+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
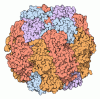
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7yk5 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Rubisco from Phaeodactylum tricornutum bound to PYCO1(452-592) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  PHOTOSYNTHESIS / PHOTOSYNTHESIS /  Rubisco / phase separation / rubisco linker protein / Rubisco / phase separation / rubisco linker protein /  condensation / condensation /  pyrenoid / pyrenoid /  phaeodactylum tricornutum phaeodactylum tricornutum | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase /  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle /  chloroplast / chloroplast /  monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oh, Z.G. / Ang, W.S.L. / Bhushan, S. / Mueller-Cajar, O. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Singapore, 2items Singapore, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023Title: A linker protein from a red-type pyrenoid phase separates with Rubisco via oligomerizing sticker motifs. Authors: Zhen Guo Oh / Warren Shou Leong Ang / Cheng Wei Poh / Soak-Kuan Lai / Siu Kwan Sze / Hoi-Yeung Li / Shashi Bhushan / Tobias Wunder / Oliver Mueller-Cajar /  Abstract: The slow kinetics and poor substrate specificity of the key photosynthetic CO-fixing enzyme Rubisco have prompted the repeated evolution of Rubisco-containing biomolecular condensates known as ...The slow kinetics and poor substrate specificity of the key photosynthetic CO-fixing enzyme Rubisco have prompted the repeated evolution of Rubisco-containing biomolecular condensates known as pyrenoids in the majority of eukaryotic microalgae. Diatoms dominate marine photosynthesis, but the interactions underlying their pyrenoids are unknown. Here, we identify and characterize the Rubisco linker protein PYCO1 from . PYCO1 is a tandem repeat protein containing prion-like domains that localizes to the pyrenoid. It undergoes homotypic liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) to form condensates that specifically partition diatom Rubisco. Saturation of PYCO1 condensates with Rubisco greatly reduces the mobility of droplet components. Cryo-electron microscopy and mutagenesis data revealed the sticker motifs required for homotypic and heterotypic phase separation. Our data indicate that the PYCO1-Rubisco network is cross-linked by PYCO1 stickers that oligomerize to bind to the small subunits lining the central solvent channel of the Rubisco holoenzyme. A second sticker motif binds to the large subunit. Pyrenoidal Rubisco condensates are highly diverse and tractable models of functional LLPS. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7yk5.cif.gz 7yk5.cif.gz | 838.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7yk5.ent.gz pdb7yk5.ent.gz | 714.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7yk5.json.gz 7yk5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/7yk5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/7yk5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/7yk5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/7yk5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33887MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 54244.527 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) / Plasmid details: Pt 1 8.6 CCMP 2561 Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) / Plasmid details: Pt 1 8.6 CCMP 2561References: UniProt: E9PAI6,  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase#2: Protein | Mass: 16039.053 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) / Plasmid details: Pt 1 8.6 CCMP 2561 / References: UniProt: A0A6B9XNC0 Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) / Plasmid details: Pt 1 8.6 CCMP 2561 / References: UniProt: A0A6B9XNC0#3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 875.973 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Pt 1 8.6 CCMP 2561 / Source: (gene. exp.)   Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom)Production host:   Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (bacteria) Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (bacteria)#4: Protein/peptide | Mass: 993.051 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Pt 1 8.6 CCMP 2561 / Source: (gene. exp.)   Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom)Production host:   Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (bacteria) Escherichia coli 'BL21-Gold(DE3)pLysS AG' (bacteria)#5: Sugar | ChemComp-CAP / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rubisco from Phaeodactylum tricornutum bound to linker protein PYCO1 Type: COMPLEX Details: Rubisco purified from source organism, PYCO1 purified from E. coli. Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 550 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Diatom) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 20 mM Tris pH 8.0 20 mM NaCl | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: 0.5 mg/mL Rubisco incubated with 21.9 uM of PYCO1(452-592). | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | |||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: Blotted for 2 sec with blot force of 1. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 5 sec. / Electron dose: 65 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 8861 Details: Images were collected in movie mode at 10 frames per second. |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Details: Gatan EF / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Details: Gatan EF / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3354751 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : D4 (2x4 fold dihedral : D4 (2x4 fold dihedral ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 259796 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Details: Coot was used for model building | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5MZ2 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj