+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20700 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
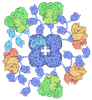
| Title | Arabidopsis thaliana acetohydroxyacid synthase complex | |||||||||
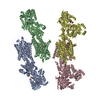
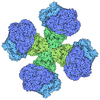
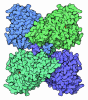
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM map of acetohydroxyacid synthase complex from Arabidopsis thaliana | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Complex / Complex /  PLANT PROTEIN PLANT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationacetolactate synthase regulator activity /  acetolactate synthase activity / acetolactate synthase activity /  acetolactate synthase / acetolactate synthase /  regulation of catalytic activity / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process / response to herbicide / regulation of catalytic activity / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process / response to herbicide /  thiamine pyrophosphate binding / thiamine pyrophosphate binding /  chloroplast stroma / chloroplast stroma /  chloroplast ...acetolactate synthase regulator activity / chloroplast ...acetolactate synthase regulator activity /  acetolactate synthase activity / acetolactate synthase activity /  acetolactate synthase / acetolactate synthase /  regulation of catalytic activity / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process / response to herbicide / regulation of catalytic activity / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process / response to herbicide /  thiamine pyrophosphate binding / thiamine pyrophosphate binding /  chloroplast stroma / chloroplast stroma /  chloroplast / chloroplast /  peroxisome / peroxisome /  : / : /  flavin adenine dinucleotide binding / response to hypoxia / magnesium ion binding flavin adenine dinucleotide binding / response to hypoxia / magnesium ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guddat LW / Low YS / Rao Z | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 2 items Australia, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Structures of fungal and plant acetohydroxyacid synthases. Authors: Thierry Lonhienne / Yu Shang Low / Mario D Garcia / Tristan Croll / Yan Gao / Quan Wang / Lou Brillault / Craig M Williams / James A Fraser / Ross P McGeary / Nicholas P West / Michael J ...Authors: Thierry Lonhienne / Yu Shang Low / Mario D Garcia / Tristan Croll / Yan Gao / Quan Wang / Lou Brillault / Craig M Williams / James A Fraser / Ross P McGeary / Nicholas P West / Michael J Landsberg / Zihe Rao / Gerhard Schenk / Luke W Guddat /    Abstract: Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS), also known as acetolactate synthase, is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-, thiamine diphosphate- and magnesium-dependent enzyme that catalyses the first step in the ...Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS), also known as acetolactate synthase, is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-, thiamine diphosphate- and magnesium-dependent enzyme that catalyses the first step in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids. It is the target for more than 50 commercial herbicides. AHAS requires both catalytic and regulatory subunits for maximal activity and functionality. Here we describe structures of the hexadecameric AHAS complexes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and dodecameric AHAS complexes of Arabidopsis thaliana. We found that the regulatory subunits of these AHAS complexes form a core to which the catalytic subunit dimers are attached, adopting the shape of a Maltese cross. The structures show how the catalytic and regulatory subunits communicate with each other to provide a pathway for activation and for feedback inhibition by branched-chain amino acids. We also show that the AHAS complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis adopts a similar structure, thus demonstrating that the overall AHAS architecture is conserved across kingdoms. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20700.map.gz emd_20700.map.gz | 14.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20700-v30.xml emd-20700-v30.xml emd-20700.xml emd-20700.xml | 14.9 KB 14.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20700.png emd_20700.png | 52 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20700.cif.gz emd-20700.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20700 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20700 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20700 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20700 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6u9hMC  6u9dC  6vz8C  6wo1C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20700.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20700.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM map of acetohydroxyacid synthase complex from Arabidopsis thaliana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Acetohydroxyacid synthase quaternary complex
