[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20613: Cryo-EM structure of a de novo designed 16-helix transmembrane na... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20613 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of a de novo designed 16-helix transmembrane nanopore, TMHC8_R. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Transmembrane / Pore / Rosetta / Transmembrane / Pore / Rosetta /  DE NOVO PROTEIN DE NOVO PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
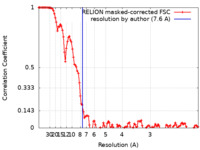
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 7.6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 7.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Johnson MJ / Reggiano G | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Computational design of transmembrane pores. Authors: Chunfu Xu / Peilong Lu / Tamer M Gamal El-Din / Xue Y Pei / Matthew C Johnson / Atsuko Uyeda / Matthew J Bick / Qi Xu / Daohua Jiang / Hua Bai / Gabriella Reggiano / Yang Hsia / T J Brunette ...Authors: Chunfu Xu / Peilong Lu / Tamer M Gamal El-Din / Xue Y Pei / Matthew C Johnson / Atsuko Uyeda / Matthew J Bick / Qi Xu / Daohua Jiang / Hua Bai / Gabriella Reggiano / Yang Hsia / T J Brunette / Jiayi Dou / Dan Ma / Eric M Lynch / Scott E Boyken / Po-Ssu Huang / Lance Stewart / Frank DiMaio / Justin M Kollman / Ben F Luisi / Tomoaki Matsuura / William A Catterall / David Baker /     Abstract: Transmembrane channels and pores have key roles in fundamental biological processes and in biotechnological applications such as DNA nanopore sequencing, resulting in considerable interest in the ...Transmembrane channels and pores have key roles in fundamental biological processes and in biotechnological applications such as DNA nanopore sequencing, resulting in considerable interest in the design of pore-containing proteins. Synthetic amphiphilic peptides have been found to form ion channels, and there have been recent advances in de novo membrane protein design and in redesigning naturally occurring channel-containing proteins. However, the de novo design of stable, well-defined transmembrane protein pores that are capable of conducting ions selectively or are large enough to enable the passage of small-molecule fluorophores remains an outstanding challenge. Here we report the computational design of protein pores formed by two concentric rings of α-helices that are stable and monodisperse in both their water-soluble and their transmembrane forms. Crystal structures of the water-soluble forms of a 12-helical pore and a 16-helical pore closely match the computational design models. Patch-clamp electrophysiology experiments show that, when expressed in insect cells, the transmembrane form of the 12-helix pore enables the passage of ions across the membrane with high selectivity for potassium over sodium; ion passage is blocked by specific chemical modification at the pore entrance. When incorporated into liposomes using in vitro protein synthesis, the transmembrane form of the 16-helix pore-but not the 12-helix pore-enables the passage of biotinylated Alexa Fluor 488. A cryo-electron microscopy structure of the 16-helix transmembrane pore closely matches the design model. The ability to produce structurally and functionally well-defined transmembrane pores opens the door to the creation of designer channels and pores for a wide variety of applications. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
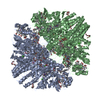
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20613.map.gz emd_20613.map.gz | 9.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20613-v30.xml emd-20613-v30.xml emd-20613.xml emd-20613.xml | 13.5 KB 13.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_20613_fsc.xml emd_20613_fsc.xml | 11.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_20613.png emd_20613.png | 63.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_20613_msk_1.map emd_20613_msk_1.map | 125 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20613.cif.gz emd-20613.cif.gz | 5.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_20613_half_map_1.map.gz emd_20613_half_map_1.map.gz emd_20613_half_map_2.map.gz emd_20613_half_map_2.map.gz | 93.7 MB 93.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20613 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20613 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20613 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20613 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6u1sMC  6m6zC  6o35C  6tj1C  6tmsC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20613.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20613.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
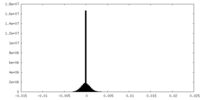
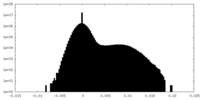
| File |  emd_20613_msk_1.map emd_20613_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_20613_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_20613_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : de novo designed transmembrane nanopore TMHC8_R
| Entire | Name: de novo designed transmembrane nanopore TMHC8_R |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: de novo designed transmembrane nanopore TMHC8_R
| Supramolecule | Name: de novo designed transmembrane nanopore TMHC8_R / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
-Macromolecule #1: de novo designed 16-helix transmembrane nanopore, TMHC8_R
| Macromolecule | Name: de novo designed 16-helix transmembrane nanopore, TMHC8_R type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.001648 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: EEFMARAISA IAELAKKAIE AIYRLADNHT TDTFMAKAIE AIAELAKEAI KAIADLAKNH TTEEFMARAI SAIAELARKA IDAIYRLAR NHTTDTFMAK AIEAIAELAK EAIKAIADLA KNHTTEDFMD EAISAIAELA RKAIEAILRL ASNLTSETYM R KAQEAIEK ...String: EEFMARAISA IAELAKKAIE AIYRLADNHT TDTFMAKAIE AIAELAKEAI KAIADLAKNH TTEEFMARAI SAIAELARKA IDAIYRLAR NHTTDTFMAK AIEAIAELAK EAIKAIADLA KNHTTEDFMD EAISAIAELA RKAIEAILRL ASNLTSETYM R KAQEAIEK IARTAEEAIR DLARNLEDQE RRERAKSARD EIKRFAEDAR KKIEVLALLK RSREYLKKVA LIQLVIAFVF LI LLILLSW RSEELIRELE EKGAASEAEL ARMKQQHMTA YLQAALTAWE IISKSVIALL LLQQNQLNLE LRH |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z
Z Y
Y X
X