Signaling by GSK3beta mutants / CTNNB1 S33 mutants aren't phosphorylated / CTNNB1 S37 mutants aren't phosphorylated / CTNNB1 S45 mutants aren't phosphorylated / CTNNB1 T41 mutants aren't phosphorylated /  regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / Disassembly of the destruction complex and recruitment of AXIN to the membrane / regulation of growth / protein phosphatase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of glycolytic process through fructose-6-phosphate / positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / myosin phosphatase activity / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / Disassembly of the destruction complex and recruitment of AXIN to the membrane / regulation of growth / protein phosphatase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of glycolytic process through fructose-6-phosphate / positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / myosin phosphatase activity /  protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity / CTLA4 inhibitory signaling / Platelet sensitization by LDL / negative regulation of MAPK cascade / protein-serine/threonine phosphatase / protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity / CTLA4 inhibitory signaling / Platelet sensitization by LDL / negative regulation of MAPK cascade / protein-serine/threonine phosphatase /  regulation of cell differentiation / T cell homeostasis / ERK/MAPK targets / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of cell differentiation / T cell homeostasis / ERK/MAPK targets / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle /  phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / phosphoprotein phosphatase activity /  regulation of DNA replication / mesoderm development / regulation of DNA replication / mesoderm development /  chromosome, centromeric region / DARPP-32 events / negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / lateral plasma membrane / potassium channel regulator activity / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / chromosome, centromeric region / DARPP-32 events / negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / lateral plasma membrane / potassium channel regulator activity / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal /  regulation of cell adhesion / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / protein dephosphorylation / regulation of cell adhesion / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / protein dephosphorylation /  RNA splicing / meiotic cell cycle / protein phosphatase 2A binding / response to organic substance / RNA splicing / meiotic cell cycle / protein phosphatase 2A binding / response to organic substance /  protein tyrosine phosphatase activity / protein tyrosine phosphatase activity /  chromosome segregation / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / positive regulation of glucose import / response to lead ion / chromosome segregation / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / positive regulation of glucose import / response to lead ion /  regulation of protein phosphorylation / Spry regulation of FGF signaling / RAF activation / PKR-mediated signaling / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / tau protein binding / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / negative regulation of cell growth / regulation of protein phosphorylation / Spry regulation of FGF signaling / RAF activation / PKR-mediated signaling / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / tau protein binding / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / negative regulation of cell growth /  spindle pole / Negative regulation of MAPK pathway / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / microtubule cytoskeleton / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / spindle pole / Negative regulation of MAPK pathway / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / microtubule cytoskeleton / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle /  Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M TransitionSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.77 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.77 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fuller, J.R. / Padi, S.K.R. / Peti, W. / Page, R. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structures of PP2A:B55-FAM122A and PP2A:B55-ARPP19. Authors: Sathish K R Padi / Margaret R Vos / Rachel J Godek / James R Fuller / Thomas Kruse / Jamin B Hein / Jakob Nilsson / Matthew S Kelker / Rebecca Page / Wolfgang Peti /   Abstract: Progression through the cell cycle is controlled by regulated and abrupt changes in phosphorylation. Mitotic entry is initiated by increased phosphorylation of mitotic proteins, a process driven by ...Progression through the cell cycle is controlled by regulated and abrupt changes in phosphorylation. Mitotic entry is initiated by increased phosphorylation of mitotic proteins, a process driven by kinases, whereas mitotic exit is achieved by counteracting dephosphorylation, a process driven by phosphatases, especially PP2A:B55. Although the role of kinases in mitotic entry is well established, recent data have shown that mitosis is only successfully initiated when the counterbalancing phosphatases are also inhibited. Inhibition of PP2A:B55 is achieved by the intrinsically disordered proteins ARPP19 and FAM122A. Despite their critical roles in mitosis, the mechanisms by which they achieve PP2A:B55 inhibition is unknown. Here, we report the single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structures of PP2A:B55 bound to phosphorylated ARPP19 and FAM122A. Consistent with our complementary NMR spectroscopy studies, both intrinsically disordered proteins bind PP2A:B55, but do so in highly distinct manners, leveraging multiple distinct binding sites on B55. Our extensive structural, biophysical and biochemical data explain how substrates and inhibitors are recruited to PP2A:B55 and provide a molecular roadmap for the development of therapeutic interventions for PP2A:B55-related diseases. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ttb.cif.gz 8ttb.cif.gz | 653.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ttb.ent.gz pdb8ttb.ent.gz | 432.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ttb.json.gz 8ttb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tt/8ttb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tt/8ttb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tt/8ttb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tt/8ttb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41604MC  8so0C  8tweC  8twiC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 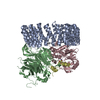
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A ... , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 64957.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP2R1A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP2R1A / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P30153 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P30153 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 52044.289 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP2R2A / Cell line (production host): expi293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP2R2A / Cell line (production host): expi293 / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63151 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63151 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 35845.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP2CA / Cell line (production host): expi293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP2CA / Cell line (production host): expi293 / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P67775, protein-serine/threonine phosphatase |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules D
| #4: Protein | Mass: 12620.241 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ARPP19 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ARPP19 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P56211 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P56211 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 


| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-FE /  Iron Iron |
|---|---|
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Quadruple complex of PP2A:B55 (PP2Aa:PP2Ac:B55) bound to thiophosphorylated ARPP19 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.165 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: CHAPSO was added only immediately prior to vitrification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 291 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 390 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2600 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 390 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2600 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 70 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 Details: Camera was operated in CDS mode, with hardware binning of super-resolution pixels, writing movies with 62 frames |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1170216 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.77 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 52934 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation Details: Iterating between manual refinement in Coot and automated real-space refinement in Phenix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 86.62 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj




