| Entire | Name: Acetohydroxyacid synthase quaternary complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Acetohydroxyacid synthase quaternary complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Acetohydroxyacid synthase quaternary complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 / Details: Recombinant expression from E. coli. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 720 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Acetolactate synthase, chloroplastic
| Macromolecule | Name: Acetolactate synthase, chloroplastic / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  acetolactate synthase acetolactate synthase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 64.025203 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21 (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MTFISRFAPD QPRKGADILV EALERQGVET VFAYPGGASM EIHQALTRSS SIRNVLPRHE QGGVFAAEGY ARSSGKPGIC IATSGPGAT NLVSGLADAL LDSVPLVAIT GQVPRRMIGT DAFQETPIVE VTRSITKHNY LVMDVEDIPR IIEEAFFLAT S GRPGPVLV ...String: MTFISRFAPD QPRKGADILV EALERQGVET VFAYPGGASM EIHQALTRSS SIRNVLPRHE QGGVFAAEGY ARSSGKPGIC IATSGPGAT NLVSGLADAL LDSVPLVAIT GQVPRRMIGT DAFQETPIVE VTRSITKHNY LVMDVEDIPR IIEEAFFLAT S GRPGPVLV DVPKDIQQQL AIPNWEQAMR LPGYMSRMPK PPEDSHLEQI VRLISESKKP VLYVGGGCLN SSDELGRFVE LT GIPVAST LMGLGSYPCD DELSLHMLGM HGTVYANYAV EHSDLLLAFG VRFDDRVTGK LEAFASRAKI VHIDIDSAEI GKN KTPHVS VCGDVKLALQ GMNKVLENRA EELKLDFGVW RNELNVQKQK FPLSFKTFGE AIPPQYAIKV LDELTDGKAI ISTG VGQHQ MWAAQFYNYK KPRQWLSSGG LGAMGFGLPA AIGASVANPD AIVVDIDGDG SFIMNVQELA TIRVENLPVK VLLLN NQHL GMVMQWEDRF YKANRAHTFL GDPAQEDEIF PNMLLFAAAC GIPAARVTKK ADLREAIQTM LDTPGPYLLD VICPHQ EHV LPMIPSGGTF NDVITEGDGR IKY UniProtKB:  Acetolactate synthase, chloroplastic Acetolactate synthase, chloroplastic |
-Macromolecule #2: Acetolactate synthase small subunit 2, chloroplastic
| Macromolecule | Name: Acetolactate synthase small subunit 2, chloroplastic / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 53.948906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MAAISVSSSP SIRCLRSACS DSSPALVSST RVSFPAKISY LSGISSHRGD EMGKRMEGFV RSVDGKISDA SFSEASSATP KSKVRKHTI SVFVGDESGM INRIAGVFAR RGYNIESLAV GLNRDKALFT IVVCGTERVL QQVIEQLQKL VNVLKVEDIS S EPQVEREL ...String: MAAISVSSSP SIRCLRSACS DSSPALVSST RVSFPAKISY LSGISSHRGD EMGKRMEGFV RSVDGKISDA SFSEASSATP KSKVRKHTI SVFVGDESGM INRIAGVFAR RGYNIESLAV GLNRDKALFT IVVCGTERVL QQVIEQLQKL VNVLKVEDIS S EPQVEREL MLVKVNAHPE SRAEIMWLVD TFRARVVDIA EHALTIEVTG DPGKMIAVER NLKKFQIREI VRTGKIALRR EK MGATAPF WRFSAASYPD LKEQAPVSVL RSSKKGAIVP QKETSAGGDV YPVEPFFDPK VHRILDAHWG LLTDEDTSGL RSH TLSLLV NDIPGVLNIV TGVFARRGYN IQSLAVGHAE TKGISRITTV IPATDESVSK LVQQLYKLVD VHEVHDLTHL PFSE RELML IKIAVNAAAR RDVLDIASIF RAKAVDVSDH TITLQLTGDL DKMVALQRLL EPYGICEVAR TGRVALARES GVDSK YLRG YSFPLTG UniProtKB:  Acetolactate synthase small subunit 1, chloroplastic Acetolactate synthase small subunit 1, chloroplastic |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: FLAVIN-ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE
| Macromolecule | Name: FLAVIN-ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: FAD |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 785.55 Da |
| Chemical component information | 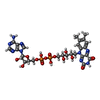 ChemComp-FAD: |
-Macromolecule #5: THIAMINE DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: THIAMINE DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: TPP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 425.314 Da |
| Chemical component information | 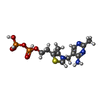 ChemComp-TPP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Material: COPPER |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
| Details | Glutaraldehyde cross linked |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 2 / Average exposure time: 3.2 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3) / Number images used: 76 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller