[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-25215: Cryo-EM structure of the Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellar filament -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-25215 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
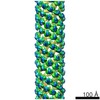
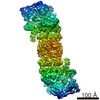
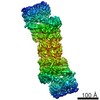
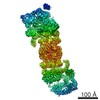
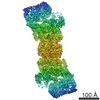
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellar filament | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology | Bacterial flagellin C-terminal helical region /  Flagellin / Flagellin /  Flagellin, N-terminal domain / Bacterial flagellin N-terminal helical region / bacterial-type flagellum / structural molecule activity / extracellular region / Flagellin A Flagellin, N-terminal domain / Bacterial flagellin N-terminal helical region / bacterial-type flagellum / structural molecule activity / extracellular region / Flagellin A Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kreutzberger MAB / Scharf BE / Egelman EH | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Flagellin outer domain dimerization modulates motility in pathogenic and soil bacteria from viscous environments. Authors: Mark A B Kreutzberger / Richard C Sobe / Amber B Sauder / Sharanya Chatterjee / Alejandro Peña / Fengbin Wang / Jorge A Giron / Volker Kiessling / Tiago R D Costa / Vincent P Conticello / ...Authors: Mark A B Kreutzberger / Richard C Sobe / Amber B Sauder / Sharanya Chatterjee / Alejandro Peña / Fengbin Wang / Jorge A Giron / Volker Kiessling / Tiago R D Costa / Vincent P Conticello / Gad Frankel / Melissa M Kendall / Birgit E Scharf / Edward H Egelman /   Abstract: Flagellar filaments function as the propellers of the bacterial flagellum and their supercoiling is key to motility. The outer domains on the surface of the filament are non-critical for motility in ...Flagellar filaments function as the propellers of the bacterial flagellum and their supercoiling is key to motility. The outer domains on the surface of the filament are non-critical for motility in many bacteria and their structures and functions are not conserved. Here, we show the atomic cryo-electron microscopy structures for flagellar filaments from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, enteropathogenic E. coli O127:H6, Achromobacter, and Sinorhizobium meliloti, where the outer domains dimerize or tetramerize to form either a sheath or a screw-like surface. These dimers are formed by 180° rotations of half of the outer domains. The outer domain sheath (ODS) plays a role in bacterial motility by stabilizing an intermediate waveform and prolonging the tumbling of E. coli cells. Bacteria with these ODS and screw-like flagellar filaments are commonly found in soil and human intestinal environments of relatively high viscosity suggesting a role for the dimerization in these environments. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25215.map.gz emd_25215.map.gz | 94.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25215-v30.xml emd-25215-v30.xml emd-25215.xml emd-25215.xml | 10.1 KB 10.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_25215.png emd_25215.png | 97.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25215 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25215 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25215 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25215 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7sn9MC  7sn4C  7sn7C  7sqdC  7sqjC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25215.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25215.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of the Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellar filament
| Entire | Name: Structure of the Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellar filament |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of the Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellar filament
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of the Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellar filament type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Flagellin A
| Macromolecule | Name: Flagellin A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 42 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.61568 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) Sinorhizobium meliloti (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MTSILTNNSA MAALSGVRSI SSSMEDTQSR ISSGLRVGSA SDNAAYWSIA TTMRSDNQAL SAVQDALGLG AAKVDTAYSG MESAIEVVK EIKAKLVAAT EDGVDKAKIQ EEITQLKDQL TSIADAASFS GENWLQADLS GGAVTKSVVG SFVRDGSGSV A VKKVDYSL ...String: MTSILTNNSA MAALSGVRSI SSSMEDTQSR ISSGLRVGSA SDNAAYWSIA TTMRSDNQAL SAVQDALGLG AAKVDTAYSG MESAIEVVK EIKAKLVAAT EDGVDKAKIQ EEITQLKDQL TSIADAASFS GENWLQADLS GGAVTKSVVG SFVRDGSGSV A VKKVDYSL NANSVLFDTV GDTGILDKVY NVSQASVTLT VNTNGVESQH TVAAYSLESL TEAGAEFQGN YALQGGNSYV KV ENVWVRA ETAATGATGQ EIAATTTAAG TITADSWVVD VGNAPAANVS AGQSVANINI VGMGAAALDA LISGVDAALT DMT SAAASL GSISSRIDLQ SEFVNKLSDS IESGVGRLVD ADMNEESTRL KALQTQQQLA IQALSIANSD SQNVLSLFR |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 222 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: Cylinder |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 9.5 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 130.9 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 16158 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller