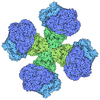
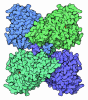
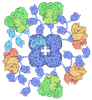
[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6wo1: Hybrid acetohydroxyacid synthase complex structure with Cryptococ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wo1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Hybrid acetohydroxyacid synthase complex structure with Cryptococcus neoformans AHAS catalytic subunit and Saccharomyces cerevisiae AHAS regulatory subunit | ||||||
 Components Components | (Acetohydroxyacid synthase ... Acetolactate synthase) x 2 Acetolactate synthase) x 2 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSFERASE / AHAS / TRANSFERASE / AHAS /  pyruvate / FAD / pyruvate / FAD /  dioxygen dioxygen | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationacetolactate synthase regulator activity /  acetolactate synthase complex / acetolactate synthase complex /  acetolactate synthase activity / acetolactate synthase activity /  acetolactate synthase / branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic process / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process / acetolactate synthase / branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic process / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process /  thiamine pyrophosphate binding / mitochondrial nucleoid / enzyme regulator activity ...acetolactate synthase regulator activity / thiamine pyrophosphate binding / mitochondrial nucleoid / enzyme regulator activity ...acetolactate synthase regulator activity /  acetolactate synthase complex / acetolactate synthase complex /  acetolactate synthase activity / acetolactate synthase activity /  acetolactate synthase / branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic process / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process / acetolactate synthase / branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic process / valine biosynthetic process / isoleucine biosynthetic process /  thiamine pyrophosphate binding / mitochondrial nucleoid / enzyme regulator activity / thiamine pyrophosphate binding / mitochondrial nucleoid / enzyme regulator activity /  flavin adenine dinucleotide binding / magnesium ion binding / flavin adenine dinucleotide binding / magnesium ion binding /  mitochondrion mitochondrionSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Cryptococcus neoformans (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans (fungus)  Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.3 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Guddat, L.W. / Lonhienne, T. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Structures of fungal and plant acetohydroxyacid synthases. Authors: Thierry Lonhienne / Yu Shang Low / Mario D Garcia / Tristan Croll / Yan Gao / Quan Wang / Lou Brillault / Craig M Williams / James A Fraser / Ross P McGeary / Nicholas P West / Michael J ...Authors: Thierry Lonhienne / Yu Shang Low / Mario D Garcia / Tristan Croll / Yan Gao / Quan Wang / Lou Brillault / Craig M Williams / James A Fraser / Ross P McGeary / Nicholas P West / Michael J Landsberg / Zihe Rao / Gerhard Schenk / Luke W Guddat /    Abstract: Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS), also known as acetolactate synthase, is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-, thiamine diphosphate- and magnesium-dependent enzyme that catalyses the first step in the ...Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS), also known as acetolactate synthase, is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-, thiamine diphosphate- and magnesium-dependent enzyme that catalyses the first step in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids. It is the target for more than 50 commercial herbicides. AHAS requires both catalytic and regulatory subunits for maximal activity and functionality. Here we describe structures of the hexadecameric AHAS complexes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and dodecameric AHAS complexes of Arabidopsis thaliana. We found that the regulatory subunits of these AHAS complexes form a core to which the catalytic subunit dimers are attached, adopting the shape of a Maltese cross. The structures show how the catalytic and regulatory subunits communicate with each other to provide a pathway for activation and for feedback inhibition by branched-chain amino acids. We also show that the AHAS complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis adopts a similar structure, thus demonstrating that the overall AHAS architecture is conserved across kingdoms. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wo1.cif.gz 6wo1.cif.gz | 310.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wo1.ent.gz pdb6wo1.ent.gz | 249 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wo1.json.gz 6wo1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wo/6wo1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wo/6wo1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wo/6wo1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wo/6wo1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6u9dC  6u9hC  6vz8C  2fgcS 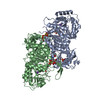 5imsS C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Acetohydroxyacid synthase ... , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 78594.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Cryptococcus neoformans (fungus) / Production host: Cryptococcus neoformans (fungus) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q96VZ6, Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q96VZ6,  acetolactate synthase acetolactate synthase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 34041.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast)Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: C7GQK9, UniProt: P25605*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: C7GQK9, UniProt: P25605*PLUS |
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 5 molecules 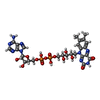







| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-FAD /  Flavin adenine dinucleotide Flavin adenine dinucleotide |
|---|---|
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-8GF / |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-DPO /  Pyrophosphate Pyrophosphate |
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
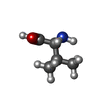
| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-VAL /  Valine Valine |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.77 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 55.62 % |
|---|---|
Crystal grow | Temperature: 291 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / Details: Potassium thiocyanate, PEG 3350 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Ambient temp details: Oxford cryostream / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Australian Synchrotron Australian Synchrotron  / Beamline: MX1 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å / Beamline: MX1 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å |
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 210r / Detector: CCD / Date: Mar 28, 2019 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: SI(III) / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 0.9537 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 0.9537 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.3→48.92 Å / Num. obs: 19890 / % possible obs: 99.8 % / Redundancy: 19.7 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 92.68 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.999 / Rpim(I) all: 0.041 / Net I/σ(I): 13.7 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 3.3→3.56 Å / Num. unique obs: 3985 / Rpim(I) all: 0.286 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 5IMS, 2FGC Resolution: 3.3→48.92 Å / SU ML: 0.42 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 26.7
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 253.15 Å2 / Biso mean: 95.6873 Å2 / Biso min: 35.56 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 3.3→48.92 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 14
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj