[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8pij: Neisseria meningitidis Type IV pilus SB-GATDH variant bound to th... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8pij | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
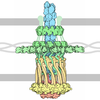
| Title | Neisseria meningitidis Type IV pilus SB-GATDH variant bound to the C24 nanobody | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL /  Pilin / Pilin /  Extracellular / Extracellular /  Adhesion / Aggregation Adhesion / Aggregation | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |   Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria)  Vicugna pacos (alpaca) Vicugna pacos (alpaca) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Fernandez-Martinez, D. / Dumenil, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1items France, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structures of type IV pili complexed with nanobodies reveal immune escape mechanisms. Authors: David Fernandez-Martinez / Youxin Kong / Sylvie Goussard / Agustin Zavala / Pauline Gastineau / Martial Rey / Gabriel Ayme / Julia Chamot-Rooke / Pierre Lafaye / Matthijn Vos / Ariel Mechaly ...Authors: David Fernandez-Martinez / Youxin Kong / Sylvie Goussard / Agustin Zavala / Pauline Gastineau / Martial Rey / Gabriel Ayme / Julia Chamot-Rooke / Pierre Lafaye / Matthijn Vos / Ariel Mechaly / Guillaume Duménil /  Abstract: Type IV pili (T4P) are prevalent, polymeric surface structures in pathogenic bacteria, making them ideal targets for effective vaccines. However, bacteria have evolved efficient strategies to evade ...Type IV pili (T4P) are prevalent, polymeric surface structures in pathogenic bacteria, making them ideal targets for effective vaccines. However, bacteria have evolved efficient strategies to evade type IV pili-directed antibody responses. Neisseria meningitidis are prototypical type IV pili-expressing Gram-negative bacteria responsible for life threatening sepsis and meningitis. This species has evolved several genetic strategies to modify the surface of its type IV pili, changing pilin subunit amino acid sequence, nature of glycosylation and phosphoforms, but how these modifications affect antibody binding at the structural level is still unknown. Here, to explore this question, we determine cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of pili of different sequence types with sufficiently high resolution to visualize posttranslational modifications. We then generate nanobodies directed against type IV pili which alter pilus function in vitro and in vivo. Cyro-EM in combination with molecular dynamics simulation of the nanobody-pilus complexes reveals how the different types of pili surface modifications alter nanobody binding. Our findings shed light on the impressive complementarity between the different strategies used by bacteria to avoid antibody binding. Importantly, we also show that structural information can be used to make informed modifications in nanobodies as countermeasures to these immune evasion mechanisms. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8pij.cif.gz 8pij.cif.gz | 67 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8pij.ent.gz pdb8pij.ent.gz | 47.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8pij.json.gz 8pij.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pi/8pij https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pi/8pij ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pi/8pij ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pi/8pij | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17683MC  8p2vC  8p36C  8p3bC  8pizC  8pjpC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 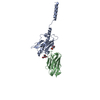
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 17067.182 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) / Production host: Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) / Production host:   Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1I9GEU1 Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1I9GEU1 |
|---|---|
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 13911.585 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Vicugna pacos (alpaca) Vicugna pacos (alpaca)Production host:   Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (bacteria) Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (bacteria) |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-G3P /  Glycerol 3-phosphate Glycerol 3-phosphate |
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-WKE / ( Mass: 292.286 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C11H20N2O7 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of Neisseria meningitidis PilE SB-GATDH and the C24 nanobody Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) Neisseria meningitidis 8013 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 434690 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj