+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ksl | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
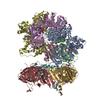
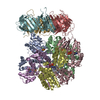
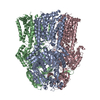
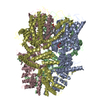
| Title | Substrate-free human mitochondrial LONP1 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Lon protease homolog, mitochondrial | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  HYDROLASE / HYDROLASE /  AAA+ / AAA+ /  ATPase / ATPase /  protease / protease /  mitochondrial / mitochondrial /  LONP1 / LON LONP1 / LON | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationoxidation-dependent protein catabolic process /  PH domain binding / PH domain binding /  endopeptidase La / G-quadruplex DNA binding / response to aluminum ion / mitochondrial DNA metabolic process / endopeptidase La / G-quadruplex DNA binding / response to aluminum ion / mitochondrial DNA metabolic process /  mitochondrial genome maintenance / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins / mitochondrial nucleoid ...oxidation-dependent protein catabolic process / mitochondrial genome maintenance / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins / mitochondrial nucleoid ...oxidation-dependent protein catabolic process /  PH domain binding / PH domain binding /  endopeptidase La / G-quadruplex DNA binding / response to aluminum ion / mitochondrial DNA metabolic process / endopeptidase La / G-quadruplex DNA binding / response to aluminum ion / mitochondrial DNA metabolic process /  mitochondrial genome maintenance / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins / mitochondrial nucleoid / mitochondrial genome maintenance / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins / mitochondrial nucleoid /  insulin receptor substrate binding / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / insulin receptor substrate binding / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly /  DNA polymerase binding / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / mitochondrion organization / proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process / response to hormone / DNA polymerase binding / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / mitochondrion organization / proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process / response to hormone /  ADP binding / protein catabolic process / ADP binding / protein catabolic process /  single-stranded DNA binding / cellular response to oxidative stress / sequence-specific DNA binding / single-stranded DNA binding / cellular response to oxidative stress / sequence-specific DNA binding /  single-stranded RNA binding / response to hypoxia / single-stranded RNA binding / response to hypoxia /  mitochondrial matrix / serine-type endopeptidase activity / mitochondrial matrix / serine-type endopeptidase activity /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shin, M. / Watson, E.R. / Song, A.S. / Mindrebo, J.T. / Novick, S.R. / Griffin, P. / Wiseman, R.L. / Lander, G.C. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Structures of the human LONP1 protease reveal regulatory steps involved in protease activation. Authors: Mia Shin / Edmond R Watson / Albert S Song / Jeffrey T Mindrebo / Scott J Novick / Patrick R Griffin / R Luke Wiseman / Gabriel C Lander /  Abstract: The human mitochondrial AAA+ protein LONP1 is a critical quality control protease involved in regulating diverse aspects of mitochondrial biology including proteostasis, electron transport chain ...The human mitochondrial AAA+ protein LONP1 is a critical quality control protease involved in regulating diverse aspects of mitochondrial biology including proteostasis, electron transport chain activity, and mitochondrial transcription. As such, genetic or aging-associated imbalances in LONP1 activity are implicated in pathologic mitochondrial dysfunction associated with numerous human diseases. Despite this importance, the molecular basis for LONP1-dependent proteolytic activity remains poorly defined. Here, we solved cryo-electron microscopy structures of human LONP1 to reveal the underlying molecular mechanisms governing substrate proteolysis. We show that, like bacterial Lon, human LONP1 adopts both an open and closed spiral staircase orientation dictated by the presence of substrate and nucleotide. Unlike bacterial Lon, human LONP1 contains a second spiral staircase within its ATPase domain that engages substrate as it is translocated toward the proteolytic chamber. Intriguingly, and in contrast to its bacterial ortholog, substrate binding within the central ATPase channel of LONP1 alone is insufficient to induce the activated conformation of the protease domains. To successfully induce the active protease conformation in substrate-bound LONP1, substrate binding within the protease active site is necessary, which we demonstrate by adding bortezomib, a peptidomimetic active site inhibitor of LONP1. These results suggest LONP1 can decouple ATPase and protease activities depending on whether AAA+ or both AAA+ and protease domains bind substrate. Importantly, our structures provide a molecular framework to define the critical importance of LONP1 in regulating mitochondrial proteostasis in health and disease. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ksl.cif.gz 7ksl.cif.gz | 413.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ksl.ent.gz pdb7ksl.ent.gz | 341.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ksl.json.gz 7ksl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ks/7ksl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ks/7ksl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ks/7ksl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ks/7ksl | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23019MC  7krzC  7ksmC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 58498.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LONP1, PRSS15 / Plasmid: pET20b / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LONP1, PRSS15 / Plasmid: pET20b / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / Strain (production host): Rosetta 2(DE3)pLysS / References: UniProt: P36776, Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / Strain (production host): Rosetta 2(DE3)pLysS / References: UniProt: P36776,  endopeptidase La endopeptidase La#2: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP /  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphateHas ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Substrate-free human mitochondrial LONP1 / Type: COMPLEX Details: Complexes consisting of homohexameric LONP1 protease from Homo sapiens Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.462 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: Matrix / Organelle Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: Matrix / Organelle : Mitochondria : Mitochondria | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / Strain: Rosetta 2(DE3)pLysS / Plasmid Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / Strain: Rosetta 2(DE3)pLysS / Plasmid : pET20b : pET20b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: Solutions were made fresh from concentrated and filtered using a 0.1 um syringe filter to avoid microbial contamination. Samples were mixed on ice and incubated for 5 minutes prior to vitrification. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES / Details: This sample was monodisperse : YES / Details: This sample was monodisperse | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: EM grids were plasma cleaned prior to sample application for 7 seconds using a Solarus plasma cleaner (Gatan, Inc.) with a 75% nitrogen, 25% oxygen atmosphere at 15W. Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K Details: 4 uL of sample was applied per grid and manually blotted for 4 seconds followed by immediately plunge-freezing in liquid ethane cooled by liquid nitrogen. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA Details: Coma-free alignment procedure from Herzik & Wu, Nature Methods (2017). Preliminary grid screening was performed manually prior to data collection. |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 36000 X / Calibrated magnification: 43478 X / Nominal defocus max: 1200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 1500 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 36000 X / Calibrated magnification: 43478 X / Nominal defocus max: 1200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 1500 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 90 K / Temperature (min): 80 K / Residual tilt: 0.14 mradians |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 11.4 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2912 Details: Images were collected in counting mode at 10 frames per second. |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 3710 / Height: 3838 / Movie frames/image: 114 / Used frames/image: 0-113 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.15.2_3472: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Details: CTF parameters were estimated with CTFFIND / Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 564930 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 83162 / Num. of class averages: 2 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 30 / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient Details: Initial rigid body docking was done using UCSF Chimera. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj


