[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
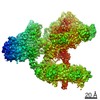
Yorodumi- PDB-7qid: tentative model of the human insulin receptor ectodomain bound by... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7qid | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | tentative model of the human insulin receptor ectodomain bound by three insulin | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN /  cell surface receptor / cell surface receptor /  insulin / insulin /  tyrosine kinase receptor / tyrosine kinase receptor /  glucose homeostasis / glucose homeostasis /  hormone / hormone /  diabetes diabetes | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of developmental growth /  insulin-like growth factor II binding / male sex determination / exocrine pancreas development / insulin-like growth factor II binding / male sex determination / exocrine pancreas development /  insulin receptor complex / insulin receptor complex /  insulin-like growth factor I binding / insulin-like growth factor I binding /  insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly ...regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of developmental growth / insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly ...regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of developmental growth /  insulin-like growth factor II binding / male sex determination / exocrine pancreas development / insulin-like growth factor II binding / male sex determination / exocrine pancreas development /  insulin receptor complex / insulin receptor complex /  insulin-like growth factor I binding / insulin-like growth factor I binding /  insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / cargo receptor activity / insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / cargo receptor activity /  dendritic spine maintenance / dendritic spine maintenance /  PTB domain binding / PTB domain binding /  insulin binding / negative regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity / neuronal cell body membrane / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / regulation of cellular amino acid metabolic process / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / Insulin processing / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / insulin binding / negative regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity / neuronal cell body membrane / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / regulation of cellular amino acid metabolic process / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / Insulin processing / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior /  regulation of protein secretion / amyloid-beta clearance / activation of protein kinase activity / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst / regulation of protein secretion / amyloid-beta clearance / activation of protein kinase activity / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst /  Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells /  regulation of embryonic development / positive regulation of receptor internalization / transport across blood-brain barrier / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / alpha-beta T cell activation / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / regulation of embryonic development / positive regulation of receptor internalization / transport across blood-brain barrier / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / alpha-beta T cell activation / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response /  insulin receptor substrate binding / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / epidermis development / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / negative regulation of protein secretion / Signal attenuation / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / fatty acid homeostasis / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / insulin receptor substrate binding / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / epidermis development / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / negative regulation of protein secretion / Signal attenuation / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / fatty acid homeostasis / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane /  phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / heart morphogenesis / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / heart morphogenesis / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process /  transport vesicle / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / dendrite membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / transport vesicle / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / dendrite membrane / Insulin receptor recycling /  insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / neuron projection maintenance / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / activation of protein kinase B activity / positive regulation of glycolytic process / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / neuron projection maintenance / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / activation of protein kinase B activity / positive regulation of glycolytic process / Insulin receptor signalling cascade /  receptor-mediated endocytosis / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / receptor-mediated endocytosis / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division /  learning / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / learning / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation /  caveola / endosome lumen / positive regulation of cytokine production / acute-phase response / positive regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / positive regulation of cell differentiation / positive regulation of glucose import / negative regulation of proteolysis / caveola / endosome lumen / positive regulation of cytokine production / acute-phase response / positive regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / positive regulation of cell differentiation / positive regulation of glucose import / negative regulation of proteolysis /  regulation of synaptic plasticity / positive regulation of MAP kinase activity / regulation of synaptic plasticity / positive regulation of MAP kinase activity /  wound healing / wound healing /  insulin receptor binding / insulin receptor binding /  hormone activity / hormone activity /  receptor internalization / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / receptor internalization / negative regulation of protein catabolic process /  receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase /  memory / cellular response to growth factor stimulus / memory / cellular response to growth factor stimulus /  cognition / positive regulation of neuron projection development / Golgi lumen / peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus cognition / positive regulation of neuron projection development / Golgi lumen / peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleusSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gutman, T. / Schaefer, I.B. / Poojari, C.S. / Vattulainen, I. / Strauss, M. / Coskun, U. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Cell Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: J Cell Biol / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM structure of the complete and ligand-saturated insulin receptor ectodomain. Authors: Theresia Gutmann / Ingmar B Schäfer / Chetan Poojari / Beate Brankatschk / Ilpo Vattulainen / Mike Strauss / Ünal Coskun /    Abstract: Glucose homeostasis and growth essentially depend on the hormone insulin engaging its receptor. Despite biochemical and structural advances, a fundamental contradiction has persisted in the current ...Glucose homeostasis and growth essentially depend on the hormone insulin engaging its receptor. Despite biochemical and structural advances, a fundamental contradiction has persisted in the current understanding of insulin ligand-receptor interactions. While biochemistry predicts two distinct insulin binding sites, 1 and 2, recent structural analyses have resolved only site 1. Using a combined approach of cryo-EM and atomistic molecular dynamics simulation, we present the structure of the entire dimeric insulin receptor ectodomain saturated with four insulin molecules. Complementing the previously described insulin-site 1 interaction, we present the first view of insulin bound to the discrete insulin receptor site 2. Insulin binding stabilizes the receptor ectodomain in a T-shaped conformation wherein the membrane-proximal domains converge and contact each other. These findings expand the current models of insulin binding to its receptor and of its regulation. In summary, we provide the structural basis for a comprehensive description of ligand-receptor interactions that ultimately will inform new approaches to structure-based drug design. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7qid.cif.gz 7qid.cif.gz | 618.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7qid.ent.gz pdb7qid.ent.gz | 533.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7qid.json.gz 7qid.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qi/7qid https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qi/7qid ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qi/7qid ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qi/7qid | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10311MUC  6sofC M: map data used to model this data U: unfit; in different coordinate system*YM C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 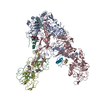
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  / IR / IRMass: 82551.742 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P06213,  receptor protein-tyrosine kinase receptor protein-tyrosine kinase#2: Protein | Mass: 21627.248 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P06213-2,  receptor protein-tyrosine kinase receptor protein-tyrosine kinase#3: Protein/peptide |  Mass: 2383.698 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P01308 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P01308#4: Protein/peptide |  Mass: 3433.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INS / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P01308 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P01308 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: insulin receptor ectodomain with three insulin bound / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.37 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10.2 sec. / Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 51 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 50079 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj





















